prefab 0.4.7__py3-none-any.whl → 1.1.8__py3-none-any.whl
This diff represents the content of publicly available package versions that have been released to one of the supported registries. The information contained in this diff is provided for informational purposes only and reflects changes between package versions as they appear in their respective public registries.
- prefab/__init__.py +15 -38
- prefab/__main__.py +95 -0
- prefab/compare.py +126 -0
- prefab/device.py +1486 -0
- prefab/geometry.py +394 -0
- prefab/models.py +114 -0
- prefab/predict.py +337 -0
- prefab/read.py +503 -0
- prefab/shapes.py +773 -0
- {prefab-0.4.7.dist-info → prefab-1.1.8.dist-info}/METADATA +47 -34
- prefab-1.1.8.dist-info/RECORD +14 -0
- {prefab-0.4.7.dist-info → prefab-1.1.8.dist-info}/WHEEL +1 -1
- prefab-1.1.8.dist-info/entry_points.txt +2 -0
- prefab/io.py +0 -200
- prefab/predictor.py +0 -161
- prefab/processor.py +0 -248
- prefab-0.4.7.dist-info/RECORD +0 -8
- {prefab-0.4.7.dist-info → prefab-1.1.8.dist-info}/licenses/LICENSE +0 -0
|
@@ -1,9 +1,11 @@
|
|
|
1
|
-
Metadata-Version: 2.
|
|
1
|
+
Metadata-Version: 2.4
|
|
2
2
|
Name: prefab
|
|
3
|
-
Version:
|
|
4
|
-
Summary:
|
|
5
|
-
Project-URL: Homepage, https://
|
|
6
|
-
|
|
3
|
+
Version: 1.1.8
|
|
4
|
+
Summary: Artificial nanofabrication of integrated photonic circuits using deep learning
|
|
5
|
+
Project-URL: Homepage, https://prefabphotonics.com
|
|
6
|
+
Project-URL: Repository, https://github.com/PreFab-Photonics/PreFab
|
|
7
|
+
Project-URL: Docs, https://docs.prefabphotonics.com
|
|
8
|
+
Author-email: "PreFab Photonics Inc." <hi@prefabphotonics.com>
|
|
7
9
|
License: GNU LESSER GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
|
|
8
10
|
Version 2.1, February 1999
|
|
9
11
|
|
|
@@ -509,54 +511,59 @@ License: GNU LESSER GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
|
|
|
509
511
|
|
|
510
512
|
That's all there is to it!
|
|
511
513
|
License-File: LICENSE
|
|
512
|
-
Keywords:
|
|
514
|
+
Keywords: computer-vision,deep-learning,electronic-design-automation,integrated-photonics,machine-learning,nanofabrication,semiconductor-manufacturing
|
|
513
515
|
Classifier: License :: OSI Approved :: GNU Lesser General Public License v2 (LGPLv2)
|
|
514
516
|
Classifier: Operating System :: OS Independent
|
|
515
517
|
Classifier: Programming Language :: Python :: 3
|
|
516
518
|
Requires-Python: >=3.9
|
|
517
|
-
Requires-Dist:
|
|
519
|
+
Requires-Dist: autograd
|
|
520
|
+
Requires-Dist: gdstk>=0.9.55
|
|
518
521
|
Requires-Dist: matplotlib
|
|
519
522
|
Requires-Dist: numpy
|
|
520
523
|
Requires-Dist: opencv-python-headless
|
|
524
|
+
Requires-Dist: pillow
|
|
525
|
+
Requires-Dist: pydantic>=2.10
|
|
521
526
|
Requires-Dist: requests
|
|
527
|
+
Requires-Dist: scikit-image
|
|
528
|
+
Requires-Dist: scipy
|
|
529
|
+
Requires-Dist: toml
|
|
530
|
+
Requires-Dist: tqdm
|
|
522
531
|
Description-Content-Type: text/markdown
|
|
523
532
|
|
|
524
533
|
# PreFab
|
|
525
534
|
|
|
526
|
-

|
|
535
|
+

|
|
527
536
|
|
|
528
|
-
|
|
537
|
+
PreFab is a _virtual nanofabrication environment_ that leverages **deep learning** and **computer vision** to predict and correct for structural variations in integrated photonic devices during nanofabrication.
|
|
538
|
+
|
|
539
|
+
> **Try Rosette**: Want a more visual experience? Try [Rosette](https://rosette.dev) - our new layout tool with PreFab models built in, designed for rapid chip design.
|
|
529
540
|
|
|
530
541
|
## Prediction
|
|
531
542
|
|
|
532
|
-
|
|
543
|
+
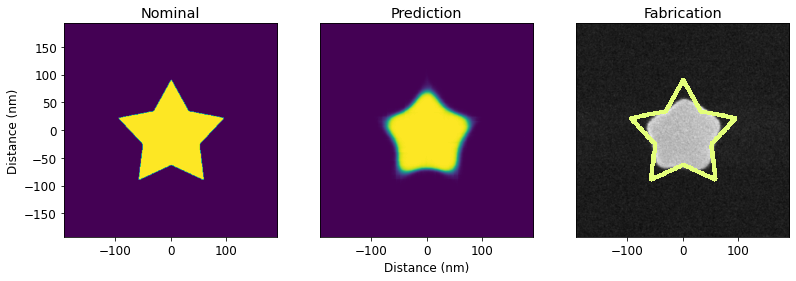
PreFab predicts process-induced structural variations, including corner rounding, loss of small lines and islands, filling of narrow holes and channels, sidewall angle deviations, and stochastic effects. This allows designers to rapidly prototype and evaluate expected performance pre-fabrication.
|
|
533
544
|
|
|
534
|
-
|
|
545
|
+

|
|
535
546
|
|
|
536
547
|
## Correction
|
|
537
548
|
|
|
538
|
-
|
|
549
|
+
PreFab corrects device designs to ensure that the fabricated outcome closely matches the intended specifications. This minimizes structural variations and reduces performance discrepancies between simulations and actual experiments.
|
|
539
550
|
|
|
540
|
-

|
|
551
|
+

|
|
541
552
|
|
|
542
553
|
## Models
|
|
543
554
|
|
|
544
|
-
|
|
555
|
+
Each photonic nanofabrication process requires unique models, which are regularly updated with the latest data. The current models include (see the full list in [`docs/models.md`](https://github.com/PreFab-Photonics/PreFab/blob/main/docs/models.md)):
|
|
545
556
|
|
|
546
|
-
| Foundry
|
|
547
|
-
|
|
|
548
|
-
| ANT
|
|
549
|
-
| ANT
|
|
550
|
-
| ANT | [SiN (Lower Edge)](https://www.appliednt.com/nanosoi/sys/resources/specs_nitride/) | v5 (Jun 3 2023) | d0 (Jun 1 2023) | ANT_SiN | v5-d0-lower | Alpha |
|
|
551
|
-
| SiEPICfab | [SOI](https://siepic.ca/fabrication/) | v5 (Jun 3 2023) | d0 (Jun 14 2023) | SiEPICfab_SOI | v5-d0 | Alpha |
|
|
557
|
+
| Foundry | Process | Latest Version | Latest Dataset | Model Name |
|
|
558
|
+
| ------- | ------- | ----------------- | ---------------- | ----------- |
|
|
559
|
+
| ANT | NanoSOI | ANF1 (May 6 2024) | d10 (Jun 8 2024) | ANT_NanoSOI_ANF1_d10 |
|
|
560
|
+
| ANT | SiN | ANF1 (May 6 2024) | d1 (Jan 31 2024) | ANT_SiN_ANF1_d1 |
|
|
552
561
|
|
|
553
|
-
_New models
|
|
562
|
+
> _New models are to be regularly added. Usage may change. For additional foundry and process models, feel free to [contact us](mailto:hi@prefabphotonics.com) or raise an issue._
|
|
554
563
|
|
|
555
564
|
## Installation
|
|
556
565
|
|
|
557
|
-
|
|
558
|
-
|
|
559
|
-
Install `PreFab` via pip:
|
|
566
|
+
Install PreFab via pip:
|
|
560
567
|
|
|
561
568
|
```sh
|
|
562
569
|
pip install prefab
|
|
@@ -570,24 +577,30 @@ cd PreFab
|
|
|
570
577
|
pip install -e .
|
|
571
578
|
```
|
|
572
579
|
|
|
573
|
-
|
|
580
|
+
## Getting Started
|
|
574
581
|
|
|
575
|
-
|
|
582
|
+
### Account setup
|
|
576
583
|
|
|
577
|
-
[
|
|
584
|
+
Before you can make PreFab requests, you will need to [create an account](https://www.prefabphotonics.com/login).
|
|
578
585
|
|
|
579
|
-
|
|
586
|
+
To link your account, you will need an token. You can do this by running the following command in your terminal. This will open a browser window where you can log in and authenticate your token.
|
|
587
|
+
|
|
588
|
+
```sh
|
|
589
|
+
python3 -m prefab setup
|
|
590
|
+
```
|
|
591
|
+
|
|
592
|
+
### Guides
|
|
580
593
|
|
|
581
|
-
Visit [`/examples`](https://github.com/PreFab-Photonics/PreFab/tree/main/examples)
|
|
594
|
+
Visit [`/docs/examples`](https://github.com/PreFab-Photonics/PreFab/tree/main/docs/examples) or our [docs](https://docs.prefabphotonics.com/) to get started with your first predictions.
|
|
582
595
|
|
|
583
596
|
## Performance and Usage
|
|
584
597
|
|
|
585
|
-
|
|
598
|
+
PreFab models are hosted on a [serverless cloud platform](https://modal.com/). Please keep in mind:
|
|
586
599
|
|
|
587
|
-
- 🐢 CPU
|
|
588
|
-
- 🥶 The first prediction may take longer due to cold start server loading. Subsequent predictions will be faster.
|
|
589
|
-
- 😊
|
|
600
|
+
- 🐢 Default CPU inference may be slower.
|
|
601
|
+
- 🥶 The first prediction using optional GPU inference may take longer due to cold start server loading. Subsequent predictions will be faster.
|
|
602
|
+
- 😊 Please be considerate of usage. Start with small tasks and limit usage during the initial stages. Thank you!
|
|
590
603
|
|
|
591
604
|
## License
|
|
592
605
|
|
|
593
|
-
This project is licensed under the LGPL-2.1 license. ©
|
|
606
|
+
This project is licensed under the LGPL-2.1 license. © 2024 PreFab Photonics.
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
prefab/__init__.py,sha256=V4m0w3VrKeMgeNeqyc_45E5KXH9fVOQKO5xyH42uDmg,425
|
|
2
|
+
prefab/__main__.py,sha256=1eXWiEoG7eetJMm1qRbK2I5MnzuRgKIoQtBeT-Ps8es,3523
|
|
3
|
+
prefab/compare.py,sha256=0Xgp3tFuP4of-ce9Opc19p8i8lIyXkbVGLuwWBaHSeE,3486
|
|
4
|
+
prefab/device.py,sha256=1rqs_VQ7am6W473C-EZTsPFDlqNIMMd26VZAUV1tNS0,54885
|
|
5
|
+
prefab/geometry.py,sha256=4fekWMlkdS_qlPNTdPXPhwKuQ5qdQ1Zjf8m9JKd1dA8,12049
|
|
6
|
+
prefab/models.py,sha256=waPNGtuISyY0f8cz7dnbD451CKYCt8EpPGt-4lSOPNU,2581
|
|
7
|
+
prefab/predict.py,sha256=h13523jasg1WbdiYbkXy43SWTGfQXjq6oEe0O8DT2U0,11731
|
|
8
|
+
prefab/read.py,sha256=WNqC3xENlndzFwXeCF2E7H3Iq2dO_6rPEPZ58DuloqY,16259
|
|
9
|
+
prefab/shapes.py,sha256=58cyXFNh1kEErq2jEbGd3dWSediU1OSmor_FWwc1V8A,25098
|
|
10
|
+
prefab-1.1.8.dist-info/METADATA,sha256=d5ide0FP2wUQALM_2SSFhA_BGU6s3waxWjtXwsbjivs,35036
|
|
11
|
+
prefab-1.1.8.dist-info/WHEEL,sha256=qtCwoSJWgHk21S1Kb4ihdzI2rlJ1ZKaIurTj_ngOhyQ,87
|
|
12
|
+
prefab-1.1.8.dist-info/entry_points.txt,sha256=h1_A9O9F3NAIoKXD1RPb3Eo-WCSiHhMB_AnagBi6XTQ,48
|
|
13
|
+
prefab-1.1.8.dist-info/licenses/LICENSE,sha256=IMF9i4xIpgCADf0U-V1cuf9HBmqWQd3qtI3FSuyW4zE,26526
|
|
14
|
+
prefab-1.1.8.dist-info/RECORD,,
|
prefab/io.py
DELETED
|
@@ -1,200 +0,0 @@
|
|
|
1
|
-
"""
|
|
2
|
-
This module offers tools to import, export, and preprocess device layouts in multiple formats for
|
|
3
|
-
nanofabrication prediction tasks.
|
|
4
|
-
"""
|
|
5
|
-
|
|
6
|
-
from typing import Optional, List, Tuple
|
|
7
|
-
import matplotlib.image as img
|
|
8
|
-
import numpy as np
|
|
9
|
-
import gdstk
|
|
10
|
-
import cv2
|
|
11
|
-
from prefab.processor import binarize_hard
|
|
12
|
-
|
|
13
|
-
|
|
14
|
-
def load_device_img(path: str, img_length_nm: int = None) -> np.ndarray:
|
|
15
|
-
"""
|
|
16
|
-
Load, process and scale device image from file for prediction.
|
|
17
|
-
|
|
18
|
-
This function reads an image file, scales it according to the provided image length in
|
|
19
|
-
nanometers, and performs preprocessing tasks such as binarization, preparing it for prediction.
|
|
20
|
-
|
|
21
|
-
Parameters
|
|
22
|
-
----------
|
|
23
|
-
path : str
|
|
24
|
-
Path to the device image file.
|
|
25
|
-
|
|
26
|
-
img_length_nm : int, optional
|
|
27
|
-
Desired length of the device image in nanometers for scaling. If not provided,
|
|
28
|
-
the length of the original image is used.
|
|
29
|
-
|
|
30
|
-
Returns
|
|
31
|
-
-------
|
|
32
|
-
np.ndarray
|
|
33
|
-
A 2D numpy array representing the preprocessed and scaled device, ready for prediction.
|
|
34
|
-
"""
|
|
35
|
-
device = img.imread(path)[:, :, 1]
|
|
36
|
-
if img_length_nm is None:
|
|
37
|
-
img_length_nm = device.shape[1]
|
|
38
|
-
scale = img_length_nm / device.shape[1]
|
|
39
|
-
device = cv2.resize(device, (0, 0), fx=scale, fy=scale)
|
|
40
|
-
device = binarize_hard(device)
|
|
41
|
-
return device
|
|
42
|
-
|
|
43
|
-
|
|
44
|
-
def load_device_gds(
|
|
45
|
-
path: str,
|
|
46
|
-
cell_name: str,
|
|
47
|
-
coords: Optional[List[List[int]]] = None,
|
|
48
|
-
layer: Tuple[int, int] = (1, 0),
|
|
49
|
-
) -> np.ndarray:
|
|
50
|
-
"""
|
|
51
|
-
Load and process a device layout from a GDSII file.
|
|
52
|
-
|
|
53
|
-
This function reads a device layout from a GDSII file, performs necessary
|
|
54
|
-
preprocessing tasks such as scaling and padding, and prepares it for prediction.
|
|
55
|
-
Only the specified layer is loaded.
|
|
56
|
-
|
|
57
|
-
Parameters
|
|
58
|
-
----------
|
|
59
|
-
path : str
|
|
60
|
-
Path to the GDSII layout file.
|
|
61
|
-
|
|
62
|
-
cell_name : str
|
|
63
|
-
Name of the GDSII cell to be loaded.
|
|
64
|
-
|
|
65
|
-
coords : List[List[int]], optional
|
|
66
|
-
A list of coordinates [[xmin, ymin], [xmax, ymax]] in nm, defining the
|
|
67
|
-
region of the cell to be loaded. If None, the entire cell is loaded.
|
|
68
|
-
|
|
69
|
-
layer : Tuple[int, int], optional
|
|
70
|
-
A tuple specifying the layer to be loaded. Default is (1, 0).
|
|
71
|
-
|
|
72
|
-
Returns
|
|
73
|
-
-------
|
|
74
|
-
np.ndarray
|
|
75
|
-
A 2D numpy array representing the preprocessed device layout, ready for prediction.
|
|
76
|
-
"""
|
|
77
|
-
gds = gdstk.read_gds(path)
|
|
78
|
-
cell = gds[cell_name]
|
|
79
|
-
polygons = cell.get_polygons(layer=layer[0], datatype=layer[1])
|
|
80
|
-
bounds = tuple(
|
|
81
|
-
tuple(1000 * x for x in sub_tuple) for sub_tuple in cell.bounding_box()
|
|
82
|
-
)
|
|
83
|
-
device = np.zeros(
|
|
84
|
-
(int(bounds[1][1] - bounds[0][1]), int(bounds[1][0] - bounds[0][0]))
|
|
85
|
-
)
|
|
86
|
-
|
|
87
|
-
contours = [
|
|
88
|
-
np.array(
|
|
89
|
-
[
|
|
90
|
-
[
|
|
91
|
-
[
|
|
92
|
-
int(1000 * vertex[0] - bounds[0][0]),
|
|
93
|
-
int(1000 * vertex[1] - bounds[0][1]),
|
|
94
|
-
]
|
|
95
|
-
]
|
|
96
|
-
for vertex in polygon.points
|
|
97
|
-
],
|
|
98
|
-
dtype=np.int32,
|
|
99
|
-
)
|
|
100
|
-
for polygon in polygons
|
|
101
|
-
]
|
|
102
|
-
|
|
103
|
-
cv2.fillPoly(img=device, pts=contours, color=(1, 1, 1))
|
|
104
|
-
|
|
105
|
-
if coords is not None:
|
|
106
|
-
new_device = np.zeros(
|
|
107
|
-
(int(bounds[1][1] - bounds[0][1]), int(bounds[1][0] - bounds[0][0]))
|
|
108
|
-
)
|
|
109
|
-
new_device[
|
|
110
|
-
int(coords[0][1] - bounds[0][1]) : int(coords[1][1] - bounds[0][1]),
|
|
111
|
-
int(coords[0][0] - bounds[0][0]) : int(coords[1][0] - bounds[0][0]),
|
|
112
|
-
] = device[
|
|
113
|
-
int(coords[0][1] - bounds[0][1]) : int(coords[1][1] - bounds[0][1]),
|
|
114
|
-
int(coords[0][0] - bounds[0][0]) : int(coords[1][0] - bounds[0][0]),
|
|
115
|
-
]
|
|
116
|
-
device = new_device
|
|
117
|
-
|
|
118
|
-
device = np.flipud(device)
|
|
119
|
-
device = np.pad(device, 100)
|
|
120
|
-
|
|
121
|
-
return device
|
|
122
|
-
|
|
123
|
-
|
|
124
|
-
def device_to_cell(
|
|
125
|
-
device: np.ndarray,
|
|
126
|
-
cell_name: str,
|
|
127
|
-
library: gdstk.Library,
|
|
128
|
-
resolution: float = 1.0,
|
|
129
|
-
layer: Tuple[int, int] = (1, 0),
|
|
130
|
-
approximation_mode: int = 2,
|
|
131
|
-
) -> gdstk.Cell:
|
|
132
|
-
"""Converts a device layout to a gdstk cell for GDSII export.
|
|
133
|
-
|
|
134
|
-
This function creates a cell that represents a device layout. The created cell
|
|
135
|
-
is ready to be exported as a GDSII file.
|
|
136
|
-
|
|
137
|
-
Parameters
|
|
138
|
-
----------
|
|
139
|
-
device : np.ndarray
|
|
140
|
-
A 2D numpy array representing the device layout.
|
|
141
|
-
|
|
142
|
-
cell_name : str
|
|
143
|
-
Name for the new cell.
|
|
144
|
-
|
|
145
|
-
library : gdstk.Library
|
|
146
|
-
Library to which the cell will be added.
|
|
147
|
-
|
|
148
|
-
resolution : float, optional
|
|
149
|
-
The resolution of the device in pixels per nm. Default is 1.0.
|
|
150
|
-
|
|
151
|
-
layer : Tuple[int, int], optional
|
|
152
|
-
A tuple specifying the layer to be exported. Default is (1, 0).
|
|
153
|
-
|
|
154
|
-
approximation_mode : int, optional
|
|
155
|
-
The approximation method to be used for finding contours. Possible values are 1, 2, 3, and
|
|
156
|
-
4. Larger values mean more approximation. Default is 1.
|
|
157
|
-
|
|
158
|
-
Returns
|
|
159
|
-
-------
|
|
160
|
-
gdstk.Cell
|
|
161
|
-
The newly created cell containing the device layout.
|
|
162
|
-
"""
|
|
163
|
-
approximation_method_mapping = {
|
|
164
|
-
1: cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE,
|
|
165
|
-
2: cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE,
|
|
166
|
-
3: cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_TC89_L1,
|
|
167
|
-
4: cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_TC89_KCOS,
|
|
168
|
-
}
|
|
169
|
-
|
|
170
|
-
device = np.flipud(device)
|
|
171
|
-
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(
|
|
172
|
-
device.astype(np.uint8),
|
|
173
|
-
cv2.RETR_CCOMP,
|
|
174
|
-
approximation_method_mapping[approximation_mode],
|
|
175
|
-
)
|
|
176
|
-
|
|
177
|
-
outer_polygons = []
|
|
178
|
-
inner_polygons = []
|
|
179
|
-
|
|
180
|
-
for idx, contour in enumerate(contours):
|
|
181
|
-
if len(contour) > 2:
|
|
182
|
-
contour = contour / 1000 # μm to nm
|
|
183
|
-
points = [tuple(point) for point in contour.squeeze().tolist()]
|
|
184
|
-
|
|
185
|
-
if hierarchy[0][idx][3] == -1:
|
|
186
|
-
outer_polygons.append(points)
|
|
187
|
-
else:
|
|
188
|
-
inner_polygons.append(points)
|
|
189
|
-
|
|
190
|
-
polygons = gdstk.boolean(
|
|
191
|
-
outer_polygons, inner_polygons, "xor", layer=layer[0], datatype=layer[1]
|
|
192
|
-
)
|
|
193
|
-
for polygon in polygons:
|
|
194
|
-
polygon.scale(resolution, resolution)
|
|
195
|
-
|
|
196
|
-
cell = library.new_cell(cell_name)
|
|
197
|
-
for polygon in polygons:
|
|
198
|
-
cell.add(polygon)
|
|
199
|
-
|
|
200
|
-
return cell
|
prefab/predictor.py
DELETED
|
@@ -1,161 +0,0 @@
|
|
|
1
|
-
"""
|
|
2
|
-
A module for making predictions on fabrication variations in photonic devices
|
|
3
|
-
using machine learning models deployed in the cloud.
|
|
4
|
-
"""
|
|
5
|
-
|
|
6
|
-
import base64
|
|
7
|
-
|
|
8
|
-
import numpy as np
|
|
9
|
-
import requests
|
|
10
|
-
from cv2 import IMREAD_GRAYSCALE, imdecode, imencode
|
|
11
|
-
|
|
12
|
-
from prefab.processor import binarize_hard
|
|
13
|
-
|
|
14
|
-
|
|
15
|
-
def predict(
|
|
16
|
-
device: np.ndarray, model_name: str, model_tags: str, binarize: bool = False
|
|
17
|
-
) -> np.ndarray:
|
|
18
|
-
"""
|
|
19
|
-
Generates a prediction for a photonic device using a specified cloud-based ML model.
|
|
20
|
-
|
|
21
|
-
The function sends an image of the device to a cloud function, which uses the specified
|
|
22
|
-
machine learning model to generate a prediction.
|
|
23
|
-
|
|
24
|
-
Parameters
|
|
25
|
-
----------
|
|
26
|
-
device : np.ndarray
|
|
27
|
-
A binary numpy matrix representing the shape of a device.
|
|
28
|
-
|
|
29
|
-
model_name : str
|
|
30
|
-
The name of the ML model to use for the prediction.
|
|
31
|
-
Consult the module's documentation for available models.
|
|
32
|
-
|
|
33
|
-
model_tags : Union[str, List[str]]
|
|
34
|
-
The tags of the ML model.
|
|
35
|
-
Consult the module's documentation for available tags.
|
|
36
|
-
|
|
37
|
-
binarize : bool, optional
|
|
38
|
-
If set to True, the prediction will be binarized (default is False).
|
|
39
|
-
|
|
40
|
-
Returns
|
|
41
|
-
-------
|
|
42
|
-
np.ndarray
|
|
43
|
-
A numpy matrix representing the predicted shape of the device. Pixel values closer
|
|
44
|
-
to 1 indicate a higher likelihood of core material, while pixel values closer to 0
|
|
45
|
-
suggest a higher likelihood of cladding material. Pixel values in between represent
|
|
46
|
-
prediction uncertainty.
|
|
47
|
-
"""
|
|
48
|
-
function_url = "https://prefab-photonics--predict.modal.run"
|
|
49
|
-
|
|
50
|
-
predict_data = {
|
|
51
|
-
"device": _encode_image(device),
|
|
52
|
-
"model_name": model_name,
|
|
53
|
-
"model_tags": model_tags,
|
|
54
|
-
"binary": binarize,
|
|
55
|
-
}
|
|
56
|
-
|
|
57
|
-
prediction = _decode_image(
|
|
58
|
-
requests.post(function_url, json=predict_data, timeout=200)
|
|
59
|
-
)
|
|
60
|
-
|
|
61
|
-
if binarize:
|
|
62
|
-
prediction = binarize_hard(prediction)
|
|
63
|
-
|
|
64
|
-
return prediction
|
|
65
|
-
|
|
66
|
-
|
|
67
|
-
def correct(
|
|
68
|
-
device: np.ndarray,
|
|
69
|
-
model_name: str,
|
|
70
|
-
model_tags: str,
|
|
71
|
-
binarize: bool = True,
|
|
72
|
-
multi_correct: bool = False,
|
|
73
|
-
) -> np.ndarray:
|
|
74
|
-
"""
|
|
75
|
-
Generates a correction for a photonic device using a specified cloud-based ML model.
|
|
76
|
-
|
|
77
|
-
The function sends an image of the device to a cloud function, which uses the specified
|
|
78
|
-
machine learning model to generate a correction.
|
|
79
|
-
|
|
80
|
-
Parameters
|
|
81
|
-
----------
|
|
82
|
-
device : np.ndarray
|
|
83
|
-
A binary numpy matrix representing the shape of a device.
|
|
84
|
-
|
|
85
|
-
model_name : str
|
|
86
|
-
The name of the ML model to use for the correction.
|
|
87
|
-
Consult the module's documentation for available models.
|
|
88
|
-
|
|
89
|
-
model_tags : Union[str, List[str]]
|
|
90
|
-
The tags of the ML model.
|
|
91
|
-
Consult the module's documentation for available tags.
|
|
92
|
-
|
|
93
|
-
binarize : bool, optional
|
|
94
|
-
If set to True, the correction will be binarized (default is True).
|
|
95
|
-
|
|
96
|
-
multi_correct : bool, optional
|
|
97
|
-
If set to True, the correction will be generated using a iterative approach.
|
|
98
|
-
(default is False).
|
|
99
|
-
|
|
100
|
-
Returns
|
|
101
|
-
-------
|
|
102
|
-
np.ndarray
|
|
103
|
-
A numpy matrix representing the corrected shape of the device. Pixel values closer
|
|
104
|
-
to 1 indicate a higher likelihood of core material, while pixel values closer to 0
|
|
105
|
-
suggest a higher likelihood of cladding material. Pixel values in between represent
|
|
106
|
-
correction uncertainty.
|
|
107
|
-
"""
|
|
108
|
-
function_url = "https://prefab-photonics--correct.modal.run"
|
|
109
|
-
|
|
110
|
-
correct_data = {
|
|
111
|
-
"device": _encode_image(device),
|
|
112
|
-
"model_name": model_name,
|
|
113
|
-
"model_tags": model_tags,
|
|
114
|
-
"binary": binarize,
|
|
115
|
-
"multi_correct": multi_correct,
|
|
116
|
-
}
|
|
117
|
-
|
|
118
|
-
correction = _decode_image(
|
|
119
|
-
requests.post(function_url, json=correct_data, timeout=200)
|
|
120
|
-
)
|
|
121
|
-
|
|
122
|
-
return correction
|
|
123
|
-
|
|
124
|
-
|
|
125
|
-
def _encode_image(image: np.ndarray) -> str:
|
|
126
|
-
"""
|
|
127
|
-
Encodes a numpy image array to its base64 representation.
|
|
128
|
-
|
|
129
|
-
Parameters
|
|
130
|
-
----------
|
|
131
|
-
image : np.ndarray
|
|
132
|
-
The image in numpy array format.
|
|
133
|
-
|
|
134
|
-
Returns
|
|
135
|
-
-------
|
|
136
|
-
str
|
|
137
|
-
The base64 encoded string of the image.
|
|
138
|
-
"""
|
|
139
|
-
encoded_image = imencode(".png", 255 * image)[1].tobytes()
|
|
140
|
-
encoded_image_base64 = base64.b64encode(encoded_image).decode("utf-8")
|
|
141
|
-
return encoded_image_base64
|
|
142
|
-
|
|
143
|
-
|
|
144
|
-
def _decode_image(encoded_image_base64: str) -> np.ndarray:
|
|
145
|
-
"""
|
|
146
|
-
Decodes a base64 encoded image to its numpy array representation.
|
|
147
|
-
|
|
148
|
-
Parameters
|
|
149
|
-
----------
|
|
150
|
-
encoded_image_base64 : str
|
|
151
|
-
The base64 encoded string of the image.
|
|
152
|
-
|
|
153
|
-
Returns
|
|
154
|
-
-------
|
|
155
|
-
np.ndarray
|
|
156
|
-
The decoded image in numpy array format.
|
|
157
|
-
"""
|
|
158
|
-
encoded_image = base64.b64decode(encoded_image_base64.json())
|
|
159
|
-
decoded_image = np.frombuffer(encoded_image, np.uint8)
|
|
160
|
-
decoded_image = imdecode(decoded_image, IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) / 255
|
|
161
|
-
return decoded_image
|