red_amber 0.5.0 → 0.5.2
This diff represents the content of publicly available package versions that have been released to one of the supported registries. The information contained in this diff is provided for informational purposes only and reflects changes between package versions as they appear in their respective public registries.
- checksums.yaml +4 -4
- data/.devcontainer/Dockerfile +75 -0
- data/.devcontainer/devcontainer.json +38 -0
- data/.devcontainer/onCreateCommand.sh +26 -0
- data/.rubocop.yml +3 -3
- data/CHANGELOG.md +102 -18
- data/Gemfile +1 -1
- data/README.ja.md +51 -32
- data/README.md +46 -30
- data/Rakefile +55 -0
- data/doc/DataFrame_Comparison.md +9 -13
- data/doc/DataFrame_Comparison_ja.md +61 -0
- data/doc/Dev_Containers.ja.md +290 -0
- data/doc/Dev_Containers.md +292 -0
- data/doc/qmd/examples_of_red_amber.qmd +4596 -0
- data/doc/qmd/red-amber.qmd +90 -0
- data/docker/Dockerfile +2 -2
- data/docker/Gemfile +1 -1
- data/docker/docker-compose.yml +1 -1
- data/docker/readme.md +5 -5
- data/lib/red_amber/data_frame_displayable.rb +1 -1
- data/lib/red_amber/data_frame_loadsave.rb +1 -1
- data/lib/red_amber/data_frame_selectable.rb +2 -2
- data/lib/red_amber/data_frame_variable_operation.rb +6 -6
- data/lib/red_amber/group.rb +287 -39
- data/lib/red_amber/subframes.rb +6 -6
- data/lib/red_amber/vector.rb +2 -1
- data/lib/red_amber/vector_selectable.rb +68 -35
- data/lib/red_amber/vector_string_function.rb +81 -13
- data/lib/red_amber/version.rb +1 -1
- data/red_amber.gemspec +3 -3
- metadata +15 -11
- data/docker/Gemfile.lock +0 -118
- data/docker/example +0 -86
- data/docker/notebook/examples_of_red_amber.ipynb +0 -8562
- data/docker/notebook/red-amber.ipynb +0 -188
data/README.md
CHANGED
|
@@ -4,10 +4,10 @@
|
|
|
4
4
|
[](https://github.com/red-data-tools/red_amber/actions/workflows/ci.yml)
|
|
5
5
|
[](https://codeclimate.com/github/heronshoes/red_amber/maintainability)
|
|
6
6
|
[](https://codeclimate.com/github/heronshoes/red_amber/test_coverage)
|
|
7
|
-
[](https://
|
|
7
|
+
[](https://red-data-tools.github.io/red_amber/)
|
|
8
8
|
[](https://github.com/red-data-tools/red_amber/discussions)
|
|
9
9
|
|
|
10
|
-
A
|
|
10
|
+
A dataframe library for Rubyists.
|
|
11
11
|
|
|
12
12
|
- Powered by [Red Arrow](https://github.com/apache/arrow/tree/master/ruby/red-arrow)
|
|
13
13
|
[](https://app.element.io/#/room/#red-data-tools_en:gitter.im) [](https://rubygems.org/gems/red-arrow)
|
|
@@ -17,30 +17,37 @@ A simple dataframe library for Ruby.
|
|
|
17
17
|
|
|
18
18
|
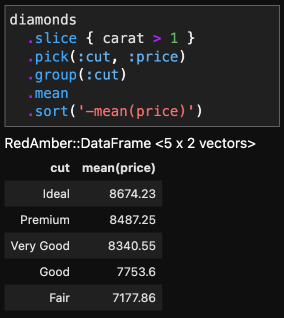
|
|
19
19
|
|
|
20
|
+
## Overview
|
|
21
|
+
* RedAmber is a dataframe library written in ruby. It uses columnar memory format based on [Apache Arrow](https://arrow.apache.org/).
|
|
22
|
+
* Our goal is to manipulate data frames in a Ruby-like writing style using blocks and collections.
|
|
23
|
+
* You can easily try RedAmber with [Dev Container](https://containers.dev/). See [RedAmber Dev Container](doc/Dev_Containers.md).
|
|
24
|
+
* We have [rich document with many examples](https://red-data-tools.github.io/red_amber/) and Jupyter Notebook with 127 operation examples. See [RedAmber Dev Container](doc/Dev_Containers.md).
|
|
25
|
+
|
|
20
26
|
## Requirements
|
|
21
27
|
### Ruby
|
|
22
|
-
Supported Ruby version is >= 3.0
|
|
28
|
+
Supported Ruby version is >= 3.0.
|
|
23
29
|
|
|
24
30
|
### Required libraries
|
|
25
31
|
```ruby
|
|
26
|
-
gem 'red-arrow', '
|
|
27
|
-
gem 'red-
|
|
28
|
-
|
|
29
|
-
gem 'red-
|
|
30
|
-
gem 'red-arrow
|
|
31
|
-
gem '
|
|
32
|
+
gem 'red-arrow', '>= 12.0.0' # Requires Apache Arrow (see installation below).
|
|
33
|
+
gem 'red-arrow-numo-narray' # Optional, recommended if you use inputs from Numo::NArray,
|
|
34
|
+
# or use random sampling feature.
|
|
35
|
+
gem 'red-parquet', '>= 12.0.0' # Optional, if you use IO from/to parquet.
|
|
36
|
+
gem 'red-datasets-arrow' # Optional, if you use Red Datasets.
|
|
37
|
+
gem 'red-arrow-activerecord' # Optional, if you use Active Record.
|
|
38
|
+
gem 'rover-df', # Optional, if you use IO from/to Rover::DataFrame.
|
|
32
39
|
```
|
|
33
40
|
|
|
34
41
|
## Installation
|
|
35
42
|
|
|
36
43
|
Install requirements before you install RedAmber.
|
|
37
44
|
|
|
38
|
-
- Apache Arrow (
|
|
39
|
-
- Apache Arrow GLib (
|
|
40
|
-
- Apache Parquet GLib (
|
|
45
|
+
- Apache Arrow (>= 12.0.0)
|
|
46
|
+
- Apache Arrow GLib (>= 12.0.0)
|
|
47
|
+
- Apache Parquet GLib (>= 12.0.0) # If you use IO from/to parquet
|
|
41
48
|
|
|
42
49
|
See [Apache Arrow install document](https://arrow.apache.org/install/).
|
|
43
|
-
|
|
50
|
+
|
|
44
51
|
- Minimum installation example for the latest Ubuntu:
|
|
45
52
|
|
|
46
53
|
```
|
|
@@ -49,50 +56,58 @@ See [Apache Arrow install document](https://arrow.apache.org/install/).
|
|
|
49
56
|
wget https://apache.jfrog.io/artifactory/arrow/$(lsb_release --id --short | tr 'A-Z' 'a-z')/apache-arrow-apt-source-latest-$(lsb_release --codename --short).deb
|
|
50
57
|
sudo apt install -y -V ./apache-arrow-apt-source-latest-$(lsb_release --codename --short).deb
|
|
51
58
|
sudo apt update
|
|
52
|
-
sudo apt install -y -V libarrow-dev
|
|
53
|
-
sudo apt install -y -V libarrow-glib-dev
|
|
59
|
+
sudo apt install -y -V libarrow-dev libarrow-glib-dev
|
|
54
60
|
```
|
|
55
61
|
|
|
56
62
|
- On Fedora 39 (Rawhide):
|
|
57
63
|
|
|
58
64
|
```
|
|
59
65
|
sudo dnf update
|
|
60
|
-
sudo dnf -y install gcc-c++ libarrow-devel libarrow-glib-devel ruby-devel
|
|
66
|
+
sudo dnf -y install gcc-c++ libarrow-devel libarrow-glib-devel ruby-devel libyaml-devel
|
|
61
67
|
```
|
|
62
68
|
|
|
63
69
|
- On macOS, using Homebrew:
|
|
64
70
|
|
|
65
71
|
```
|
|
66
|
-
brew install apache-arrow
|
|
67
|
-
brew install apache-arrow-glib
|
|
72
|
+
brew install apache-arrow apache-arrow-glib
|
|
68
73
|
```
|
|
69
74
|
|
|
70
75
|
If you prepared Apache Arrow, add these lines to your Gemfile:
|
|
71
76
|
|
|
72
77
|
```ruby
|
|
73
|
-
gem 'red-arrow', '
|
|
78
|
+
gem 'red-arrow', '>= 12.0.0'
|
|
74
79
|
gem 'red_amber'
|
|
75
|
-
gem 'red-parquet', '~> 12.0.0' # Optional, if you use IO from/to parquet
|
|
76
|
-
gem 'red-datasets-arrow' # Optional, recommended if you use Red Datasets
|
|
77
80
|
gem 'red-arrow-numo-narray' # Optional, recommended if you use inputs from Numo::NArray
|
|
81
|
+
# or use random sampling feature.
|
|
82
|
+
gem 'red-parquet', '>= 12.0.0' # Optional, if you use IO from/to parquet
|
|
83
|
+
gem 'red-datasets-arrow' # Optional, recommended if you use Red Datasets
|
|
78
84
|
gem 'red-arrow-activerecord' # Optional, if you use Active Record
|
|
79
|
-
gem 'rover-df',
|
|
85
|
+
gem 'rover-df', # Optional, if you use IO from/to Rover::DataFrame.
|
|
80
86
|
```
|
|
81
87
|
|
|
82
88
|
And then execute `bundle install` or install them yourself such as `gem install red_amber`.
|
|
83
89
|
|
|
90
|
+
## Development Containers
|
|
91
|
+
|
|
92
|
+
This repository supports [Dev Containers](https://containers.dev/). You can create a container as a full-featured development environment for RedAmber. The environment includes Ruby, Apache Arrow, RedAmber with source tree, GitHub CLI, sample datasets and Jupyter Lab with IRuby kernel. And you don't need to worry about the change of your local environment.
|
|
93
|
+
|
|
94
|
+
`.devcontainer` directory in this repository includes settings of Dev Container for RedAmber.
|
|
95
|
+
Please refer [How to use Dev Containers in RedAmber](doc/Dev_Containers.md) to use it.
|
|
96
|
+
|
|
84
97
|
## Docker image and Jupyter Notebook
|
|
85
98
|
|
|
99
|
+
(Notice: This feature may be removed in the future. Try Dev Container above.)
|
|
100
|
+
|
|
86
101
|
Docker image is available from `docker` folder. See [readme](docker/readme.md) for instruction. Integrated Jypyter notebook is in docker/notebook folder.
|
|
87
102
|
|
|
88
|
-
You can try the contents of this README interactively by [Binder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/heronshoes/docker-stacks/RedAmber-binder?filepath=red-amber.ipynb).
|
|
103
|
+
You can try the contents of this README interactively by [Binder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/heronshoes/docker-stacks/RedAmber-binder?filepath=red-amber.ipynb).
|
|
89
104
|
[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/heronshoes/docker-stacks/RedAmber-binder?filepath=red-amber.ipynb)
|
|
90
105
|
|
|
91
106
|
[RubyData Docker Stacks](https://github.com/RubyData/docker-stacks) is available as a ready-to-run Docker image containing Jupyter and useful data tools as well as RedAmber (Thanks to Kenta Murata).
|
|
92
107
|
|
|
93
108
|
## Comparison of DataFrames
|
|
94
109
|
|
|
95
|
-
Comparison of basic features of RedAmber with Python
|
|
110
|
+
Comparison of basic features of RedAmber with Python
|
|
96
111
|
[pandas](https://pandas.pydata.org/),
|
|
97
112
|
R [Tidyverse](https://www.tidyverse.org/) and
|
|
98
113
|
Julia [Dataframes](https://dataframes.juliadata.org/stable/) is in [DataFrame_Comparison.md](doc/DataFrame_Comparison.md) (Thanks to Benson Muite).
|
|
@@ -100,7 +115,7 @@ Julia [Dataframes](https://dataframes.juliadata.org/stable/) is in [DataFrame_Co
|
|
|
100
115
|
## Data frame in `RedAmber`
|
|
101
116
|
|
|
102
117
|
Class `RedAmber::DataFrame` represents a set of data in 2D-shape.
|
|
103
|
-
Its entity is a Red Arrow's Table object.
|
|
118
|
+
Its entity is a Red Arrow's Table object.
|
|
104
119
|
|
|
105
120
|
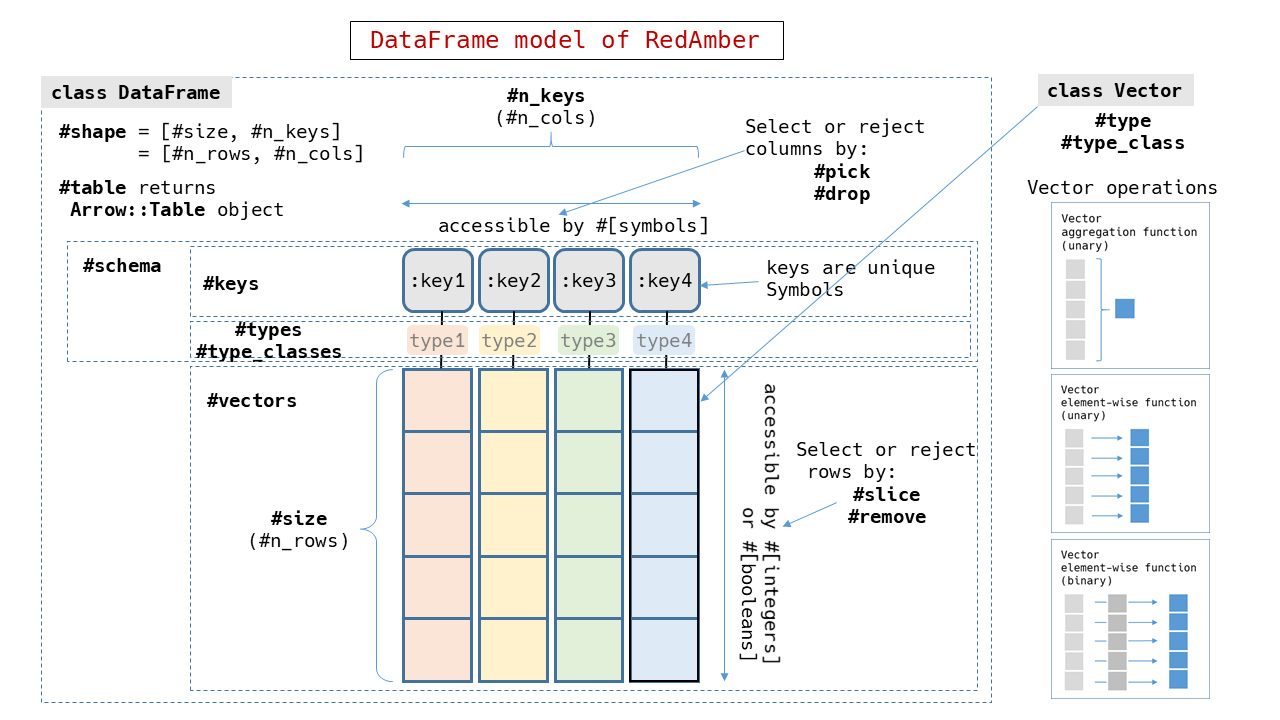
|
|
106
121
|
|
|
@@ -219,14 +234,13 @@ See [Vector.md](doc/Vector.md) for details.
|
|
|
219
234
|
|
|
220
235
|
## Jupyter notebook
|
|
221
236
|
|
|
222
|
-
|
|
223
|
-
([raw file](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/heronshoes/docker-stacks/RedAmber-binder/binder/examples_of_red_amber.ipynb)) shows more examples in jupyter notebook.
|
|
237
|
+
We are managing the source of Jupyter Notebook in qmd format by Quarto. You can easily create Notebooks and try it with Jupyter Lab in [Dev Container](doc/Dev_Containers.md).
|
|
224
238
|
|
|
225
|
-
|
|
226
|
-
[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/heronshoes/docker-stacks/RedAmber-binder?filepath=examples_of_red_amber.ipynb)
|
|
239
|
+
## Development
|
|
227
240
|
|
|
241
|
+
The recommended way to develop RedAmber is to use Dev Container. Please refer [How to use Dev Containers in RedAmber](doc/Dev_Containers.md) to use it.
|
|
228
242
|
|
|
229
|
-
|
|
243
|
+
Otherwise run below commands after install required libraries in your local system.
|
|
230
244
|
|
|
231
245
|
```shell
|
|
232
246
|
git clone https://github.com/red-data-tools/red_amber.git
|
|
@@ -235,6 +249,8 @@ bundle install
|
|
|
235
249
|
bundle exec rake test
|
|
236
250
|
```
|
|
237
251
|
|
|
252
|
+
We need to pass `rake test` in development of RedAmber, but not require to pass `rake rubocop` when you make a contribution. In this project we respect your preferences in code style. However, we may unify the style during merging.
|
|
253
|
+
|
|
238
254
|
## Community
|
|
239
255
|
|
|
240
256
|
I will appreciate if you could help to improve this project. Here are a few ways you can help:
|
data/Rakefile
CHANGED
|
@@ -2,6 +2,7 @@
|
|
|
2
2
|
|
|
3
3
|
require 'bundler/gem_tasks'
|
|
4
4
|
require 'rake/testtask'
|
|
5
|
+
require 'rake/clean'
|
|
5
6
|
|
|
6
7
|
Rake::TestTask.new(:test) do |t|
|
|
7
8
|
t.libs << 'test'
|
|
@@ -15,3 +16,57 @@ require 'rubocop/rake_task'
|
|
|
15
16
|
RuboCop::RakeTask.new
|
|
16
17
|
|
|
17
18
|
task default: %i[test rubocop]
|
|
19
|
+
|
|
20
|
+
def install_gems_for_examples
|
|
21
|
+
sh 'cd bin; bundle install; cd -'
|
|
22
|
+
end
|
|
23
|
+
|
|
24
|
+
# Example
|
|
25
|
+
desc 'Start example environment'
|
|
26
|
+
task :example do
|
|
27
|
+
install_gems_for_examples
|
|
28
|
+
sh 'bundle exec --gemfile=bin/Gemfile bin/example'
|
|
29
|
+
end
|
|
30
|
+
|
|
31
|
+
# Quarto
|
|
32
|
+
namespace :quarto do
|
|
33
|
+
qmd_dir = 'doc/qmd'
|
|
34
|
+
notebook_dir = 'doc/notebook'
|
|
35
|
+
|
|
36
|
+
directory notebook_dir
|
|
37
|
+
|
|
38
|
+
qmd_files = FileList["#{qmd_dir}/*.qmd"]
|
|
39
|
+
qmd_files.exclude('~*.qmd')
|
|
40
|
+
notebooks = qmd_files.pathmap('%{qmd,notebook}p').ext('.ipynb')
|
|
41
|
+
|
|
42
|
+
qmd_files.zip(notebooks).each do |qmd, notebook|
|
|
43
|
+
file notebook => notebook_dir
|
|
44
|
+
file notebook => qmd do
|
|
45
|
+
sh "quarto convert #{qmd} -o #{notebook}"
|
|
46
|
+
end
|
|
47
|
+
end
|
|
48
|
+
|
|
49
|
+
desc 'Convert qmd to ipynb files'
|
|
50
|
+
task convert: notebooks
|
|
51
|
+
file notebooks => notebook_dir
|
|
52
|
+
|
|
53
|
+
desc 'test to execute notebooks'
|
|
54
|
+
task test: notebooks do
|
|
55
|
+
install_gems_for_examples
|
|
56
|
+
notebooks.each do |notebook|
|
|
57
|
+
quarto_options = '--execute-daemon-restart --execute'
|
|
58
|
+
sh "bundle exec --gemfile=bin/Gemfile quarto render #{notebook} #{quarto_options}"
|
|
59
|
+
end
|
|
60
|
+
end
|
|
61
|
+
end
|
|
62
|
+
|
|
63
|
+
desc 'Start jupyter lab'
|
|
64
|
+
task jupyter: 'quarto:convert' do
|
|
65
|
+
install_gems_for_examples
|
|
66
|
+
|
|
67
|
+
jupyter_options =
|
|
68
|
+
"--notebook-dir='doc/notebook' --NotebookApp.token=''"
|
|
69
|
+
sh "bundle exec --gemfile=bin/Gemfile jupyter lab #{jupyter_options}"
|
|
70
|
+
end
|
|
71
|
+
|
|
72
|
+
CLEAN << 'doc/notebook'
|
data/doc/DataFrame_Comparison.md
CHANGED
|
@@ -1,9 +1,8 @@
|
|
|
1
1
|
# Comparison of DataFrames
|
|
2
2
|
|
|
3
|
-
Compare basic features of RedAmber with Python
|
|
4
|
-
[
|
|
5
|
-
|
|
6
|
-
Julia [Dataframes](https://dataframes.juliadata.org/stable/).
|
|
3
|
+
Compare basic features of RedAmber with [Python pandas](https://pandas.pydata.org/),
|
|
4
|
+
[R Tidyverse](https://www.tidyverse.org/) and
|
|
5
|
+
[Julia DataFrames](https://dataframes.juliadata.org/stable/).
|
|
7
6
|
|
|
8
7
|
## Select columns (variables)
|
|
9
8
|
|
|
@@ -51,15 +50,12 @@ Julia [Dataframes](https://dataframes.juliadata.org/stable/).
|
|
|
51
50
|
|--- |--- |--- |--- |--- |
|
|
52
51
|
| Combine additional columns | merge, bind_cols | dplyr::bind_cols | concat | combine |
|
|
53
52
|
| Combine additional rows | concatenate, concat, bind_rows | dplyr::bind_rows | concat | transform |
|
|
54
|
-
| Join right to left, leaving only the matching rows|
|
|
55
|
-
| Join right to left, leaving all rows |
|
|
56
|
-
| Join matching values to left from right |
|
|
57
|
-
| Join matching values from left to right |
|
|
58
|
-
| Return rows of left that have a match in right |
|
|
59
|
-
| Return rows of left that do not have a match in right |
|
|
53
|
+
| Join right to left, leaving only the matching rows| inner_join, join | dplyr::inner_join | merge | innerjoin |
|
|
54
|
+
| Join right to left, leaving all rows | full_join, outer_join, join | dplyr::full_join | merge | outerjoin |
|
|
55
|
+
| Join matching values to left from right | left_join, join | dplyr::left_join | merge | leftjoin |
|
|
56
|
+
| Join matching values from left to right | right_join, join | dplyr::right_join | merge | rightjoin |
|
|
57
|
+
| Return rows of left that have a match in right | semi_join, join | dplyr::semi_join | [isin] | semijoin |
|
|
58
|
+
| Return rows of left that do not have a match in right | anti_join, join | dplyr::anti_join | [isin] | antijoin |
|
|
60
59
|
| Collect rows that appear in left or right | union | dplyr::union | merge | |
|
|
61
60
|
| Collect rows that appear in both left and right | intersect | dplyr::intersect | merge | |
|
|
62
61
|
| Collect rows that appear in left but not right | difference, setdiff | dplyr::setdiff | merge | |
|
|
63
|
-
|
|
64
|
-
|
|
65
|
-
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
# DataFrames 操作メソッドの比較
|
|
2
|
+
|
|
3
|
+
RedAmberの基本的な操作メソッドを [Python pandas](https://pandas.pydata.org/),
|
|
4
|
+
[R Tidyverse](https://www.tidyverse.org/),
|
|
5
|
+
[Julia DataFrames](https://dataframes.juliadata.org/stable/) と比較します。
|
|
6
|
+
|
|
7
|
+
## 列 (variables) を選択する
|
|
8
|
+
|
|
9
|
+
| 機能 | RedAmber | Tidyverse (R) | pandas | DataFrames.jl |
|
|
10
|
+
|--- |--- |--- |--- |--- |
|
|
11
|
+
| 列を選択して dataframe で返す | pick, drop, [] | dplyr::select, dplyr::select_if | [], loc[], iloc[], drop, select_dtypes | [], select |
|
|
12
|
+
| 列を選択して vector で返す | [], v | dplyr::pull, [, x] | [], loc[], iloc[] | [!, :x] |
|
|
13
|
+
| 列の順番を入れ替えた dataframeを返す | pick, [] | relocate | [], reindex, loc[], iloc[] | select,transform |
|
|
14
|
+
|
|
15
|
+
## 行 (records, observations) を選択する
|
|
16
|
+
|
|
17
|
+
| 機能 | RedAmber | Tidyverse (R) | pandas | DataFrames.jl |
|
|
18
|
+
|--- |--- |--- |--- |--- |
|
|
19
|
+
| 論理値に従って行を選択して dataframe で返す | slice, filter, remove, [] | dplyr::filter | [], filter, query, loc[] | filter |
|
|
20
|
+
| インデックスで行を選択して dataframe で返す | slice, remove, [] | dplyr::slice | iloc[], drop | subset |
|
|
21
|
+
| 行の順番を入れ替えた dataframeを返す | slice, [] | dplyr::filter, dplyr::slice | reindex, loc[], iloc[] | permute |
|
|
22
|
+
|
|
23
|
+
## 列を更新する / 新しい列を作る
|
|
24
|
+
|
|
25
|
+
|機能 | RedAmber | Tidyverse (R) | pandas | DataFrames.jl |
|
|
26
|
+
|--- |--- |--- |--- |--- |
|
|
27
|
+
| 既存の列の内容を変更する | assign | dplyr::mutate | assign, []= | mapcols |
|
|
28
|
+
| 新しい列を作成する | assign, assign_left | dplyr::mutate | apply | insertcols,.+ |
|
|
29
|
+
| 新しい列を作成し、残りは捨てる | new | transmute | (dfply:)transmute | transform,insertcols,mapcols |
|
|
30
|
+
| 列の名前を変更する | rename | dplyr::rename, dplyr::rename_with, purrr::set_names | rename, set_axis | rename |
|
|
31
|
+
| dataframe をソートする | sort | dplyr::arrange | sort_values | sort |
|
|
32
|
+
|
|
33
|
+
## dataframe を変形する
|
|
34
|
+
|
|
35
|
+
| 機能 | RedAmber | Tidyverse (R) | pandas | DataFrames.jl |
|
|
36
|
+
|--- |--- |--- |--- |--- |
|
|
37
|
+
| 列を行に積む (long dataframe にする) | to_long | tidyr::pivot_longer | melt | stack |
|
|
38
|
+
| 行を列に集める (wide dataframe にする) | to_wide | tidyr::pivot_wider | pivot | unstack |
|
|
39
|
+
| wide dataframe を転置する | transpose | transpose, t | transpose, T | permutedims |
|
|
40
|
+
|
|
41
|
+
## グループ化
|
|
42
|
+
|
|
43
|
+
| 機能 | RedAmber | Tidyverse | pandas | DataFrames.jl |
|
|
44
|
+
|--- |--- |--- |--- |--- |
|
|
45
|
+
|グループ化する | group, group.summarize | dplyr::group_by %>% dplyr::summarise | groupby.agg | combine,groupby |
|
|
46
|
+
|
|
47
|
+
## dataframes または tables を結合する
|
|
48
|
+
|
|
49
|
+
| 機能 | RedAmber | Tidyverse | pandas | DataFrames.jl |
|
|
50
|
+
|--- |--- |--- |--- |--- |
|
|
51
|
+
| 列として連結する (横方向に連結する) | merge, bind_cols | dplyr::bind_cols | concat | combine |
|
|
52
|
+
| 行として連結する (縦方向に連結する) | concatenate, concat, bind_rows | dplyr::bind_rows | concat | transform |
|
|
53
|
+
| 一致した行だけを連結する (内部結合) | inner_join, join | dplyr::inner_join | merge | innerjoin |
|
|
54
|
+
| 全ての行を残して連結する (外部結合) | full_join, outer_join, join | dplyr::full_join | merge | outerjoin |
|
|
55
|
+
| 左の一致した値を残して連結する (左外部結合) | left_join, join | dplyr::left_join | merge | leftjoin |
|
|
56
|
+
| 右の一致した値を残して連結する (右外部結合) | right_join, join | dplyr::right_join | merge | rightjoin |
|
|
57
|
+
| 左の行のうち、右と一致したものを返す | semi_join, join | dplyr::semi_join | [isin] | semijoin |
|
|
58
|
+
| 左の行のうち、右と一致しなかったものを返す | anti_join, join | dplyr::anti_join | [isin] | antijoin |
|
|
59
|
+
| 左か右のどちらかに現れる行を返す | union | dplyr::union | merge | |
|
|
60
|
+
| 左とみごの両方に現れる行を返す | intersect | dplyr::intersect | merge | |
|
|
61
|
+
| 左にはあるが右にはない行を返す | difference, setdiff | dplyr::setdiff | merge | |
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,290 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
# 開発コンテナ(Development Containers)の利用
|
|
2
|
+
|
|
3
|
+
このリポジトリでは [開発コンテナ(Dev Container)](https://containers.dev/)をサポートしています。
|
|
4
|
+
これを使うと、ローカルの環境を汚すことなく、RedAmberに必要なツール一式を含んだ環境を準備することができます。この環境には、Ruby、Apache Arrow、RedAmberのソースツリー、GitHub CI、サンプルデータセット、IRubyカーネルを含んだJupyter Labなどが含まれていて、簡単でメンテナンスしやすく、かつ再利用性が高い構成になっています。
|
|
5
|
+
|
|
6
|
+
RedAmber用のDev Containerは、`.devcontainer` ディレクトリに必要な設定が書かれています。現在の実装では、Dockerfileを使用せず、Dev Containers用のUbuntuベースイメージに、Dev Container Featuresを使って、Python、GitHub CIの環境を加えて作っています。Ruby は Container ができてから走らせるスクリプトでインストールしています。
|
|
7
|
+
|
|
8
|
+
Dockerfileで作るのと比べて、
|
|
9
|
+
- User周りの設定を自動的にやってくれる
|
|
10
|
+
- 言語環境をFeatureとして個別に追加することができる
|
|
11
|
+
- PythonではJupyter Labをオプションとして追加できる
|
|
12
|
+
- Rubyは`rbenv`をインストールしてあって後から別のバージョンを追加できる
|
|
13
|
+
- Quartoを動かせる環境を簡単に追加でき、Jupyter notebookのソース管理に利用できる
|
|
14
|
+
|
|
15
|
+
等の利点があります。
|
|
16
|
+
|
|
17
|
+
ここでは代表的な利用法を2つ紹介します。
|
|
18
|
+
|
|
19
|
+
## 1. GitHub Codespacesでクラウド上のVMをブラウザから使う
|
|
20
|
+
|
|
21
|
+
### 必要なもの
|
|
22
|
+
GitHubアカウントにサインインしている必要があります。
|
|
23
|
+
|
|
24
|
+
### 注意
|
|
25
|
+
以下の手順では、Codespacesを起動するあなたのアカウントのクォータを消費します。GitHub Freeに対しては120時間/月・コア(2コアでは60時間)、ストレージ15GB/月が無料で使用できます。使用状況については [Billing and plans](https://github.com/settings/billing)のCodespacesの項を参照してください。
|
|
26
|
+
|
|
27
|
+
### 手順
|
|
28
|
+
- GitHubの[RedAmberのリポジトリ](https://github.com/red-data-tools/red_amber)を開いてください。
|
|
29
|
+
- 開発を行う場合は、フォークしてご自身のリポジトリを作り、それを開いてください。
|
|
30
|
+
|
|
31
|
+
- リポジトリ内の「<>Code」ボタン、「Codespaces」タブにある、「Create codespace on main」ボタンを押して新しいCodespacesを作成してください。
|
|
32
|
+
* 既にCodespacesがある場合は、該当するコンテナ名をクリックすると再接続できます。
|
|
33
|
+
- Codespacesの作成には時間がかかります。「View log」をクリックしてぼーっとログを眺めるか、コーヒーを淹れに行くとよいでしょう。
|
|
34
|
+
* 今後、GitHub Container Registoryにキャッシュを保存して、速く起動できるようにする予定です。
|
|
35
|
+
- VS Code for ブラウザでリポジトリが開きます。
|
|
36
|
+
|
|
37
|
+
動作の確認は、下の[動作の確認](#動作の確認)を参照してください。
|
|
38
|
+
|
|
39
|
+
### 詳細
|
|
40
|
+
より詳しくは、[(GitHub Docs)リポジトリの codespace を作成する](https://docs.github.com/ja/codespaces/developing-in-codespaces/creating-a-codespace-for-a-repository)を参照してください。
|
|
41
|
+
|
|
42
|
+
## 2. ローカルにクローンしたリポジトリ―からDev Containerを立ち上げ、VS Codeで使う
|
|
43
|
+
|
|
44
|
+
### 必要なもの
|
|
45
|
+
- Visual Studio Code (October 2020 Release 1.51以降)
|
|
46
|
+
|
|
47
|
+
GitHub Codespaces 拡張機能をインストールして、GitHub 資格情報を使用してサインインする必要があります。[GitHub Docs - GitHub Codespaces - 前提条件](https://docs.github.com/ja/codespaces/developing-in-codespaces/using-github-codespaces-in-visual-studio-code#prerequisites)を参照して設定を済ませておいてください。
|
|
48
|
+
|
|
49
|
+
- Docker
|
|
50
|
+
- Windows
|
|
51
|
+
|
|
52
|
+
Windows 10 Pro/Enterprise では Docker Desktop 2.0 以降。
|
|
53
|
+
Windows 10 Home (2004+) では、Docker Desktop 2.3 以降と WSL 2 バックエンド。
|
|
54
|
+
|
|
55
|
+
- Mac
|
|
56
|
+
|
|
57
|
+
Docker Desktop 2.0 以降
|
|
58
|
+
|
|
59
|
+
- Linux
|
|
60
|
+
|
|
61
|
+
Docker CE/EE 18.06 以降と Docker Compose 1.21 以降
|
|
62
|
+
|
|
63
|
+
- Git
|
|
64
|
+
|
|
65
|
+
### 手順
|
|
66
|
+
|
|
67
|
+
- ローカルに RedAmberリポジトリのクローンを作成します。
|
|
68
|
+
|
|
69
|
+
- 開発を行う場合は、フォークしてご自身のリポジトリを作り、それをクローンしてください。
|
|
70
|
+
|
|
71
|
+
```
|
|
72
|
+
$ git clone https://github.com/red-data-toolsまたは貴方のアカウント名/red_amber.git
|
|
73
|
+
```
|
|
74
|
+
または、GitHub CLIで、
|
|
75
|
+
```
|
|
76
|
+
$ gh repo clone red-data-toolsまたは貴方のアカウント名/red_amber
|
|
77
|
+
```
|
|
78
|
+
とします。
|
|
79
|
+
|
|
80
|
+
- 作成したローカルのリポジトリフォルダーをVS Codeで開きます。
|
|
81
|
+
```
|
|
82
|
+
$ code red_amber
|
|
83
|
+
```
|
|
84
|
+
|
|
85
|
+
- コンテナーで開く
|
|
86
|
+
|
|
87
|
+
今のフォルダーをコンテナーで再度開きます。
|
|
88
|
+
|
|
89
|
+
- 左下隅のステータスバーのリモートホスト表示(今はローカルなので「><」の後ろに何もついていない)をクリックするとリモートウィンドウを開くオプションが表示されるので、「コンテナーで再度開く」を選択します。
|
|
90
|
+
|
|
91
|
+
- コンテナーの構築が開始されます
|
|
92
|
+
|
|
93
|
+
最初の構築には、数分かかることがあります。それ以降の構築は高速になります。
|
|
94
|
+
構築が完了すると、左下隅のステータスバーのリモートホスト表示にコンテナー名が表示されます。
|
|
95
|
+
|
|
96
|
+
## 動作の確認
|
|
97
|
+
|
|
98
|
+
### ターミナルでインストールされているツールを確認する
|
|
99
|
+
|
|
100
|
+
ターミナルが開いていない場合は、 ``CTRL + ` `` で開いてください。
|
|
101
|
+
|
|
102
|
+
下記のコマンドを実行して、ツールがインストール済みであることを確かめてください。
|
|
103
|
+
|
|
104
|
+
```shell
|
|
105
|
+
$ ruby -v --jit
|
|
106
|
+
$ rbenv versions
|
|
107
|
+
$ gem -v
|
|
108
|
+
$ gem list
|
|
109
|
+
$ bundler -v
|
|
110
|
+
$ iruby -v
|
|
111
|
+
|
|
112
|
+
$ python --version
|
|
113
|
+
$ pip --version
|
|
114
|
+
$ pip list
|
|
115
|
+
$ pipenv --version
|
|
116
|
+
$ jupyter --version
|
|
117
|
+
$ jupyter kenelspec list
|
|
118
|
+
|
|
119
|
+
$ git -v
|
|
120
|
+
$ git config user.name
|
|
121
|
+
$ gh --version
|
|
122
|
+
```
|
|
123
|
+
|
|
124
|
+
ユーザーは、`vscode` という名前で、`uid/gid` はローカルのユーザーと同じになっています。
|
|
125
|
+
|
|
126
|
+
```shell
|
|
127
|
+
$ id
|
|
128
|
+
```
|
|
129
|
+
|
|
130
|
+
### RedAmberのテストを走らせてみる
|
|
131
|
+
|
|
132
|
+
```shell
|
|
133
|
+
$ bundle exec rake
|
|
134
|
+
```
|
|
135
|
+
|
|
136
|
+
### REPLでRedAmberを試す
|
|
137
|
+
|
|
138
|
+
プリロードされたデータセットを使って、irbの環境でRedAmberの動作を確認できます。初回はRed Datasetsのデータをロードするため少し時間がかかります。
|
|
139
|
+
|
|
140
|
+
```ruby
|
|
141
|
+
$ rake example
|
|
142
|
+
|
|
143
|
+
(snip)
|
|
144
|
+
|
|
145
|
+
81: # Welcome to RedAmber example!
|
|
146
|
+
82: # This environment will offer these pre-loaded datasets:
|
|
147
|
+
83: # penguins, diamonds, iris, starwars, simpsons_paradox_covid,
|
|
148
|
+
84: # mtcars, band_members, band_instruments, band_instruments2
|
|
149
|
+
85: # import_cars, comecome, rubykaigi, dataframe, subframes
|
|
150
|
+
=> 86: binding.irb
|
|
151
|
+
|
|
152
|
+
irb(main):001:0>
|
|
153
|
+
```
|
|
154
|
+
|
|
155
|
+
irbの動作を途中で止めているので、ここで表示されているデータセットが変数に読み込まれています。
|
|
156
|
+
|
|
157
|
+
```ruby
|
|
158
|
+
irb(main):001:0> import_cars
|
|
159
|
+
=>
|
|
160
|
+
#<RedAmber::DataFrame : 5 x 6 Vectors, 0x0000000000010914>
|
|
161
|
+
Year Audi BMW BMW_MINI Mercedes-Benz VW
|
|
162
|
+
<int64> <int64> <int64> <int64> <int64> <int64>
|
|
163
|
+
0 2017 28336 52527 25427 68221 49040
|
|
164
|
+
1 2018 26473 50982 25984 67554 51961
|
|
165
|
+
2 2019 24222 46814 23813 66553 46794
|
|
166
|
+
3 2020 22304 35712 20196 57041 36576
|
|
167
|
+
4 2021 22535 35905 18211 51722 35215
|
|
168
|
+
```
|
|
169
|
+
|
|
170
|
+
名前空間の`RedAmber` はインクルードされています。
|
|
171
|
+
```ruby
|
|
172
|
+
irb(main):002:0> VERSION
|
|
173
|
+
=> "0.5.0"
|
|
174
|
+
irb(main):003:0> Arrow::VERSION
|
|
175
|
+
=> "12.0.1"
|
|
176
|
+
```
|
|
177
|
+
|
|
178
|
+
`@`を入力すると最初のブレークポイントに戻ることができます。
|
|
179
|
+
|
|
180
|
+
`exit` を入力するとirbを抜けます。
|
|
181
|
+
|
|
182
|
+
### Jupyter LabでRedAmberを試す
|
|
183
|
+
|
|
184
|
+
Python と IRuby カーネルを持ったJupyter Labをブラウザで起動することができます。
|
|
185
|
+
|
|
186
|
+
```shell
|
|
187
|
+
$ rake jupyter
|
|
188
|
+
```
|
|
189
|
+
|
|
190
|
+
で、ローカルの8888ポートでブラウザが立ち上がります。
|
|
191
|
+
|
|
192
|
+
- Notebookフォルダーとして、`doc/notebook` が割り当てられていて、そこには2つの`.ipynb`ファイルがあります。
|
|
193
|
+
- `red_amber.ipynb` : `README.md` で紹介している操作例。
|
|
194
|
+
- `examples_of_red_amber.ipynb` : 様々な例を集めたもの。
|
|
195
|
+
- `require 'red_amber'` は `lib` 以下のソースを読み込んでいます。
|
|
196
|
+
|
|
197
|
+
## Quarto によるドキュメント操作
|
|
198
|
+
|
|
199
|
+
[Quarto](https://quarto.org/)はオープンソースの科学技術ドキュメントの出版システムです。
|
|
200
|
+
|
|
201
|
+
この環境では、RedAmber の動作例を活用するために Quarto CLI を使っています。
|
|
202
|
+
|
|
203
|
+
```mermaid
|
|
204
|
+
---
|
|
205
|
+
title: Quartoを利用したドキュメント管理
|
|
206
|
+
---
|
|
207
|
+
flowchart LR
|
|
208
|
+
id1["Source management
|
|
209
|
+
(.qmd)"]
|
|
210
|
+
id2["Analyze and edit by JupyterLab
|
|
211
|
+
(.ipynb)"]
|
|
212
|
+
id3["Publish document
|
|
213
|
+
(.pdf)"]
|
|
214
|
+
|
|
215
|
+
id1 -- convert --> id2 -- convert --> id1
|
|
216
|
+
id2 -- render --> id3
|
|
217
|
+
id1 -- render --> id3
|
|
218
|
+
```
|
|
219
|
+
|
|
220
|
+
* Quartoのドキュメント `qmd` 形式でソース管理できます。
|
|
221
|
+
* `.qmd`ファイルを Jupyter notebook ファイル(`.ipynb`)に変換して、
|
|
222
|
+
Jupyter Lab上で編集したりデータ解析ができます。
|
|
223
|
+
* `pdf`形式 に変換することができます。
|
|
224
|
+
|
|
225
|
+
### Quarto の動作を確認する
|
|
226
|
+
|
|
227
|
+
Quarto のバージョンと動作環境をチェックするには次のようにします。
|
|
228
|
+
|
|
229
|
+
```shell
|
|
230
|
+
$ quarto -v
|
|
231
|
+
$ quarto check
|
|
232
|
+
```
|
|
233
|
+
|
|
234
|
+
ヘルプを表示するには下記のようにします。
|
|
235
|
+
|
|
236
|
+
```shell
|
|
237
|
+
$ quarto --help
|
|
238
|
+
$ quarto render --help
|
|
239
|
+
```
|
|
240
|
+
|
|
241
|
+
### ソースからJupyter Notebookを生成する
|
|
242
|
+
`.qmd`ソースファイルから `.ipynb` を生成するには、
|
|
243
|
+
|
|
244
|
+
```shell
|
|
245
|
+
$ bundle exec rake quarto:convert
|
|
246
|
+
```
|
|
247
|
+
とします。`doc/qmd`フォルダー以下にあるqmdソースファイルから `doc/notebook`フォルダーに`ipynb`ノートブックファイルが作成されます。
|
|
248
|
+
|
|
249
|
+
より一般的には、
|
|
250
|
+
|
|
251
|
+
```shell
|
|
252
|
+
$ quarto convert ソースファイル.qmd
|
|
253
|
+
$ quarto convert ソースファイル.qmd --output 出力先ノートブック.ipynb
|
|
254
|
+
```
|
|
255
|
+
上の書き方では、出力ファイルはソースファイルの拡張子を `.ipynb`に変えて、ソースファイルと同じディレクトリに保存されます。
|
|
256
|
+
|
|
257
|
+
下記のコマンドは、Notebookを作成後、Jupyter Labを開きます。
|
|
258
|
+
|
|
259
|
+
```shell
|
|
260
|
+
$ bundle exec rake jupyter
|
|
261
|
+
```
|
|
262
|
+
|
|
263
|
+
### Jupyter Notebookファイルを`qmd`形式で保存する
|
|
264
|
+
|
|
265
|
+
編集したJupyter Notebookをqmd形式に変換できます。
|
|
266
|
+
|
|
267
|
+
```shell
|
|
268
|
+
$ quarto convert ノートブック.ipynb
|
|
269
|
+
$ quarto convert ノートブック.ipynb --output 出力先ソースファイル.qmd
|
|
270
|
+
```
|
|
271
|
+
|
|
272
|
+
### その他の活用方法
|
|
273
|
+
|
|
274
|
+
下記のコマンドは`doc/qmd`フォルダー以下にあるqmdソースファイルを`ipynb`に変換し、実行してpdfを作成します。
|
|
275
|
+
|
|
276
|
+
```shell
|
|
277
|
+
$ bundle exec rake quarto:test
|
|
278
|
+
```
|
|
279
|
+
|
|
280
|
+
下記は`doc/notebook`フォルダーを含めたrakeの生成物を消去します。
|
|
281
|
+
|
|
282
|
+
```shell
|
|
283
|
+
$ rake clean
|
|
284
|
+
```
|
|
285
|
+
|
|
286
|
+
Quartoについてより詳しくは、コマンドラインヘルプ(`quarto --help`)、または[Quarto](https://quarto.org/)公式ページをご覧ください。
|
|
287
|
+
|
|
288
|
+
### 謝辞
|
|
289
|
+
|
|
290
|
+
Quarto の利用は、西田孝三さんの2022年度のRubyアソシエーション開発助成事業プロジェクト『RubyDataエコシステムへのQuartoの導入とその利用の促進のためのコミュニティ活動』 がきっかけとなりました。この場をお借りして感謝申し上げます。
|