prefab 0.5.1__py3-none-any.whl → 1.0.0__py3-none-any.whl
This diff represents the content of publicly available package versions that have been released to one of the supported registries. The information contained in this diff is provided for informational purposes only and reflects changes between package versions as they appear in their respective public registries.
- prefab/__init__.py +12 -40
- prefab/__main__.py +8 -10
- prefab/compare.py +92 -0
- prefab/device.py +1233 -0
- prefab/geometry.py +302 -0
- prefab/models.py +114 -0
- prefab/read.py +293 -0
- {prefab-0.5.1.dist-info → prefab-1.0.0.dist-info}/METADATA +25 -31
- prefab-1.0.0.dist-info/RECORD +11 -0
- {prefab-0.5.1.dist-info → prefab-1.0.0.dist-info}/WHEEL +1 -1
- prefab/io.py +0 -214
- prefab/predictor.py +0 -231
- prefab/processor.py +0 -248
- prefab-0.5.1.dist-info/RECORD +0 -9
- {prefab-0.5.1.dist-info → prefab-1.0.0.dist-info}/licenses/LICENSE +0 -0
|
@@ -1,8 +1,10 @@
|
|
|
1
|
-
Metadata-Version: 2.
|
|
1
|
+
Metadata-Version: 2.3
|
|
2
2
|
Name: prefab
|
|
3
|
-
Version: 0.
|
|
4
|
-
Summary:
|
|
5
|
-
Project-URL: Homepage, https://
|
|
3
|
+
Version: 1.0.0
|
|
4
|
+
Summary: Artificial nanofabrication of integrated photonic circuits using deep learning
|
|
5
|
+
Project-URL: Homepage, https://prefabphotonics.com
|
|
6
|
+
Project-URL: Repository, https://github.com/PreFab-Photonics/PreFab
|
|
7
|
+
Project-URL: Docs, https://docs.prefabphotonics.com
|
|
6
8
|
Author-email: Dusan Gostimirovic <dusan@prefabphotonics.com>
|
|
7
9
|
License: GNU LESSER GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
|
|
8
10
|
Version 2.1, February 1999
|
|
@@ -509,54 +511,52 @@ License: GNU LESSER GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
|
|
|
509
511
|
|
|
510
512
|
That's all there is to it!
|
|
511
513
|
License-File: LICENSE
|
|
512
|
-
Keywords:
|
|
514
|
+
Keywords: machine-learning,nanofabrication,photonics
|
|
513
515
|
Classifier: License :: OSI Approved :: GNU Lesser General Public License v2 (LGPLv2)
|
|
514
516
|
Classifier: Operating System :: OS Independent
|
|
515
517
|
Classifier: Programming Language :: Python :: 3
|
|
516
518
|
Requires-Python: >=3.9
|
|
517
|
-
Requires-Dist:
|
|
519
|
+
Requires-Dist: gdstk
|
|
518
520
|
Requires-Dist: matplotlib
|
|
519
521
|
Requires-Dist: numpy
|
|
520
522
|
Requires-Dist: opencv-python-headless
|
|
523
|
+
Requires-Dist: pydantic
|
|
521
524
|
Requires-Dist: requests
|
|
525
|
+
Requires-Dist: toml
|
|
522
526
|
Description-Content-Type: text/markdown
|
|
523
527
|
|
|
524
528
|
# PreFab
|
|
525
529
|
|
|
526
|
-

|
|
530
|
+

|
|
527
531
|
|
|
528
|
-
|
|
532
|
+
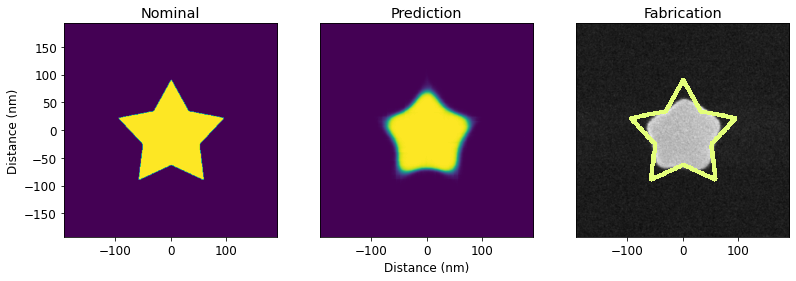
PreFab leverages **deep learning** to model fabrication-induced structural variations in integrated photonic devices. Through this _virtual nanofabrication environment_, we uncover valuable insights into nanofabrication processes and enhance device design accuracy.
|
|
529
533
|
|
|
530
534
|
## Prediction
|
|
531
535
|
|
|
532
|
-
|
|
536
|
+
PreFab accurately predicts process-induced structural alterations such as corner rounding, washing away of small lines and islands, and filling of narrow holes in planar photonic devices. This enables designers to quickly prototype expected performance and rectify designs prior to nanofabrication.
|
|
533
537
|
|
|
534
|
-
|
|
538
|
+

|
|
535
539
|
|
|
536
540
|
## Correction
|
|
537
541
|
|
|
538
|
-
|
|
542
|
+
PreFab automates corrections to device designs, ensuring the fabricated outcome aligns with the original design. This results in reduced structural variation and performance disparity from simulation to experiment.
|
|
539
543
|
|
|
540
|
-

|
|
544
|
+

|
|
541
545
|
|
|
542
546
|
## Models
|
|
543
547
|
|
|
544
|
-
|
|
548
|
+
PreFab accommodates unique _predictor_ and _corrector_ models for each photonic foundry, regularly updated based on recent fabrication data. Current models include (see full list on [`docs/models.md`](https://github.com/PreFab-Photonics/PreFab/blob/main/docs/models.md)):
|
|
545
549
|
|
|
546
|
-
| Foundry
|
|
547
|
-
|
|
|
548
|
-
| ANT
|
|
549
|
-
| ANT
|
|
550
|
-
| ANT | [SiN (Lower Edge)](https://www.appliednt.com/nanosoi/sys/resources/specs_nitride/) | v5 (Jun 3 2023) | d0 (Jun 1 2023) | ANT_SiN | v5-d0-lower | Alpha |
|
|
551
|
-
| SiEPICfab | [SOI](https://siepic.ca/fabrication/) | v5 (Jun 3 2023) | d0 (Jun 14 2023) | SiEPICfab_SOI | v5-d0 | Alpha |
|
|
550
|
+
| Foundry | Process | Latest Version | Latest Dataset | Model Name | Model Tag |
|
|
551
|
+
| ------- | ------- | ----------------- | ---------------- | ----------- | --------- |
|
|
552
|
+
| ANT | NanoSOI | ANF1 (May 6 2023) | d9 (Feb 6 2024) | ANT_NanoSOI | ANF1-d9 |
|
|
553
|
+
| ANT | SiN | ANF1 (May 6 2023) | d1 (Jan 31 2024) | ANT_SiN | ANF1-d1 |
|
|
552
554
|
|
|
553
|
-
_New models and foundries are to be added. Usage may change. For additional foundry and process models, feel free to contact us
|
|
555
|
+
> _New models and foundries are to be regularly added. Usage may change. For additional foundry and process models, feel free to contact us._
|
|
554
556
|
|
|
555
557
|
## Installation
|
|
556
558
|
|
|
557
|
-
|
|
558
|
-
|
|
559
|
-
Install `PreFab` via pip:
|
|
559
|
+
Install PreFab via pip:
|
|
560
560
|
|
|
561
561
|
```sh
|
|
562
562
|
pip install prefab
|
|
@@ -570,12 +570,6 @@ cd PreFab
|
|
|
570
570
|
pip install -e .
|
|
571
571
|
```
|
|
572
572
|
|
|
573
|
-
### Online
|
|
574
|
-
|
|
575
|
-
Use `PreFab` online through GitHub Codespaces:
|
|
576
|
-
|
|
577
|
-
[](https://github.com/codespaces/new?machine=basicLinux32gb&repo=608330448&ref=main&devcontainer_path=.devcontainer%2Fdevcontainer.json&location=EastUs)
|
|
578
|
-
|
|
579
573
|
## Getting Started
|
|
580
574
|
|
|
581
575
|
### Account setup
|
|
@@ -590,11 +584,11 @@ python3 -m prefab setup
|
|
|
590
584
|
|
|
591
585
|
### Guides
|
|
592
586
|
|
|
593
|
-
Visit [`/examples`](https://github.com/PreFab-Photonics/PreFab/tree/main/examples) or our [
|
|
587
|
+
Visit [`/docs/examples`](https://github.com/PreFab-Photonics/PreFab/tree/main/docs/examples) or our [docs](https://docs.prefabphotonics.com/) to get started with your first predictions.
|
|
594
588
|
|
|
595
589
|
## Performance and Usage
|
|
596
590
|
|
|
597
|
-
|
|
591
|
+
PreFab models are served via a serverless cloud platform. Please note:
|
|
598
592
|
|
|
599
593
|
- 🐢 CPU inference may result in slower performance. Future updates will introduce GPU inference.
|
|
600
594
|
- 🥶 The first prediction may take longer due to cold start server loading. Subsequent predictions will be faster.
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
prefab/__init__.py,sha256=z9DWthyzmj_EuBt7ywbT3G-lnMmUl4haRYgizvVhlYw,337
|
|
2
|
+
prefab/__main__.py,sha256=aAgt1WXa44k1nJqsiSD3uAfNeGpwtjWqMUYCHN5_Qrw,2759
|
|
3
|
+
prefab/compare.py,sha256=EIUQnCjZWMPTc_hibz2UsKCGLEciSJTXFttPQrW3V9o,2369
|
|
4
|
+
prefab/device.py,sha256=UZyz_85mmvIXfjT0Uz22MHW7vDHXR8pr9TkNuvQo_cE,47173
|
|
5
|
+
prefab/geometry.py,sha256=fMQlSJ1fIUUSHBJ1ILk-ATvnOFreK8BLRPWcVbLNkLU,9395
|
|
6
|
+
prefab/models.py,sha256=iVObzxOPct6nnNBNyYM2uk7Jr8w7mRY4ndxvr9Iby8Y,2576
|
|
7
|
+
prefab/read.py,sha256=dGd8-O5-xC5B_dB_VC4E2XLlDt5wIGCU0-VNP-04R94,10116
|
|
8
|
+
prefab-1.0.0.dist-info/METADATA,sha256=JGtW2yaBKey1JlCZ7BxdJqTRtCO-AHB3bA_nGiwXPWE,34674
|
|
9
|
+
prefab-1.0.0.dist-info/WHEEL,sha256=zEMcRr9Kr03x1ozGwg5v9NQBKn3kndp6LSoSlVg-jhU,87
|
|
10
|
+
prefab-1.0.0.dist-info/licenses/LICENSE,sha256=IMF9i4xIpgCADf0U-V1cuf9HBmqWQd3qtI3FSuyW4zE,26526
|
|
11
|
+
prefab-1.0.0.dist-info/RECORD,,
|
prefab/io.py
DELETED
|
@@ -1,214 +0,0 @@
|
|
|
1
|
-
"""
|
|
2
|
-
This module offers tools to import, export, and preprocess device layouts in multiple formats for
|
|
3
|
-
nanofabrication prediction tasks.
|
|
4
|
-
"""
|
|
5
|
-
|
|
6
|
-
from typing import List, Optional, Tuple
|
|
7
|
-
|
|
8
|
-
import cv2
|
|
9
|
-
import gdstk
|
|
10
|
-
import matplotlib.image as img
|
|
11
|
-
import numpy as np
|
|
12
|
-
|
|
13
|
-
from prefab.processor import binarize_hard
|
|
14
|
-
|
|
15
|
-
|
|
16
|
-
def load_device_img(path: str, img_length_nm: int = None) -> np.ndarray:
|
|
17
|
-
"""
|
|
18
|
-
Load, process and scale device image from file for prediction.
|
|
19
|
-
|
|
20
|
-
This function reads an image file, scales it according to the provided image length in
|
|
21
|
-
nanometers, and performs preprocessing tasks such as binarization, preparing it for prediction.
|
|
22
|
-
|
|
23
|
-
Parameters
|
|
24
|
-
----------
|
|
25
|
-
path : str
|
|
26
|
-
Path to the device image file.
|
|
27
|
-
|
|
28
|
-
img_length_nm : int, optional
|
|
29
|
-
Desired length of the device image in nanometers for scaling. If not provided,
|
|
30
|
-
the length of the original image is used.
|
|
31
|
-
|
|
32
|
-
Returns
|
|
33
|
-
-------
|
|
34
|
-
np.ndarray
|
|
35
|
-
A 2D numpy array representing the preprocessed and scaled device, ready for prediction.
|
|
36
|
-
"""
|
|
37
|
-
device = img.imread(path)[:, :, 1]
|
|
38
|
-
if img_length_nm is None:
|
|
39
|
-
img_length_nm = device.shape[1]
|
|
40
|
-
scale = img_length_nm / device.shape[1]
|
|
41
|
-
device = cv2.resize(device, (0, 0), fx=scale, fy=scale)
|
|
42
|
-
device = binarize_hard(device)
|
|
43
|
-
return device
|
|
44
|
-
|
|
45
|
-
|
|
46
|
-
def load_device_gds(
|
|
47
|
-
path: str,
|
|
48
|
-
cell_name: str,
|
|
49
|
-
coords: Optional[List[List[int]]] = None,
|
|
50
|
-
layer: Tuple[int, int] = (1, 0),
|
|
51
|
-
) -> np.ndarray:
|
|
52
|
-
"""
|
|
53
|
-
Load and process a device layout from a GDSII file.
|
|
54
|
-
|
|
55
|
-
This function reads a device layout from a GDSII file, performs necessary
|
|
56
|
-
preprocessing tasks such as scaling and padding, and prepares it for prediction.
|
|
57
|
-
Only the specified layer is loaded.
|
|
58
|
-
|
|
59
|
-
Parameters
|
|
60
|
-
----------
|
|
61
|
-
path : str
|
|
62
|
-
Path to the GDSII layout file.
|
|
63
|
-
|
|
64
|
-
cell_name : str
|
|
65
|
-
Name of the GDSII cell to be loaded.
|
|
66
|
-
|
|
67
|
-
coords : List[List[int]], optional
|
|
68
|
-
A list of coordinates [[xmin, ymin], [xmax, ymax]] in nm, defining the
|
|
69
|
-
region of the cell to be loaded. If None, the entire cell is loaded.
|
|
70
|
-
|
|
71
|
-
layer : Tuple[int, int], optional
|
|
72
|
-
A tuple specifying the layer to be loaded. Default is (1, 0).
|
|
73
|
-
|
|
74
|
-
Returns
|
|
75
|
-
-------
|
|
76
|
-
np.ndarray
|
|
77
|
-
A 2D numpy array representing the preprocessed device layout, ready for prediction.
|
|
78
|
-
"""
|
|
79
|
-
gds = gdstk.read_gds(path)
|
|
80
|
-
cell = gds[cell_name]
|
|
81
|
-
polygons = cell.get_polygons(layer=layer[0], datatype=layer[1])
|
|
82
|
-
bounds = tuple(
|
|
83
|
-
tuple(1000 * x for x in sub_tuple) for sub_tuple in cell.bounding_box()
|
|
84
|
-
)
|
|
85
|
-
device = np.zeros(
|
|
86
|
-
(int(bounds[1][1] - bounds[0][1]), int(bounds[1][0] - bounds[0][0]))
|
|
87
|
-
)
|
|
88
|
-
|
|
89
|
-
contours = [
|
|
90
|
-
np.array(
|
|
91
|
-
[
|
|
92
|
-
[
|
|
93
|
-
[
|
|
94
|
-
int(1000 * vertex[0] - bounds[0][0]),
|
|
95
|
-
int(1000 * vertex[1] - bounds[0][1]),
|
|
96
|
-
]
|
|
97
|
-
]
|
|
98
|
-
for vertex in polygon.points
|
|
99
|
-
],
|
|
100
|
-
dtype=np.int32,
|
|
101
|
-
)
|
|
102
|
-
for polygon in polygons
|
|
103
|
-
]
|
|
104
|
-
|
|
105
|
-
cv2.fillPoly(img=device, pts=contours, color=(1, 1, 1))
|
|
106
|
-
|
|
107
|
-
if coords is not None:
|
|
108
|
-
new_device = np.zeros(
|
|
109
|
-
(int(bounds[1][1] - bounds[0][1]), int(bounds[1][0] - bounds[0][0]))
|
|
110
|
-
)
|
|
111
|
-
new_device[
|
|
112
|
-
int(coords[0][1] - bounds[0][1]) : int(coords[1][1] - bounds[0][1]),
|
|
113
|
-
int(coords[0][0] - bounds[0][0]) : int(coords[1][0] - bounds[0][0]),
|
|
114
|
-
] = device[
|
|
115
|
-
int(coords[0][1] - bounds[0][1]) : int(coords[1][1] - bounds[0][1]),
|
|
116
|
-
int(coords[0][0] - bounds[0][0]) : int(coords[1][0] - bounds[0][0]),
|
|
117
|
-
]
|
|
118
|
-
device = new_device
|
|
119
|
-
|
|
120
|
-
device = np.flipud(device)
|
|
121
|
-
device = np.pad(device, 200)
|
|
122
|
-
|
|
123
|
-
return device.astype(np.float32)
|
|
124
|
-
|
|
125
|
-
|
|
126
|
-
def device_to_cell(
|
|
127
|
-
device: np.ndarray,
|
|
128
|
-
cell_name: str,
|
|
129
|
-
library: gdstk.Library,
|
|
130
|
-
resolution: float = 1.0,
|
|
131
|
-
layer: Tuple[int, int] = (1, 0),
|
|
132
|
-
approximation_mode: int = 2,
|
|
133
|
-
) -> gdstk.Cell:
|
|
134
|
-
"""Converts a device layout to a gdstk cell for GDSII export.
|
|
135
|
-
|
|
136
|
-
This function creates a cell that represents a device layout. The created cell
|
|
137
|
-
is ready to be exported as a GDSII file.
|
|
138
|
-
|
|
139
|
-
Parameters
|
|
140
|
-
----------
|
|
141
|
-
device : np.ndarray
|
|
142
|
-
A 2D numpy array representing the device layout.
|
|
143
|
-
|
|
144
|
-
cell_name : str
|
|
145
|
-
Name for the new cell.
|
|
146
|
-
|
|
147
|
-
library : gdstk.Library
|
|
148
|
-
Library to which the cell will be added.
|
|
149
|
-
|
|
150
|
-
resolution : float, optional
|
|
151
|
-
The resolution of the device in pixels per nm. Default is 1.0.
|
|
152
|
-
|
|
153
|
-
layer : Tuple[int, int], optional
|
|
154
|
-
A tuple specifying the layer to be exported. Default is (1, 0).
|
|
155
|
-
|
|
156
|
-
approximation_mode : int, optional
|
|
157
|
-
The approximation method to be used for finding contours. Possible values are 1, 2, 3, and
|
|
158
|
-
4. Larger values mean more approximation. Default is 1.
|
|
159
|
-
|
|
160
|
-
Returns
|
|
161
|
-
-------
|
|
162
|
-
gdstk.Cell
|
|
163
|
-
The newly created cell containing the device layout.
|
|
164
|
-
"""
|
|
165
|
-
approximation_method_mapping = {
|
|
166
|
-
1: cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE,
|
|
167
|
-
2: cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE,
|
|
168
|
-
3: cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_TC89_L1,
|
|
169
|
-
4: cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_TC89_KCOS,
|
|
170
|
-
}
|
|
171
|
-
|
|
172
|
-
device = np.flipud(device)
|
|
173
|
-
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(
|
|
174
|
-
device.astype(np.uint8),
|
|
175
|
-
cv2.RETR_TREE,
|
|
176
|
-
approximation_method_mapping[approximation_mode],
|
|
177
|
-
)
|
|
178
|
-
|
|
179
|
-
hierarchy_polygons = {}
|
|
180
|
-
|
|
181
|
-
for idx, contour in enumerate(contours):
|
|
182
|
-
level = 0
|
|
183
|
-
current_idx = idx
|
|
184
|
-
while hierarchy[0][current_idx][3] != -1:
|
|
185
|
-
level += 1
|
|
186
|
-
current_idx = hierarchy[0][current_idx][3]
|
|
187
|
-
|
|
188
|
-
if len(contour) > 2:
|
|
189
|
-
contour = contour / 1000 # μm to nm
|
|
190
|
-
points = [tuple(point) for point in contour.squeeze().tolist()]
|
|
191
|
-
if level not in hierarchy_polygons:
|
|
192
|
-
hierarchy_polygons[level] = []
|
|
193
|
-
hierarchy_polygons[level].append(points)
|
|
194
|
-
|
|
195
|
-
cell = library.new_cell(cell_name)
|
|
196
|
-
processed_polygons = []
|
|
197
|
-
# Process polygons by hierarchy level, alternating between adding and XORing
|
|
198
|
-
for level in sorted(hierarchy_polygons.keys()):
|
|
199
|
-
operation = "or" if level % 2 == 0 else "xor"
|
|
200
|
-
polygons_to_process = hierarchy_polygons[level]
|
|
201
|
-
|
|
202
|
-
if polygons_to_process:
|
|
203
|
-
processed_polygons = gdstk.boolean(
|
|
204
|
-
polygons_to_process,
|
|
205
|
-
processed_polygons,
|
|
206
|
-
operation,
|
|
207
|
-
layer=layer[0],
|
|
208
|
-
datatype=layer[1],
|
|
209
|
-
)
|
|
210
|
-
for polygon in processed_polygons:
|
|
211
|
-
polygon.scale(resolution, resolution)
|
|
212
|
-
cell.add(polygon)
|
|
213
|
-
|
|
214
|
-
return cell
|
prefab/predictor.py
DELETED
|
@@ -1,231 +0,0 @@
|
|
|
1
|
-
"""
|
|
2
|
-
A module for making predictions on fabrication variations in photonic devices
|
|
3
|
-
using machine learning models deployed in the cloud.
|
|
4
|
-
"""
|
|
5
|
-
|
|
6
|
-
import base64
|
|
7
|
-
import os
|
|
8
|
-
|
|
9
|
-
import numpy as np
|
|
10
|
-
import requests
|
|
11
|
-
import toml
|
|
12
|
-
from cv2 import IMREAD_GRAYSCALE, imdecode, imencode
|
|
13
|
-
|
|
14
|
-
from prefab.processor import binarize_hard
|
|
15
|
-
|
|
16
|
-
|
|
17
|
-
def predict(
|
|
18
|
-
device: np.ndarray, model_name: str, model_tags: str, binarize: bool = False
|
|
19
|
-
) -> np.ndarray:
|
|
20
|
-
"""
|
|
21
|
-
Generates a prediction for a photonic device using a specified cloud-based ML model.
|
|
22
|
-
|
|
23
|
-
The function sends an image of the device to a cloud function, which uses the specified
|
|
24
|
-
machine learning model to generate a prediction.
|
|
25
|
-
|
|
26
|
-
Parameters
|
|
27
|
-
----------
|
|
28
|
-
device : np.ndarray
|
|
29
|
-
A binary numpy matrix representing the shape of a device.
|
|
30
|
-
|
|
31
|
-
model_name : str
|
|
32
|
-
The name of the ML model to use for the prediction.
|
|
33
|
-
Consult the module's documentation for available models.
|
|
34
|
-
|
|
35
|
-
model_tags : Union[str, List[str]]
|
|
36
|
-
The tags of the ML model.
|
|
37
|
-
Consult the module's documentation for available tags.
|
|
38
|
-
|
|
39
|
-
binarize : bool, optional
|
|
40
|
-
If set to True, the prediction will be binarized (default is False).
|
|
41
|
-
|
|
42
|
-
Returns
|
|
43
|
-
-------
|
|
44
|
-
np.ndarray
|
|
45
|
-
A numpy matrix representing the predicted shape of the device. Pixel values closer
|
|
46
|
-
to 1 indicate a higher likelihood of core material, while pixel values closer to 0
|
|
47
|
-
suggest a higher likelihood of cladding material. Pixel values in between represent
|
|
48
|
-
prediction uncertainty.
|
|
49
|
-
"""
|
|
50
|
-
function_url = "https://prefab-photonics--predict.modal.run"
|
|
51
|
-
|
|
52
|
-
predict_data = {
|
|
53
|
-
"device": _encode_image(device),
|
|
54
|
-
"model_name": model_name,
|
|
55
|
-
"model_tags": model_tags,
|
|
56
|
-
"binary": binarize,
|
|
57
|
-
}
|
|
58
|
-
|
|
59
|
-
with open(os.path.expanduser("~/.prefab.toml"), "r") as file:
|
|
60
|
-
content = file.readlines()
|
|
61
|
-
for line in content:
|
|
62
|
-
if "access_token" in line:
|
|
63
|
-
access_token = line.split("=")[1].strip().strip('"')
|
|
64
|
-
if "refresh_token" in line:
|
|
65
|
-
refresh_token = line.split("=")[1].strip().strip('"')
|
|
66
|
-
break
|
|
67
|
-
|
|
68
|
-
headers = {
|
|
69
|
-
"Authorization": f"Bearer {access_token}",
|
|
70
|
-
"X-Refresh-Token": refresh_token,
|
|
71
|
-
}
|
|
72
|
-
response = requests.post(
|
|
73
|
-
url=function_url,
|
|
74
|
-
json=predict_data,
|
|
75
|
-
headers=headers,
|
|
76
|
-
)
|
|
77
|
-
|
|
78
|
-
if response.status_code != 200:
|
|
79
|
-
raise ValueError(response.text)
|
|
80
|
-
else:
|
|
81
|
-
response_data = response.json()
|
|
82
|
-
if "error" in response_data:
|
|
83
|
-
raise ValueError(response_data["error"])
|
|
84
|
-
if "prediction" in response_data:
|
|
85
|
-
prediction = _decode_image(response_data["prediction"])
|
|
86
|
-
if "new_refresh_token" in response_data:
|
|
87
|
-
prefab_file_path = os.path.expanduser("~/.prefab.toml")
|
|
88
|
-
with open(prefab_file_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as toml_file:
|
|
89
|
-
toml.dump(
|
|
90
|
-
{
|
|
91
|
-
"access_token": response_data["new_access_token"],
|
|
92
|
-
"refresh_token": response_data["new_refresh_token"],
|
|
93
|
-
},
|
|
94
|
-
toml_file,
|
|
95
|
-
)
|
|
96
|
-
|
|
97
|
-
if binarize:
|
|
98
|
-
prediction = binarize_hard(prediction)
|
|
99
|
-
|
|
100
|
-
return prediction
|
|
101
|
-
|
|
102
|
-
|
|
103
|
-
def correct(
|
|
104
|
-
device: np.ndarray,
|
|
105
|
-
model_name: str,
|
|
106
|
-
model_tags: str,
|
|
107
|
-
binarize: bool = True,
|
|
108
|
-
multi_correct: bool = False,
|
|
109
|
-
) -> np.ndarray:
|
|
110
|
-
"""
|
|
111
|
-
Generates a correction for a photonic device using a specified cloud-based ML model.
|
|
112
|
-
|
|
113
|
-
The function sends an image of the device to a cloud function, which uses the specified
|
|
114
|
-
machine learning model to generate a correction.
|
|
115
|
-
|
|
116
|
-
Parameters
|
|
117
|
-
----------
|
|
118
|
-
device : np.ndarray
|
|
119
|
-
A binary numpy matrix representing the shape of a device.
|
|
120
|
-
|
|
121
|
-
model_name : str
|
|
122
|
-
The name of the ML model to use for the correction.
|
|
123
|
-
Consult the module's documentation for available models.
|
|
124
|
-
|
|
125
|
-
model_tags : Union[str, List[str]]
|
|
126
|
-
The tags of the ML model.
|
|
127
|
-
Consult the module's documentation for available tags.
|
|
128
|
-
|
|
129
|
-
binarize : bool, optional
|
|
130
|
-
If set to True, the correction will be binarized (default is True).
|
|
131
|
-
|
|
132
|
-
multi_correct : bool, optional
|
|
133
|
-
If set to True, the correction will be generated using a iterative approach.
|
|
134
|
-
(default is False).
|
|
135
|
-
|
|
136
|
-
Returns
|
|
137
|
-
-------
|
|
138
|
-
np.ndarray
|
|
139
|
-
A numpy matrix representing the corrected shape of the device. Pixel values closer
|
|
140
|
-
to 1 indicate a higher likelihood of core material, while pixel values closer to 0
|
|
141
|
-
suggest a higher likelihood of cladding material. Pixel values in between represent
|
|
142
|
-
correction uncertainty.
|
|
143
|
-
"""
|
|
144
|
-
function_url = "https://prefab-photonics--correct.modal.run"
|
|
145
|
-
|
|
146
|
-
correct_data = {
|
|
147
|
-
"device": _encode_image(device),
|
|
148
|
-
"model_name": model_name,
|
|
149
|
-
"model_tags": model_tags,
|
|
150
|
-
"binary": binarize,
|
|
151
|
-
"multi_correct": multi_correct,
|
|
152
|
-
}
|
|
153
|
-
|
|
154
|
-
with open(os.path.expanduser("~/.prefab.toml"), "r") as file:
|
|
155
|
-
content = file.readlines()
|
|
156
|
-
for line in content:
|
|
157
|
-
if "access_token" in line:
|
|
158
|
-
access_token = line.split("=")[1].strip().strip('"')
|
|
159
|
-
if "refresh_token" in line:
|
|
160
|
-
refresh_token = line.split("=")[1].strip().strip('"')
|
|
161
|
-
break
|
|
162
|
-
|
|
163
|
-
headers = {
|
|
164
|
-
"Authorization": f"Bearer {access_token}",
|
|
165
|
-
"X-Refresh-Token": refresh_token,
|
|
166
|
-
}
|
|
167
|
-
response = requests.post(
|
|
168
|
-
url=function_url,
|
|
169
|
-
json=correct_data,
|
|
170
|
-
headers=headers,
|
|
171
|
-
)
|
|
172
|
-
|
|
173
|
-
if response.status_code != 200:
|
|
174
|
-
raise ValueError(response.text)
|
|
175
|
-
else:
|
|
176
|
-
response_data = response.json()
|
|
177
|
-
if "error" in response_data:
|
|
178
|
-
raise ValueError(response_data["error"])
|
|
179
|
-
if "correction" in response_data:
|
|
180
|
-
correction = _decode_image(response_data["correction"])
|
|
181
|
-
if "new_refresh_token" in response_data:
|
|
182
|
-
prefab_file_path = os.path.expanduser("~/.prefab.toml")
|
|
183
|
-
with open(prefab_file_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as toml_file:
|
|
184
|
-
toml.dump(
|
|
185
|
-
{
|
|
186
|
-
"access_token": response_data["new_access_token"],
|
|
187
|
-
"refresh_token": response_data["new_refresh_token"],
|
|
188
|
-
},
|
|
189
|
-
toml_file,
|
|
190
|
-
)
|
|
191
|
-
|
|
192
|
-
return correction
|
|
193
|
-
|
|
194
|
-
|
|
195
|
-
def _encode_image(image: np.ndarray) -> str:
|
|
196
|
-
"""
|
|
197
|
-
Encodes a numpy image array to its base64 representation.
|
|
198
|
-
|
|
199
|
-
Parameters
|
|
200
|
-
----------
|
|
201
|
-
image : np.ndarray
|
|
202
|
-
The image in numpy array format.
|
|
203
|
-
|
|
204
|
-
Returns
|
|
205
|
-
-------
|
|
206
|
-
str
|
|
207
|
-
The base64 encoded string of the image.
|
|
208
|
-
"""
|
|
209
|
-
encoded_image = imencode(".png", 255 * image)[1].tobytes()
|
|
210
|
-
encoded_image_base64 = base64.b64encode(encoded_image).decode("utf-8")
|
|
211
|
-
return encoded_image_base64
|
|
212
|
-
|
|
213
|
-
|
|
214
|
-
def _decode_image(encoded_image_base64: str) -> np.ndarray:
|
|
215
|
-
"""
|
|
216
|
-
Decodes a base64 encoded image to its numpy array representation.
|
|
217
|
-
|
|
218
|
-
Parameters
|
|
219
|
-
----------
|
|
220
|
-
encoded_image_base64 : str
|
|
221
|
-
The base64 encoded string of the image.
|
|
222
|
-
|
|
223
|
-
Returns
|
|
224
|
-
-------
|
|
225
|
-
np.ndarray
|
|
226
|
-
The decoded image in numpy array format.
|
|
227
|
-
"""
|
|
228
|
-
encoded_image = base64.b64decode(encoded_image_base64)
|
|
229
|
-
decoded_image = np.frombuffer(encoded_image, np.uint8)
|
|
230
|
-
decoded_image = imdecode(decoded_image, IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) / 255
|
|
231
|
-
return decoded_image
|