@aigne/doc-smith 0.8.10-beta → 0.8.10-beta.2
This diff represents the content of publicly available package versions that have been released to one of the supported registries. The information contained in this diff is provided for informational purposes only and reflects changes between package versions as they appear in their respective public registries.
- package/.aigne/doc-smith/config.yaml +3 -1
- package/.aigne/doc-smith/preferences.yml +4 -4
- package/.aigne/doc-smith/upload-cache.yaml +180 -0
- package/.release-please-manifest.json +1 -1
- package/CHANGELOG.md +22 -0
- package/README.md +2 -2
- package/RELEASE.md +3 -3
- package/agents/generate/check-need-generate-structure.mjs +40 -18
- package/agents/generate/index.yaml +7 -0
- package/agents/generate/user-review-document-structure.mjs +173 -0
- package/agents/init/index.mjs +5 -11
- package/agents/update/generate-and-translate-document.yaml +3 -3
- package/agents/utils/check-feedback-refiner.mjs +2 -0
- package/agents/utils/save-docs.mjs +16 -22
- package/aigne.yaml +1 -0
- package/docs/advanced-how-it-works.md +26 -24
- package/docs/advanced-how-it-works.zh.md +32 -30
- package/docs/advanced-quality-assurance.md +6 -9
- package/docs/advanced-quality-assurance.zh.md +19 -22
- package/docs/cli-reference.md +35 -76
- package/docs/cli-reference.zh.md +48 -89
- package/docs/configuration-interactive-setup.md +18 -18
- package/docs/configuration-interactive-setup.zh.md +33 -33
- package/docs/configuration-language-support.md +12 -12
- package/docs/configuration-language-support.zh.md +20 -20
- package/docs/configuration-llm-setup.md +14 -13
- package/docs/configuration-llm-setup.zh.md +16 -15
- package/docs/configuration-preferences.md +22 -27
- package/docs/configuration-preferences.zh.md +35 -40
- package/docs/configuration.md +31 -45
- package/docs/configuration.zh.md +48 -62
- package/docs/features-generate-documentation.md +6 -7
- package/docs/features-generate-documentation.zh.md +21 -22
- package/docs/features-publish-your-docs.md +38 -30
- package/docs/features-publish-your-docs.zh.md +45 -37
- package/docs/features-translate-documentation.md +14 -74
- package/docs/features-translate-documentation.zh.md +19 -79
- package/docs/features-update-and-refine.md +19 -18
- package/docs/features-update-and-refine.zh.md +33 -32
- package/docs-mcp/get-docs-structure.mjs +1 -1
- package/package.json +9 -9
- package/prompts/detail/custom/custom-components.md +113 -18
- package/prompts/detail/detail-example.md +58 -65
- package/prompts/detail/document-rules.md +2 -1
- package/prompts/structure/check-document-structure.md +11 -15
- package/prompts/translate/translate-document.md +20 -9
- package/tests/agents/generate/check-need-generate-structure.test.mjs +21 -24
- package/tests/agents/generate/user-review-document-structure.test.mjs +294 -0
- package/tests/agents/init/init.test.mjs +2 -8
- package/utils/auth-utils.mjs +2 -2
|
@@ -1,21 +1,21 @@
|
|
|
1
1
|
# 管理偏好
|
|
2
2
|
|
|
3
|
-
AIGNE DocSmith
|
|
3
|
+
AIGNE DocSmith 旨在通过你的反馈进行学习。当你优化或更正生成的内容时,DocSmith 可以将该反馈转换为持久性规则,称为偏好。这些规则确保你特定的风格、结构要求和内容策略在未来的文档任务中得到一致应用。所有偏好都存储在项目根目录下一个名为 `.aigne/doc-smith/preferences.yml` 的人类可读 YAML 文件中。
|
|
4
4
|
|
|
5
5
|
## 偏好生命周期
|
|
6
6
|
|
|
7
|
-
|
|
7
|
+
下图说明了你的反馈如何成为一个可重用的规则,该规则可应用于未来的任务,并可通过命令行进行管理。
|
|
8
8
|
|
|
9
9
|
```d2 偏好生命周期
|
|
10
10
|
direction: down
|
|
11
11
|
|
|
12
12
|
feedback: {
|
|
13
|
-
label: "1.
|
|
13
|
+
label: "1. 用户在“优化”或“翻译”期间提供反馈"
|
|
14
14
|
shape: rectangle
|
|
15
15
|
}
|
|
16
16
|
|
|
17
17
|
refiner: {
|
|
18
|
-
label: "2.
|
|
18
|
+
label: "2. 反馈优化 Agent\n分析反馈"
|
|
19
19
|
shape: rectangle
|
|
20
20
|
}
|
|
21
21
|
|
|
@@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ pref_file: {
|
|
|
30
30
|
}
|
|
31
31
|
|
|
32
32
|
future_tasks: {
|
|
33
|
-
label: "4.
|
|
33
|
+
label: "4. 未来任务\n应用已保存的规则"
|
|
34
34
|
shape: rectangle
|
|
35
35
|
}
|
|
36
36
|
|
|
@@ -48,87 +48,82 @@ cli <-> pref_file: "管理"
|
|
|
48
48
|
|
|
49
49
|
```
|
|
50
50
|
|
|
51
|
-
###
|
|
51
|
+
### 如何创建偏好
|
|
52
52
|
|
|
53
|
-
|
|
53
|
+
当你在 `refine` 或 `translate` 阶段提供反馈时,一个内部 Agent 会分析你的输入。它会判断该反馈是一次性修复(例如,更正一个拼写错误)还是一个可重用的策略(例如,“始终用英语编写代码注释”)。如果它代表一个持久性指令,它就会创建一个新的偏好规则。
|
|
54
54
|
|
|
55
|
-
|
|
55
|
+
### 规则属性
|
|
56
56
|
|
|
57
|
-
|
|
58
|
-
|---|---|
|
|
59
|
-
| **id** | 规则的唯一标识符(例如,`pref_a1b2c3d4`)。 |
|
|
60
|
-
| **active** | 一个布尔值(`true`/`false`),指示规则当前是否已启用。 |
|
|
61
|
-
| **scope** | 定义规则的应用时机:`global`、`structure`、`document` 或 `translation`。 |
|
|
62
|
-
| **rule** | 将在未来任务中传递给 AI 的指令。 |
|
|
63
|
-
| **feedback** | 您提供的原始自然语言反馈。 |
|
|
64
|
-
| **createdAt** | 规则创建时的 ISO 8601 时间戳。 |
|
|
65
|
-
| **paths** | 一个可选的文件路径列表。如果存在,该规则仅适用于为这些特定路径生成的内容。 |
|
|
57
|
+
保存在 `preferences.yml` 中的每个规则都具有以下结构:
|
|
66
58
|
|
|
67
|
-
|
|
59
|
+
<x-field data-name="id" data-type="string" data-desc="规则的唯一、随机生成的标识符(例如,pref_a1b2c3d4e5f6g7h8)。"></x-field>
|
|
60
|
+
<x-field data-name="active" data-type="boolean" data-desc="指示规则当前是否已启用。未启用的规则在生成任务期间将被忽略。"></x-field>
|
|
61
|
+
<x-field data-name="scope" data-type="string" data-desc="定义规则何时应用。有效范围为 'global'、'structure'、'document' 或 'translation'。"></x-field>
|
|
62
|
+
<x-field data-name="rule" data-type="string" data-desc="将在未来任务中传递给 AI 的具体、提炼后的指令。"></x-field>
|
|
63
|
+
<x-field data-name="feedback" data-type="string" data-desc="用户提供的原始自然语言反馈,保留以供参考。"></x-field>
|
|
64
|
+
<x-field data-name="createdAt" data-type="string" data-desc="表示规则创建时间的 ISO 8601 时间戳。"></x-field>
|
|
65
|
+
<x-field data-name="paths" data-type="string[]" data-required="false" data-desc="一个可选的文件路径列表。如果存在,该规则仅适用于为这些特定源文件生成的内容。"></x-field>
|
|
68
66
|
|
|
69
|
-
|
|
67
|
+
## 使用 CLI 管理偏好
|
|
68
|
+
|
|
69
|
+
你可以使用 `aigne doc prefs` 命令查看和管理所有已保存的偏好。这允许你列出、激活、停用或永久删除规则。
|
|
70
70
|
|
|
71
71
|
### 列出所有偏好
|
|
72
72
|
|
|
73
|
-
|
|
73
|
+
要查看所有已保存的偏好,包括已激活和未激活的,请使用 `--list` 标志。
|
|
74
74
|
|
|
75
75
|
```bash 列出所有偏好 icon=lucide:terminal
|
|
76
76
|
aigne doc prefs --list
|
|
77
77
|
```
|
|
78
78
|
|
|
79
|
-
|
|
80
|
-
|
|
81
|
-
**示例输出:**
|
|
79
|
+
该命令会显示一个格式化列表,展示每个规则的状态、范围、ID 以及任何路径限制。
|
|
82
80
|
|
|
83
|
-
```text
|
|
81
|
+
```text 输出示例 icon=lucide:clipboard-list
|
|
84
82
|
# 用户偏好
|
|
85
83
|
|
|
86
84
|
**格式说明:**
|
|
87
|
-
- 🟢 =
|
|
85
|
+
- 🟢 = 已激活的偏好, ⚪ = 未激活的偏好
|
|
88
86
|
- [scope] = 偏好范围 (global, structure, document, translation)
|
|
89
|
-
- ID =
|
|
87
|
+
- ID = 唯一偏好标识符
|
|
90
88
|
- Paths = 特定文件路径 (如果适用)
|
|
91
89
|
|
|
92
90
|
🟢 [structure] pref_a1b2c3d4e5f6g7h8 | Paths: overview.md
|
|
93
|
-
|
|
91
|
+
在概览文档末尾添加“后续步骤”部分。
|
|
94
92
|
|
|
95
93
|
⚪ [document] pref_i9j0k1l2m3n4o5p6
|
|
96
94
|
代码注释必须用英语编写。
|
|
97
|
-
|
|
98
95
|
```
|
|
99
96
|
|
|
100
|
-
###
|
|
101
|
-
|
|
102
|
-
如果您想临时禁用某个规则而不删除它,可以切换其活动状态。请使用 `--toggle` 标志。
|
|
97
|
+
### 停用和重新激活偏好
|
|
103
98
|
|
|
104
|
-
|
|
99
|
+
如果你想临时禁用一个规则而不删除它,可以使用 `--toggle` 标志来切换其激活状态。不带 ID 运行该命令将启动一个交互模式,允许你选择一个或多个偏好进行切换。
|
|
105
100
|
|
|
106
101
|
```bash 以交互方式切换偏好 icon=lucide:terminal
|
|
107
102
|
aigne doc prefs --toggle
|
|
108
103
|
```
|
|
109
104
|
|
|
110
|
-
要直接切换特定规则,请使用 `--id` 标志提供其 ID
|
|
105
|
+
要直接切换特定规则,请使用 `--id` 标志提供其 ID。这对应于 `deactivateRule` 函数,该函数将规则的 `active` 属性设置为 `false`。
|
|
111
106
|
|
|
112
107
|
```bash 切换特定偏好 icon=lucide:terminal
|
|
113
108
|
aigne doc prefs --toggle --id pref_i9j0k1l2m3n4o5p6
|
|
114
109
|
```
|
|
115
110
|
|
|
116
|
-
###
|
|
111
|
+
### 删除偏好
|
|
117
112
|
|
|
118
|
-
要永久删除一个或多个偏好,请使用 `--remove`
|
|
113
|
+
要永久删除一个或多个偏好,请使用 `--remove` 标志。此操作对应于 `removeRule` 函数,且无法撤销。
|
|
119
114
|
|
|
120
|
-
要进入交互式选择提示,请不带 ID
|
|
115
|
+
要进入交互式选择提示,请不带 ID 运行该命令。
|
|
121
116
|
|
|
122
|
-
```bash
|
|
117
|
+
```bash 以交互方式删除偏好 icon=lucide:terminal
|
|
123
118
|
aigne doc prefs --remove
|
|
124
119
|
```
|
|
125
120
|
|
|
126
|
-
要通过 ID
|
|
121
|
+
要通过 ID 直接删除特定规则,请使用 `--id` 标志。
|
|
127
122
|
|
|
128
|
-
```bash
|
|
123
|
+
```bash 删除特定偏好 icon=lucide:terminal
|
|
129
124
|
aigne doc prefs --remove --id pref_a1b2c3d4e5f6g7h8
|
|
130
125
|
```
|
|
131
126
|
|
|
132
127
|
## 后续步骤
|
|
133
128
|
|
|
134
|
-
管理偏好是根据项目特定需求定制 DocSmith
|
|
129
|
+
管理偏好是根据项目特定需求定制 DocSmith 的关键部分。有关更多自定义选项,请查阅主要的[配置指南](./configuration.md)。
|
package/docs/configuration.md
CHANGED
|
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
|
|
1
1
|
# Configuration Guide
|
|
2
2
|
|
|
3
|
-
AIGNE DocSmith's behavior is controlled by a central file, `config.yaml`,
|
|
3
|
+
AIGNE DocSmith's behavior is controlled by a central file, `config.yaml`, located at `.aigne/doc-smith/config.yaml`. This file dictates the style, target audience, languages, and structure of your documentation.
|
|
4
4
|
|
|
5
5
|
You can create and manage this file using the interactive setup wizard by running `aigne doc init`. For a step-by-step walkthrough, see the [Interactive Setup](./configuration-interactive-setup.md) guide.
|
|
6
6
|
|
|
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ Your documentation is shaped by several key areas of configuration. Explore thes
|
|
|
10
10
|
|
|
11
11
|
<x-cards data-columns="2">
|
|
12
12
|
<x-card data-title="Interactive Setup" data-icon="lucide:wand-2" data-href="/configuration/interactive-setup">
|
|
13
|
-
Learn about the guided wizard that helps you configure your documentation project
|
|
13
|
+
Learn about the guided wizard that helps you configure your documentation project, including setting recommendations and conflict detection.
|
|
14
14
|
</x-card>
|
|
15
15
|
<x-card data-title="LLM Setup" data-icon="lucide:brain-circuit" data-href="/configuration/llm-setup">
|
|
16
16
|
Discover how to connect different AI models, including using the built-in AIGNE Hub which requires no API keys.
|
|
@@ -33,8 +33,8 @@ These settings provide basic context about your project, which is used when publ
|
|
|
33
33
|
|
|
34
34
|
| Parameter | Description |
|
|
35
35
|
|---|---|
|
|
36
|
-
| `projectName` | The name of your project.
|
|
37
|
-
| `projectDesc` | A short description of your project.
|
|
36
|
+
| `projectName` | The name of your project. Detected from `package.json` if available. |
|
|
37
|
+
| `projectDesc` | A short description of your project. Detected from `package.json`. |
|
|
38
38
|
| `projectLogo` | A path or URL to your project's logo image. |
|
|
39
39
|
|
|
40
40
|
### Documentation Strategy
|
|
@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ These settings provide basic context about your project, which is used when publ
|
|
|
42
42
|
These parameters define the tone, style, and depth of the generated content.
|
|
43
43
|
|
|
44
44
|
#### `documentPurpose`
|
|
45
|
-
|
|
45
|
+
Defines the main outcome you want readers to achieve. This setting influences the overall structure and focus of the documentation.
|
|
46
46
|
|
|
47
47
|
| Option | Name | Description |
|
|
48
48
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
@@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ What is the main outcome you want readers to achieve? This setting influences th
|
|
|
54
54
|
| `mixedPurpose` | Serve multiple purposes | Documentation covering multiple needs. |
|
|
55
55
|
|
|
56
56
|
#### `targetAudienceTypes`
|
|
57
|
-
|
|
57
|
+
Defines who will be reading this documentation most often. This choice affects the writing style and examples.
|
|
58
58
|
|
|
59
59
|
| Option | Name | Description |
|
|
60
60
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
@@ -66,7 +66,7 @@ Who will be reading this documentation most often? This choice affects the writi
|
|
|
66
66
|
| `mixedTechnical`| Mixed technical audience | Developers, DevOps, and other technical users. |
|
|
67
67
|
|
|
68
68
|
#### `readerKnowledgeLevel`
|
|
69
|
-
|
|
69
|
+
Defines what readers typically know when they arrive. This adjusts how much foundational knowledge is assumed.
|
|
70
70
|
|
|
71
71
|
| Option | Name | Description |
|
|
72
72
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
@@ -77,7 +77,7 @@ What do readers typically know when they arrive? This adjusts how much foundatio
|
|
|
77
77
|
| `exploringEvaluating` | Is evaluating this tool against others | Trying to understand if this fits their needs. |
|
|
78
78
|
|
|
79
79
|
#### `documentationDepth`
|
|
80
|
-
|
|
80
|
+
Defines how comprehensive the documentation should be.
|
|
81
81
|
|
|
82
82
|
| Option | Name | Description |
|
|
83
83
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
@@ -92,8 +92,8 @@ For more granular control, you can provide free-text instructions.
|
|
|
92
92
|
|
|
93
93
|
| Parameter | Description |
|
|
94
94
|
|---|---|
|
|
95
|
-
| `rules` | A multi-line string where you can define specific documentation generation rules
|
|
96
|
-
| `targetAudience`| A multi-line string to describe your specific target audience
|
|
95
|
+
| `rules` | A multi-line string where you can define specific documentation generation rules (e.g., "Always include performance benchmarks"). |
|
|
96
|
+
| `targetAudience`| A multi-line string to describe your specific target audience in more detail than the presets allow. |
|
|
97
97
|
|
|
98
98
|
### Language and Path Configuration
|
|
99
99
|
|
|
@@ -109,56 +109,35 @@ These settings control localization and file locations.
|
|
|
109
109
|
|
|
110
110
|
## Example `config.yaml`
|
|
111
111
|
|
|
112
|
-
Here is an example of a complete configuration file
|
|
112
|
+
Here is an example of a complete configuration file. You can edit this file directly to change settings at any time.
|
|
113
113
|
|
|
114
114
|
```yaml Example config.yaml icon=logos:yaml
|
|
115
115
|
# Project information for documentation publishing
|
|
116
116
|
projectName: AIGNE DocSmith
|
|
117
|
-
projectDesc:
|
|
117
|
+
projectDesc: An AI-driven documentation generation tool.
|
|
118
118
|
projectLogo: https://docsmith.aigne.io/image-bin/uploads/def424c20bbdb3c77483894fe0e22819.png
|
|
119
119
|
|
|
120
120
|
# =============================================================================
|
|
121
121
|
# Documentation Configuration
|
|
122
122
|
# =============================================================================
|
|
123
123
|
|
|
124
|
-
# Purpose: What
|
|
125
|
-
#
|
|
126
|
-
# getStarted - Get started quickly: Help new users go from zero to working in <30 minutes
|
|
127
|
-
# completeTasks - Complete specific tasks: Guide users through common workflows and use cases
|
|
128
|
-
# findAnswers - Find answers fast: Provide searchable reference for all features and APIs
|
|
129
|
-
# understandSystem - Understand the system: Explain how it works, why design decisions were made
|
|
130
|
-
# solveProblems - Troubleshoot common issues: Help users troubleshoot and fix issues
|
|
131
|
-
# mixedPurpose - Serve multiple purposes: Comprehensive documentation covering multiple needs
|
|
124
|
+
# Purpose: What is the main outcome you want readers to achieve?
|
|
125
|
+
# Options: getStarted, completeTasks, findAnswers, understandSystem, solveProblems, mixedPurpose
|
|
132
126
|
documentPurpose:
|
|
133
127
|
- completeTasks
|
|
134
128
|
- findAnswers
|
|
135
129
|
|
|
136
130
|
# Target Audience: Who will be reading this most often?
|
|
137
|
-
#
|
|
138
|
-
# endUsers - End users (non-technical): People who use the product but don't code
|
|
139
|
-
# developers - Developers integrating your product/API: Engineers adding this to their projects
|
|
140
|
-
# devops - DevOps / SRE / Infrastructure teams: Teams deploying, monitoring, maintaining systems
|
|
141
|
-
# decisionMakers - Technical decision makers: Architects, leads evaluating or planning implementation
|
|
142
|
-
# supportTeams - Support teams: People helping others use the product
|
|
143
|
-
# mixedTechnical - Mixed technical audience: Developers, DevOps, and technical users
|
|
131
|
+
# Options: endUsers, developers, devops, decisionMakers, supportTeams, mixedTechnical
|
|
144
132
|
targetAudienceTypes:
|
|
145
133
|
- developers
|
|
146
134
|
|
|
147
135
|
# Reader Knowledge Level: What do readers typically know when they arrive?
|
|
148
|
-
#
|
|
149
|
-
# completeBeginners - Is a total beginner, starting from scratch: New to this domain/technology entirely
|
|
150
|
-
# domainFamiliar - Has used similar tools before: Know the problem space, new to this specific solution
|
|
151
|
-
# experiencedUsers - Is an expert trying to do something specific: Regular users needing reference/advanced topics
|
|
152
|
-
# emergencyTroubleshooting - Emergency/troubleshooting: Something's broken, need to fix it quickly
|
|
153
|
-
# exploringEvaluating - Is evaluating this tool against others: Trying to understand if this fits their needs
|
|
136
|
+
# Options: completeBeginners, domainFamiliar, experiencedUsers, emergencyTroubleshooting, exploringEvaluating
|
|
154
137
|
readerKnowledgeLevel: domainFamiliar
|
|
155
138
|
|
|
156
139
|
# Documentation Depth: How comprehensive should the documentation be?
|
|
157
|
-
#
|
|
158
|
-
# essentialOnly - Essential only: Cover the 80% use cases, keep it concise
|
|
159
|
-
# balancedCoverage - Balanced coverage: Good depth with practical examples [RECOMMENDED]
|
|
160
|
-
# comprehensive - Comprehensive: Cover all features, edge cases, and advanced scenarios
|
|
161
|
-
# aiDecide - Let AI decide: Analyze code complexity and suggest appropriate depth
|
|
140
|
+
# Options: essentialOnly, balancedCoverage, comprehensive, aiDecide
|
|
162
141
|
documentationDepth: balancedCoverage
|
|
163
142
|
|
|
164
143
|
# Custom Rules: Define specific documentation generation rules and requirements
|
|
@@ -169,15 +148,22 @@ rules: |+
|
|
|
169
148
|
targetAudience: |+
|
|
170
149
|
|
|
171
150
|
|
|
172
|
-
# Glossary:
|
|
173
|
-
# glossary: "@glossary.md"
|
|
151
|
+
# Glossary: Path to markdown file containing project-specific terms and definitions
|
|
152
|
+
# glossary: "@glossary.md"
|
|
174
153
|
|
|
154
|
+
# Primary language for the documentation
|
|
175
155
|
locale: en
|
|
176
|
-
|
|
177
|
-
#
|
|
178
|
-
#
|
|
179
|
-
|
|
180
|
-
|
|
156
|
+
|
|
157
|
+
# List of languages to translate the documentation into
|
|
158
|
+
# translateLanguages:
|
|
159
|
+
# - zh
|
|
160
|
+
# - fr
|
|
161
|
+
|
|
162
|
+
# Directory to save generated documentation
|
|
163
|
+
docsDir: .aigne/doc-smith/docs
|
|
164
|
+
|
|
165
|
+
# Source code paths to analyze
|
|
166
|
+
sourcesPath:
|
|
181
167
|
- ./
|
|
182
168
|
```
|
|
183
169
|
|
package/docs/configuration.zh.md
CHANGED
|
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
|
|
|
1
1
|
# 配置指南
|
|
2
2
|
|
|
3
|
-
AIGNE DocSmith
|
|
3
|
+
AIGNE DocSmith 的行为由一个位于 `.aigne/doc-smith/config.yaml` 的核心文件 `config.yaml` 控制。该文件决定了文档的风格、目标受众、语言和结构。
|
|
4
4
|
|
|
5
|
-
你可以通过运行 `aigne doc init
|
|
5
|
+
你可以通过运行 `aigne doc init` 使用交互式设置向导来创建和管理此文件。有关分步演练,请参阅 [交互式设置](./configuration-interactive-setup.md) 指南。
|
|
6
6
|
|
|
7
7
|
## 核心配置区域
|
|
8
8
|
|
|
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ AIGNE DocSmith 的行为由一个中心文件 `config.yaml` 控制,该文件
|
|
|
10
10
|
|
|
11
11
|
<x-cards data-columns="2">
|
|
12
12
|
<x-card data-title="交互式设置" data-icon="lucide:wand-2" data-href="/configuration/interactive-setup">
|
|
13
|
-
|
|
13
|
+
了解引导式向导如何帮助你配置文档项目,包括设置建议和冲突检测。
|
|
14
14
|
</x-card>
|
|
15
15
|
<x-card data-title="LLM 设置" data-icon="lucide:brain-circuit" data-href="/configuration/llm-setup">
|
|
16
16
|
了解如何连接不同的 AI 模型,包括使用无需 API 密钥的内置 AIGNE Hub。
|
|
@@ -29,12 +29,12 @@ AIGNE DocSmith 的行为由一个中心文件 `config.yaml` 控制,该文件
|
|
|
29
29
|
|
|
30
30
|
### 项目信息
|
|
31
31
|
|
|
32
|
-
|
|
32
|
+
这些设置提供了关于项目的基本背景信息,用于发布文档。
|
|
33
33
|
|
|
34
34
|
| Parameter | Description |
|
|
35
35
|
|---|---|
|
|
36
|
-
| `projectName` |
|
|
37
|
-
| `projectDesc` |
|
|
36
|
+
| `projectName` | 你的项目名称。如果可用,将从 `package.json` 中检测。 |
|
|
37
|
+
| `projectDesc` | 你的项目的简短描述。从 `package.json` 中检测。 |
|
|
38
38
|
| `projectLogo` | 你的项目徽标图片的路径或 URL。 |
|
|
39
39
|
|
|
40
40
|
### 文档策略
|
|
@@ -42,23 +42,23 @@ AIGNE DocSmith 的行为由一个中心文件 `config.yaml` 控制,该文件
|
|
|
42
42
|
这些参数定义了生成内容的基调、风格和深度。
|
|
43
43
|
|
|
44
44
|
#### `documentPurpose`
|
|
45
|
-
|
|
45
|
+
定义你希望读者达到的主要成果。此设置会影响文档的整体结构和重点。
|
|
46
46
|
|
|
47
47
|
| Option | Name | Description |
|
|
48
48
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
49
49
|
| `getStarted` | 快速入门 | 帮助新用户在 30 分钟内从零开始上手。 |
|
|
50
|
-
| `completeTasks` | 完成特定任务 |
|
|
50
|
+
| `completeTasks` | 完成特定任务 | 引导用户完成常见工作流程和用例。 |
|
|
51
51
|
| `findAnswers` | 快速查找答案 | 为所有功能和 API 提供可搜索的参考。 |
|
|
52
52
|
| `understandSystem`| 理解系统 | 解释其工作原理以及做出设计决策的原因。 |
|
|
53
|
-
| `solveProblems` |
|
|
53
|
+
| `solveProblems` | 解决常见问题 | 帮助用户排查和修复问题。 |
|
|
54
54
|
| `mixedPurpose` | 服务于多种目的 | 涵盖多种需求的文档。 |
|
|
55
55
|
|
|
56
56
|
#### `targetAudienceTypes`
|
|
57
|
-
|
|
57
|
+
定义最常阅读此文档的受众。此选择会影响写作风格和示例。
|
|
58
58
|
|
|
59
59
|
| Option | Name | Description |
|
|
60
60
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
61
|
-
| `endUsers` | 最终用户(非技术人员) |
|
|
61
|
+
| `endUsers` | 最终用户(非技术人员) | 使用产品但不编码的人员。 |
|
|
62
62
|
| `developers` | 集成你的产品/API 的开发者 | 将此添加到其项目中的工程师。 |
|
|
63
63
|
| `devops` | DevOps / SRE / 基础设施团队 | 部署、监控和维护系统的团队。 |
|
|
64
64
|
| `decisionMakers`| 技术决策者 | 评估或规划实施的架构师或负责人。 |
|
|
@@ -66,25 +66,25 @@ AIGNE DocSmith 的行为由一个中心文件 `config.yaml` 控制,该文件
|
|
|
66
66
|
| `mixedTechnical`| 混合技术受众 | 开发者、DevOps 和其他技术用户。 |
|
|
67
67
|
|
|
68
68
|
#### `readerKnowledgeLevel`
|
|
69
|
-
|
|
69
|
+
定义读者通常具备的知识水平。这会调整对基础知识的假设程度。
|
|
70
70
|
|
|
71
71
|
| Option | Name | Description |
|
|
72
72
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
73
|
-
| `completeBeginners` | 完全的初学者,从零开始 |
|
|
74
|
-
| `domainFamiliar` |
|
|
75
|
-
| `experiencedUsers` |
|
|
73
|
+
| `completeBeginners` | 完全的初学者,从零开始 | 完全不熟悉此领域/技术。 |
|
|
74
|
+
| `domainFamiliar` | 之前使用过类似工具 | 了解问题领域,但对这个特定解决方案不熟悉。 |
|
|
75
|
+
| `experiencedUsers` | 试图做特定事情的专家 | 需要参考或高级主题的常规用户。 |
|
|
76
76
|
| `emergencyTroubleshooting`| 紧急情况/故障排查 | 出现问题,需要快速修复。 |
|
|
77
77
|
| `exploringEvaluating` | 正在评估此工具并与其他工具进行比较 | 试图了解这是否符合他们的需求。 |
|
|
78
78
|
|
|
79
79
|
#### `documentationDepth`
|
|
80
|
-
|
|
80
|
+
定义文档应达到的全面程度。
|
|
81
81
|
|
|
82
82
|
| Option | Name | Description |
|
|
83
83
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
84
|
-
| `essentialOnly` |
|
|
84
|
+
| `essentialOnly` | 仅限基本内容 | 涵盖 80% 的用例,保持简洁。 |
|
|
85
85
|
| `balancedCoverage`| 均衡覆盖 | 具有良好深度和实际示例 [推荐]。 |
|
|
86
|
-
| `comprehensive` | 全面 |
|
|
87
|
-
| `aiDecide` |
|
|
86
|
+
| `comprehensive` | 全面 | 涵盖所有功能、边缘情况和高级场景。 |
|
|
87
|
+
| `aiDecide` | 让 AI 决定 | 分析代码复杂性并建议适当的深度。 |
|
|
88
88
|
|
|
89
89
|
### 自定义指令
|
|
90
90
|
|
|
@@ -92,8 +92,8 @@ AIGNE DocSmith 的行为由一个中心文件 `config.yaml` 控制,该文件
|
|
|
92
92
|
|
|
93
93
|
| Parameter | Description |
|
|
94
94
|
|---|---|
|
|
95
|
-
| `rules` |
|
|
96
|
-
| `targetAudience`|
|
|
95
|
+
| `rules` | 一个多行字符串,你可以在其中定义特定的文档生成规则(例如,“始终包含性能基准测试”)。 |
|
|
96
|
+
| `targetAudience`| 一个多行字符串,用于比预设更详细地描述你的特定目标受众。 |
|
|
97
97
|
|
|
98
98
|
### 语言和路径配置
|
|
99
99
|
|
|
@@ -101,7 +101,7 @@ AIGNE DocSmith 的行为由一个中心文件 `config.yaml` 控制,该文件
|
|
|
101
101
|
|
|
102
102
|
| Parameter | Description |
|
|
103
103
|
|---|---|
|
|
104
|
-
| `locale` |
|
|
104
|
+
| `locale` | 文档的主语言(例如,`en`、`zh`)。 |
|
|
105
105
|
| `translateLanguages` | 要将文档翻译成的语言代码列表(例如,`[ja, fr, es]`)。 |
|
|
106
106
|
| `docsDir` | 保存生成的文档文件的目录。 |
|
|
107
107
|
| `sourcesPath` | 供 DocSmith 分析的源代码路径或 glob 模式列表(例如,`['./src', './lib/**/*.js']`)。 |
|
|
@@ -109,59 +109,38 @@ AIGNE DocSmith 的行为由一个中心文件 `config.yaml` 控制,该文件
|
|
|
109
109
|
|
|
110
110
|
## config.yaml 示例
|
|
111
111
|
|
|
112
|
-
|
|
112
|
+
这是一个完整的配置文件示例。你可以随时直接编辑此文件以更改设置。
|
|
113
113
|
|
|
114
114
|
```yaml Example config.yaml icon=logos:yaml
|
|
115
115
|
# 用于文档发布的项目信息
|
|
116
116
|
projectName: AIGNE DocSmith
|
|
117
|
-
projectDesc:
|
|
117
|
+
projectDesc: An AI-driven documentation generation tool.
|
|
118
118
|
projectLogo: https://docsmith.aigne.io/image-bin/uploads/def424c20bbdb3c77483894fe0e22819.png
|
|
119
119
|
|
|
120
120
|
# =============================================================================
|
|
121
121
|
# 文档配置
|
|
122
122
|
# =============================================================================
|
|
123
123
|
|
|
124
|
-
#
|
|
125
|
-
#
|
|
126
|
-
# getStarted - 快速入门:帮助新用户在 30 分钟内从零开始上手
|
|
127
|
-
# completeTasks - 完成特定任务:引导用户完成常见工作流和用例
|
|
128
|
-
# findAnswers - 快速查找答案:为所有功能和 API 提供可搜索的参考
|
|
129
|
-
# understandSystem - 理解系统:解释其工作原理以及做出设计决策的原因
|
|
130
|
-
# solveProblems - 排查常见问题:帮助用户排查和修复问题
|
|
131
|
-
# mixedPurpose - 服务于多种目的:涵盖多种需求的综合性文档
|
|
124
|
+
# 目的:你希望读者达到的主要成果是什么?
|
|
125
|
+
# 选项:getStarted, completeTasks, findAnswers, understandSystem, solveProblems, mixedPurpose
|
|
132
126
|
documentPurpose:
|
|
133
127
|
- completeTasks
|
|
134
128
|
- findAnswers
|
|
135
129
|
|
|
136
|
-
#
|
|
137
|
-
#
|
|
138
|
-
# endUsers - 最终用户(非技术人员):使用产品但不编写代码的人员
|
|
139
|
-
# developers - 集成你的产品/API 的开发者:将此添加到其项目中的工程师
|
|
140
|
-
# devops - DevOps / SRE / 基础设施团队:部署、监控、维护系统的团队
|
|
141
|
-
# decisionMakers - 技术决策者:评估或规划实施的架构师、负责人
|
|
142
|
-
# supportTeams - 支持团队:帮助他人使用产品的人员
|
|
143
|
-
# mixedTechnical - 混合技术受众:开发者、DevOps 和技术用户
|
|
130
|
+
# 目标受众:谁会最常阅读此文档?
|
|
131
|
+
# 选项:endUsers, developers, devops, decisionMakers, supportTeams, mixedTechnical
|
|
144
132
|
targetAudienceTypes:
|
|
145
133
|
- developers
|
|
146
134
|
|
|
147
|
-
#
|
|
148
|
-
#
|
|
149
|
-
# completeBeginners - 完全的初学者,从零开始:完全不了解此领域/技术
|
|
150
|
-
# domainFamiliar - 之前使用过类似的工具:了解问题领域,但对这个具体解决方案不熟悉
|
|
151
|
-
# experiencedUsers - 希望完成特定任务的专家:需要参考/高级主题的普通用户
|
|
152
|
-
# emergencyTroubleshooting - 紧急情况/故障排查:出现问题,需要快速修复
|
|
153
|
-
# exploringEvaluating - 正在评估此工具并与其他工具进行比较:试图了解这是否符合他们的需求
|
|
135
|
+
# 读者知识水平:读者通常具备什么知识?
|
|
136
|
+
# 选项:completeBeginners, domainFamiliar, experiencedUsers, emergencyTroubleshooting, exploringEvaluating
|
|
154
137
|
readerKnowledgeLevel: domainFamiliar
|
|
155
138
|
|
|
156
|
-
#
|
|
157
|
-
#
|
|
158
|
-
# essentialOnly - 仅包含核心内容:覆盖 80% 的用例,保持简洁
|
|
159
|
-
# balancedCoverage - 均衡覆盖:具有良好深度和实际示例 [推荐]
|
|
160
|
-
# comprehensive - 全面:覆盖所有功能、边缘情况和高级场景
|
|
161
|
-
# aiDecide - 由 AI 决定:分析代码复杂性并建议合适的深度
|
|
139
|
+
# 文档深度:文档应该有多全面?
|
|
140
|
+
# 选项:essentialOnly, balancedCoverage, comprehensive, aiDecide
|
|
162
141
|
documentationDepth: balancedCoverage
|
|
163
142
|
|
|
164
|
-
#
|
|
143
|
+
# 自定义规则:定义特定的文档生成规则和要求
|
|
165
144
|
rules: |+
|
|
166
145
|
|
|
167
146
|
|
|
@@ -169,18 +148,25 @@ rules: |+
|
|
|
169
148
|
targetAudience: |+
|
|
170
149
|
|
|
171
150
|
|
|
172
|
-
#
|
|
173
|
-
# glossary: "@glossary.md"
|
|
151
|
+
# 术语表:包含项目特定术语和定义的 markdown 文件的路径
|
|
152
|
+
# glossary: "@glossary.md"
|
|
174
153
|
|
|
154
|
+
# 文档的主语言
|
|
175
155
|
locale: en
|
|
176
|
-
|
|
177
|
-
#
|
|
178
|
-
#
|
|
179
|
-
|
|
180
|
-
|
|
156
|
+
|
|
157
|
+
# 要将文档翻译成的语言列表
|
|
158
|
+
# translateLanguages:
|
|
159
|
+
# - zh
|
|
160
|
+
# - fr
|
|
161
|
+
|
|
162
|
+
# 保存生成的文档的目录
|
|
163
|
+
docsDir: .aigne/doc-smith/docs
|
|
164
|
+
|
|
165
|
+
# 要分析的源代码路径
|
|
166
|
+
sourcesPath:
|
|
181
167
|
- ./
|
|
182
168
|
```
|
|
183
169
|
|
|
184
|
-
|
|
170
|
+
完成配置后,你就可以创建符合项目需求的文档了。下一步是运行生成命令。
|
|
185
171
|
|
|
186
172
|
➡️ **下一步:** [生成文档](./features-generate-documentation.md)
|
|
@@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
|
|
|
1
1
|
# Generate Documentation
|
|
2
2
|
|
|
3
|
-
The `aigne doc generate` command is the core function
|
|
4
|
-
|
|
5
|
-
This process analyzes your codebase, plans a logical document structure, and then generates content for each section. It's the primary way to create your documentation from scratch.
|
|
3
|
+
The `aigne doc generate` command is the core function for creating a complete documentation set from your source code. This process analyzes your codebase, plans a logical document structure, and then generates content for each section. It's the primary way to create your documentation from scratch.
|
|
6
4
|
|
|
7
5
|
## Your First Generation
|
|
8
6
|
|
|
@@ -14,17 +12,18 @@ aigne doc generate
|
|
|
14
12
|
|
|
15
13
|
### Automatic Configuration
|
|
16
14
|
|
|
17
|
-
If you
|
|
15
|
+
If you run this command for the first time in a project, DocSmith detects that no configuration exists. It will then launch an interactive setup wizard to guide you through the initial setup. This ensures you have a properly configured environment before generation begins.
|
|
18
16
|
|
|
19
17
|
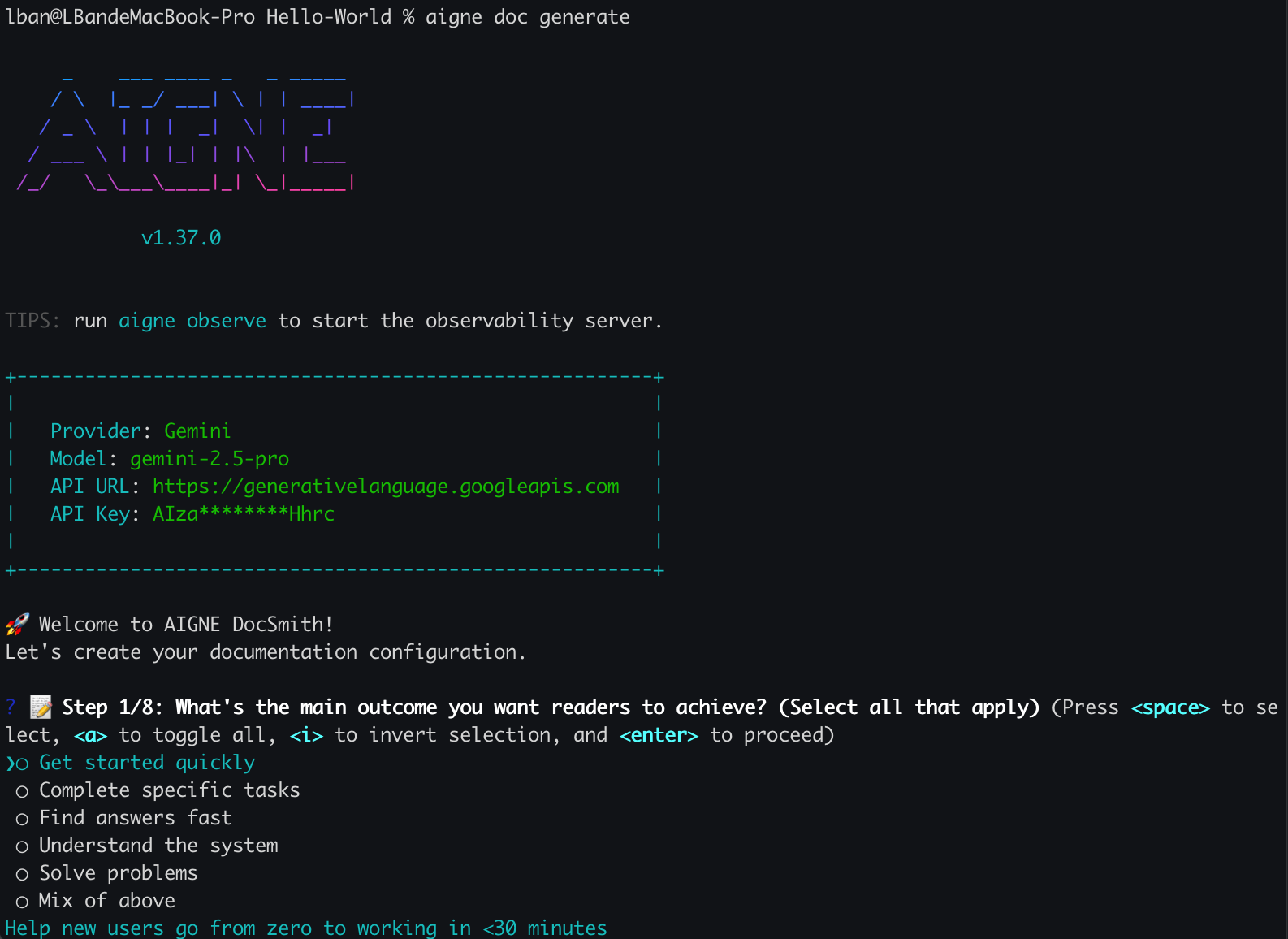
|
|
20
18
|
|
|
21
19
|
You will be asked a series of questions to define:
|
|
20
|
+
|
|
22
21
|
- Document generation rules and style
|
|
23
22
|
- The target audience
|
|
24
23
|
- Primary and translation languages
|
|
25
24
|
- Source code and output paths
|
|
26
25
|
|
|
27
|
-
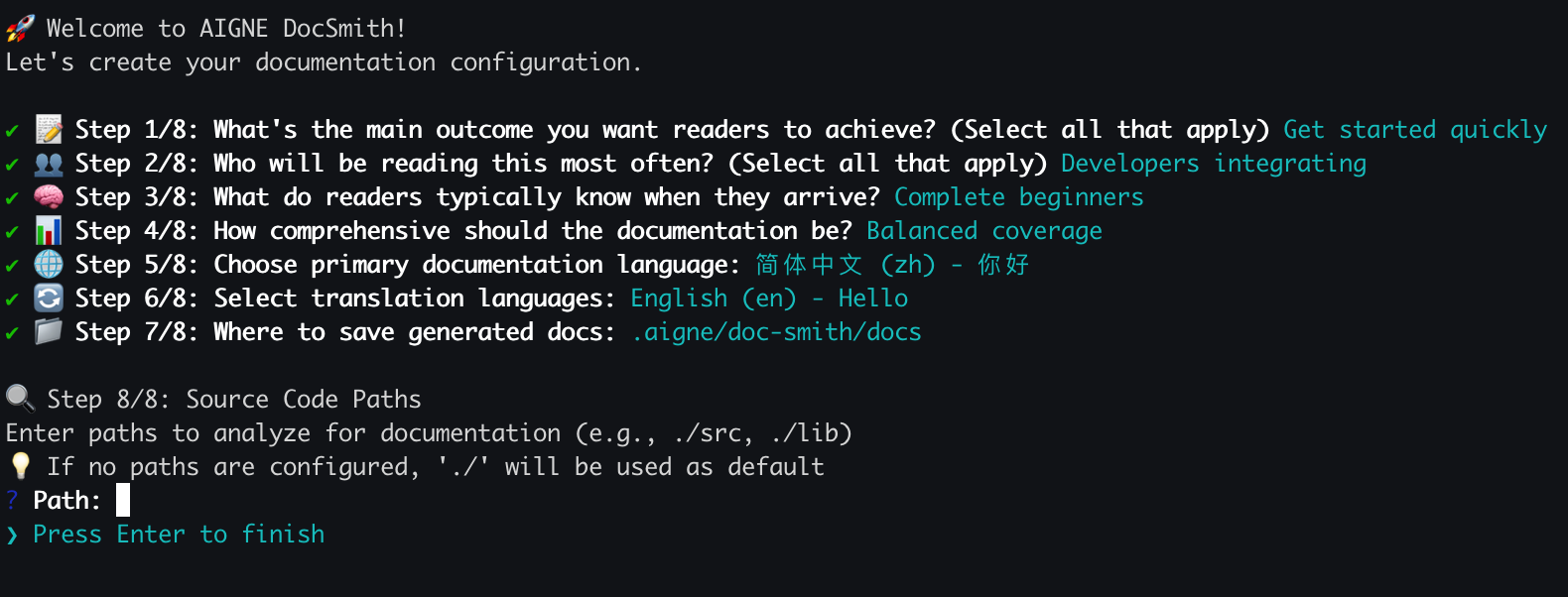
|
|
28
27
|
|
|
29
28
|
Once the configuration is complete, DocSmith proceeds with the documentation generation.
|
|
30
29
|
|
|
@@ -36,7 +35,7 @@ Upon successful completion, your newly created documentation will be available i
|
|
|
36
35
|
|
|
37
36
|
## The Generation Process
|
|
38
37
|
|
|
39
|
-
The `generate` command follows an automated workflow
|
|
38
|
+
The `generate` command follows an automated workflow. The process can be visualized as follows:
|
|
40
39
|
|
|
41
40
|
```d2
|
|
42
41
|
direction: down
|
|
@@ -98,5 +97,5 @@ While the default `generate` command is sufficient for most use cases, you can u
|
|
|
98
97
|
Now that you have generated your initial documentation, your project will continue to evolve. To keep your documents synchronized with your code, you will need to update them. Proceed to the next section to learn how to make targeted changes and regenerate specific files.
|
|
99
98
|
|
|
100
99
|
<x-card data-title="Update and Refine" data-icon="lucide:file-edit" data-href="/features/update-and-refine">
|
|
101
|
-
|
|
100
|
+
Learn how to update documents when your code changes or make specific improvements using feedback.
|
|
102
101
|
</x-card>
|