fastquadtree 0.4.0__cp38-abi3-macosx_10_12_x86_64.macosx_11_0_arm64.macosx_10_12_universal2.whl
This diff represents the content of publicly available package versions that have been released to one of the supported registries. The information contained in this diff is provided for informational purposes only and reflects changes between package versions as they appear in their respective public registries.
- fastquadtree/__init__.py +388 -0
- fastquadtree/__init__.pyi +67 -0
- fastquadtree/_bimap.py +111 -0
- fastquadtree/_item.py +23 -0
- fastquadtree/_native.abi3.so +0 -0
- fastquadtree/py.typed +0 -0
- fastquadtree-0.4.0.dist-info/METADATA +288 -0
- fastquadtree-0.4.0.dist-info/RECORD +10 -0
- fastquadtree-0.4.0.dist-info/WHEEL +4 -0
- fastquadtree-0.4.0.dist-info/licenses/LICENSE +21 -0
fastquadtree/__init__.py
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,388 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
from __future__ import annotations
|
|
2
|
+
|
|
3
|
+
from typing import Any, Iterable, List, Optional, Tuple, overload
|
|
4
|
+
from typing import Literal
|
|
5
|
+
|
|
6
|
+
# Compiled Rust module is provided by maturin (tool.maturin.module-name)
|
|
7
|
+
from ._native import QuadTree as _RustQuadTree
|
|
8
|
+
from ._bimap import BiMap # type: ignore[attr-defined]
|
|
9
|
+
from ._item import Item
|
|
10
|
+
|
|
11
|
+
Bounds = Tuple[float, float, float, float]
|
|
12
|
+
"""Axis-aligned rectangle as (min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y)."""
|
|
13
|
+
|
|
14
|
+
Point = Tuple[float, float]
|
|
15
|
+
"""2D point as (x, y)."""
|
|
16
|
+
|
|
17
|
+
_IdCoord = Tuple[int, float, float]
|
|
18
|
+
"""Result tuple as (id, x, y)."""
|
|
19
|
+
|
|
20
|
+
|
|
21
|
+
class QuadTree:
|
|
22
|
+
"""
|
|
23
|
+
High-level Python wrapper over the Rust quadtree engine.
|
|
24
|
+
|
|
25
|
+
The quadtree stores points with integer IDs. You may attach an arbitrary
|
|
26
|
+
Python object per ID when object tracking is enabled.
|
|
27
|
+
|
|
28
|
+
Performance characteristics:
|
|
29
|
+
Inserts: average O(log n)
|
|
30
|
+
Rect queries: average O(log n + k) where k is matches returned
|
|
31
|
+
Nearest neighbor: average O(log n)
|
|
32
|
+
|
|
33
|
+
Thread-safety:
|
|
34
|
+
Instances are not thread-safe. Use external synchronization if you
|
|
35
|
+
mutate the same tree from multiple threads.
|
|
36
|
+
|
|
37
|
+
Args:
|
|
38
|
+
bounds: World bounds as (min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y).
|
|
39
|
+
capacity: Max number of points per node before splitting.
|
|
40
|
+
max_depth: Optional max tree depth. If omitted, engine decides.
|
|
41
|
+
track_objects: Enable id <-> object mapping inside Python.
|
|
42
|
+
start_id: Starting auto-assigned id when you omit id on insert.
|
|
43
|
+
|
|
44
|
+
Raises:
|
|
45
|
+
ValueError: If parameters are invalid or inserts are out of bounds.
|
|
46
|
+
"""
|
|
47
|
+
|
|
48
|
+
__slots__ = ("_native", "_items", "_next_id", "_count", "_bounds")
|
|
49
|
+
|
|
50
|
+
def __init__(
|
|
51
|
+
self,
|
|
52
|
+
bounds: Bounds,
|
|
53
|
+
capacity: int,
|
|
54
|
+
*,
|
|
55
|
+
max_depth: Optional[int] = None,
|
|
56
|
+
track_objects: bool = False,
|
|
57
|
+
start_id: int = 1,
|
|
58
|
+
):
|
|
59
|
+
if max_depth is None:
|
|
60
|
+
self._native = _RustQuadTree(bounds, capacity)
|
|
61
|
+
else:
|
|
62
|
+
self._native = _RustQuadTree(bounds, capacity, max_depth=max_depth)
|
|
63
|
+
self._items: Optional[BiMap] = BiMap() if track_objects else None
|
|
64
|
+
self._next_id: int = int(start_id)
|
|
65
|
+
self._count: int = 0
|
|
66
|
+
self._bounds = bounds
|
|
67
|
+
|
|
68
|
+
# ---------- inserts ----------
|
|
69
|
+
|
|
70
|
+
def insert(self, xy: Point, *, id: Optional[int] = None, obj: Any = None) -> int:
|
|
71
|
+
"""
|
|
72
|
+
Insert a single point.
|
|
73
|
+
|
|
74
|
+
Args:
|
|
75
|
+
xy: Point (x, y).
|
|
76
|
+
id: Optional integer id. If None, an auto id is assigned.
|
|
77
|
+
obj: Optional Python object to associate with id. Stored only if
|
|
78
|
+
object tracking is enabled.
|
|
79
|
+
|
|
80
|
+
Returns:
|
|
81
|
+
The id used for this insert.
|
|
82
|
+
|
|
83
|
+
Raises:
|
|
84
|
+
ValueError: If the point is outside tree bounds.
|
|
85
|
+
"""
|
|
86
|
+
if id is None:
|
|
87
|
+
id = self._next_id
|
|
88
|
+
self._next_id += 1
|
|
89
|
+
else:
|
|
90
|
+
# ensure future auto-ids do not collide
|
|
91
|
+
if id >= self._next_id:
|
|
92
|
+
self._next_id = id + 1
|
|
93
|
+
|
|
94
|
+
if not self._native.insert(id, xy):
|
|
95
|
+
x, y = xy
|
|
96
|
+
bx0, by0, bx1, by1 = self._bounds
|
|
97
|
+
raise ValueError(
|
|
98
|
+
f"Point ({x}, {y}) is outside bounds ({bx0}, {by0}, {bx1}, {by1})"
|
|
99
|
+
)
|
|
100
|
+
|
|
101
|
+
if self._items is not None:
|
|
102
|
+
self._items.add(Item(id, xy[0], xy[1], obj))
|
|
103
|
+
|
|
104
|
+
self._count += 1
|
|
105
|
+
return id
|
|
106
|
+
|
|
107
|
+
def insert_many_points(self, points: Iterable[Point]) -> int:
|
|
108
|
+
"""
|
|
109
|
+
Bulk insert points with auto-assigned ids.
|
|
110
|
+
|
|
111
|
+
Args:
|
|
112
|
+
points: Iterable of (x, y) points.
|
|
113
|
+
|
|
114
|
+
Returns:
|
|
115
|
+
Number of points successfully inserted.
|
|
116
|
+
|
|
117
|
+
Raises:
|
|
118
|
+
ValueError: If any point is outside tree bounds.
|
|
119
|
+
"""
|
|
120
|
+
ins = self._native.insert
|
|
121
|
+
nid = self._next_id
|
|
122
|
+
inserted = 0
|
|
123
|
+
bx0, by0, bx1, by1 = self._bounds
|
|
124
|
+
for xy in points:
|
|
125
|
+
id_ = nid
|
|
126
|
+
nid += 1
|
|
127
|
+
if not ins(id_, xy):
|
|
128
|
+
x, y = xy
|
|
129
|
+
raise ValueError(
|
|
130
|
+
f"Point ({x}, {y}) is outside bounds ({bx0}, {by0}, {bx1}, {by1})"
|
|
131
|
+
)
|
|
132
|
+
inserted += 1
|
|
133
|
+
if self._items is not None:
|
|
134
|
+
self._items.add(Item(id_, xy[0], xy[1], None))
|
|
135
|
+
self._next_id = nid
|
|
136
|
+
self._count += inserted
|
|
137
|
+
return inserted
|
|
138
|
+
|
|
139
|
+
def attach(self, id: int, obj: Any) -> None:
|
|
140
|
+
"""
|
|
141
|
+
Attach or replace the Python object for an existing id.
|
|
142
|
+
Tracking must be enabled.
|
|
143
|
+
|
|
144
|
+
Args:
|
|
145
|
+
id: Target id.
|
|
146
|
+
obj: Object to associate with id.
|
|
147
|
+
"""
|
|
148
|
+
if self._items is None:
|
|
149
|
+
raise ValueError("Cannot attach objects when track_objects=False")
|
|
150
|
+
|
|
151
|
+
item = self._items.by_id(id)
|
|
152
|
+
if item is None:
|
|
153
|
+
raise KeyError(f"Id {id} not found in quadtree")
|
|
154
|
+
self._items.add(Item(id, item.x, item.y, obj))
|
|
155
|
+
|
|
156
|
+
def delete(self, id: int, xy: Point) -> bool:
|
|
157
|
+
"""
|
|
158
|
+
Delete an item by id and exact coordinates.
|
|
159
|
+
|
|
160
|
+
Args:
|
|
161
|
+
id: Integer id to remove.
|
|
162
|
+
xy: Coordinates (x, y) of the item.
|
|
163
|
+
|
|
164
|
+
Returns:
|
|
165
|
+
True if the item was found and deleted, else False.
|
|
166
|
+
"""
|
|
167
|
+
deleted = self._native.delete(id, xy)
|
|
168
|
+
if deleted:
|
|
169
|
+
self._count -= 1
|
|
170
|
+
if self._items is not None:
|
|
171
|
+
self._items.pop_id(id) # ignore result
|
|
172
|
+
return deleted
|
|
173
|
+
|
|
174
|
+
def delete_by_object(self, obj: Any) -> bool:
|
|
175
|
+
"""
|
|
176
|
+
Delete an item by Python object.
|
|
177
|
+
|
|
178
|
+
Requires object tracking to be enabled. Performs an O(1) reverse
|
|
179
|
+
lookup to get the id, then deletes that entry at the given location.
|
|
180
|
+
|
|
181
|
+
Args:
|
|
182
|
+
obj: The tracked Python object to remove.
|
|
183
|
+
|
|
184
|
+
Returns:
|
|
185
|
+
True if the item was found and deleted, else False.
|
|
186
|
+
|
|
187
|
+
Raises:
|
|
188
|
+
ValueError: If object tracking is disabled.
|
|
189
|
+
"""
|
|
190
|
+
if self._items is None:
|
|
191
|
+
raise ValueError(
|
|
192
|
+
"Cannot delete by object when track_objects=False. Use delete(id, xy) instead."
|
|
193
|
+
)
|
|
194
|
+
|
|
195
|
+
item = self._items.by_obj(obj)
|
|
196
|
+
if item is None:
|
|
197
|
+
return False
|
|
198
|
+
|
|
199
|
+
return self.delete(item.id, (item.x, item.y))
|
|
200
|
+
|
|
201
|
+
# ---------- queries ----------
|
|
202
|
+
|
|
203
|
+
@overload
|
|
204
|
+
def query(
|
|
205
|
+
self, rect: Bounds, *, as_items: Literal[False] = ...
|
|
206
|
+
) -> List[_IdCoord]: ...
|
|
207
|
+
|
|
208
|
+
@overload
|
|
209
|
+
def query(self, rect: Bounds, *, as_items: Literal[True]) -> List[Item]: ...
|
|
210
|
+
|
|
211
|
+
def query(
|
|
212
|
+
self, rect: Bounds, *, as_items: bool = False
|
|
213
|
+
) -> List[_IdCoord] | List[Item]:
|
|
214
|
+
"""
|
|
215
|
+
Return all points inside an axis-aligned rectangle.
|
|
216
|
+
|
|
217
|
+
Args:
|
|
218
|
+
rect: Query rectangle as (min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y).
|
|
219
|
+
as_items: If True, return Item wrappers. If False, return raw tuples.
|
|
220
|
+
|
|
221
|
+
Returns:
|
|
222
|
+
If as_items is False: list of (id, x, y) tuples.
|
|
223
|
+
If as_items is True: list of Item objects.
|
|
224
|
+
"""
|
|
225
|
+
raw = self._native.query(rect)
|
|
226
|
+
if not as_items:
|
|
227
|
+
return raw
|
|
228
|
+
|
|
229
|
+
if self._items is None:
|
|
230
|
+
raise ValueError("Cannot return results as items with track_objects=False")
|
|
231
|
+
out: List[Item] = []
|
|
232
|
+
for id_, x, y in raw:
|
|
233
|
+
item = self._items.by_id(id_)
|
|
234
|
+
if item is None:
|
|
235
|
+
raise RuntimeError(
|
|
236
|
+
f"Internal error: id {id_} found in native tree but missing from object tracker. "
|
|
237
|
+
f"Ensure all inserts/deletes are done via this wrapper."
|
|
238
|
+
)
|
|
239
|
+
out.append(item)
|
|
240
|
+
return out
|
|
241
|
+
|
|
242
|
+
@overload
|
|
243
|
+
def nearest_neighbor(
|
|
244
|
+
self, xy: Point, *, as_item: Literal[False] = ...
|
|
245
|
+
) -> Optional[_IdCoord]: ...
|
|
246
|
+
|
|
247
|
+
@overload
|
|
248
|
+
def nearest_neighbor(
|
|
249
|
+
self, xy: Point, *, as_item: Literal[True]
|
|
250
|
+
) -> Optional[Item]: ...
|
|
251
|
+
|
|
252
|
+
def nearest_neighbor(self, xy: Point, *, as_item: bool = False):
|
|
253
|
+
"""
|
|
254
|
+
Return the single nearest neighbor to the query point.
|
|
255
|
+
|
|
256
|
+
Args:
|
|
257
|
+
xy: Query point (x, y).
|
|
258
|
+
as_item: If True, return Item. If False, return (id, x, y).
|
|
259
|
+
|
|
260
|
+
Returns:
|
|
261
|
+
The nearest neighbor or None if the tree is empty.
|
|
262
|
+
"""
|
|
263
|
+
t = self._native.nearest_neighbor(xy)
|
|
264
|
+
if t is None or not as_item:
|
|
265
|
+
return t
|
|
266
|
+
|
|
267
|
+
if self._items is None:
|
|
268
|
+
raise ValueError("Cannot return result as item with track_objects=False")
|
|
269
|
+
id_, x, y = t
|
|
270
|
+
item = self._items.by_id(id_)
|
|
271
|
+
if item is None:
|
|
272
|
+
raise RuntimeError(
|
|
273
|
+
f"Internal error: id {id_} found in native tree but missing from object tracker. "
|
|
274
|
+
f"Ensure all inserts/deletes are done via this wrapper."
|
|
275
|
+
)
|
|
276
|
+
return item
|
|
277
|
+
|
|
278
|
+
@overload
|
|
279
|
+
def nearest_neighbors(
|
|
280
|
+
self, xy: Point, k: int, *, as_items: Literal[False] = ...
|
|
281
|
+
) -> List[_IdCoord]: ...
|
|
282
|
+
|
|
283
|
+
@overload
|
|
284
|
+
def nearest_neighbors(
|
|
285
|
+
self, xy: Point, k: int, *, as_items: Literal[True]
|
|
286
|
+
) -> List[Item]: ...
|
|
287
|
+
|
|
288
|
+
def nearest_neighbors(self, xy: Point, k: int, *, as_items: bool = False):
|
|
289
|
+
"""
|
|
290
|
+
Return the k nearest neighbors to the query point.
|
|
291
|
+
|
|
292
|
+
Args:
|
|
293
|
+
xy: Query point (x, y).
|
|
294
|
+
k: Number of neighbors to return.
|
|
295
|
+
as_items: If True, return Item wrappers. If False, return raw tuples.
|
|
296
|
+
|
|
297
|
+
Returns:
|
|
298
|
+
List of results in ascending distance order.
|
|
299
|
+
"""
|
|
300
|
+
raw = self._native.nearest_neighbors(xy, k)
|
|
301
|
+
if not as_items:
|
|
302
|
+
return raw
|
|
303
|
+
if self._items is None:
|
|
304
|
+
raise ValueError("Cannot return results as items with track_objects=False")
|
|
305
|
+
|
|
306
|
+
out: List[Item] = []
|
|
307
|
+
for id_, _, _ in raw:
|
|
308
|
+
item = self._items.by_id(id_)
|
|
309
|
+
if item is None:
|
|
310
|
+
raise RuntimeError(
|
|
311
|
+
f"Internal error: id {id_} found in native tree but missing from object tracker. "
|
|
312
|
+
f"Ensure all inserts/deletes are done via this wrapper."
|
|
313
|
+
)
|
|
314
|
+
out.append(item)
|
|
315
|
+
return out
|
|
316
|
+
|
|
317
|
+
# ---------- misc ----------
|
|
318
|
+
|
|
319
|
+
def get(self, id: int) -> Any | None:
|
|
320
|
+
"""
|
|
321
|
+
Return the object associated with id.
|
|
322
|
+
|
|
323
|
+
Returns:
|
|
324
|
+
The tracked object if present and tracking is enabled, else None.
|
|
325
|
+
"""
|
|
326
|
+
if self._items is None:
|
|
327
|
+
raise ValueError("Cannot get objects when track_objects=False")
|
|
328
|
+
item = self._items.by_id(id)
|
|
329
|
+
if item is None:
|
|
330
|
+
return None
|
|
331
|
+
return item.obj
|
|
332
|
+
|
|
333
|
+
def get_all_rectangles(self) -> List[Bounds]:
|
|
334
|
+
"""
|
|
335
|
+
Return all node rectangles in the current quadtree.
|
|
336
|
+
|
|
337
|
+
Returns:
|
|
338
|
+
List of (min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y) for each node in the tree.
|
|
339
|
+
"""
|
|
340
|
+
return self._native.get_all_rectangles()
|
|
341
|
+
|
|
342
|
+
def get_all_objects(self) -> List[Any]:
|
|
343
|
+
"""
|
|
344
|
+
Return all tracked objects.
|
|
345
|
+
|
|
346
|
+
Returns:
|
|
347
|
+
List of objects if tracking is enabled, else an empty list.
|
|
348
|
+
"""
|
|
349
|
+
if self._items is None:
|
|
350
|
+
raise ValueError("Cannot get objects when track_objects=False")
|
|
351
|
+
return [t.obj for t in self._items.items() if t.obj is not None]
|
|
352
|
+
|
|
353
|
+
def get_all_items(self) -> List[Item]:
|
|
354
|
+
"""
|
|
355
|
+
Return all tracked items.
|
|
356
|
+
|
|
357
|
+
Returns:
|
|
358
|
+
List of Item if tracking is enabled, else an empty list.
|
|
359
|
+
"""
|
|
360
|
+
if self._items is None:
|
|
361
|
+
raise ValueError("Cannot get items when track_objects=False")
|
|
362
|
+
return list(self._items.items())
|
|
363
|
+
|
|
364
|
+
def count_items(self) -> int:
|
|
365
|
+
"""
|
|
366
|
+
Return the number of items stored in the native tree.
|
|
367
|
+
|
|
368
|
+
Notes:
|
|
369
|
+
This calls the native engine and may differ from len(self) if
|
|
370
|
+
you create multiple wrappers around the same native structure.
|
|
371
|
+
"""
|
|
372
|
+
return self._native.count_items()
|
|
373
|
+
|
|
374
|
+
def __len__(self) -> int:
|
|
375
|
+
"""
|
|
376
|
+
Return the number of successful inserts done via this wrapper.
|
|
377
|
+
|
|
378
|
+
Notes:
|
|
379
|
+
This is the Python-side counter that tracks calls that returned True.
|
|
380
|
+
use count_items() to get the authoritative native-side count.
|
|
381
|
+
"""
|
|
382
|
+
return self._count
|
|
383
|
+
|
|
384
|
+
# Power users can access the raw class
|
|
385
|
+
NativeQuadTree = _RustQuadTree
|
|
386
|
+
|
|
387
|
+
|
|
388
|
+
__all__ = ["QuadTree", "Item", "Bounds", "Point"]
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
from typing import Any, Iterable, List, Optional, Tuple, Type, overload
|
|
2
|
+
from typing import Literal as _Literal # avoid polluting public namespace
|
|
3
|
+
|
|
4
|
+
Bounds = Tuple[float, float, float, float]
|
|
5
|
+
Point = Tuple[float, float]
|
|
6
|
+
|
|
7
|
+
class Item:
|
|
8
|
+
id: int
|
|
9
|
+
x: float
|
|
10
|
+
y: float
|
|
11
|
+
obj: Any | None
|
|
12
|
+
|
|
13
|
+
class QuadTree:
|
|
14
|
+
# Expose the raw native class for power users
|
|
15
|
+
NativeQuadTree: Type
|
|
16
|
+
|
|
17
|
+
def __init__(
|
|
18
|
+
self,
|
|
19
|
+
bounds: Bounds,
|
|
20
|
+
capacity: int,
|
|
21
|
+
*,
|
|
22
|
+
max_depth: Optional[int] = None,
|
|
23
|
+
track_objects: bool = False,
|
|
24
|
+
start_id: int = 1,
|
|
25
|
+
) -> None: ...
|
|
26
|
+
|
|
27
|
+
# Inserts
|
|
28
|
+
def insert(self, xy: Point, *, id: Optional[int] = ..., obj: Any = ...) -> int: ...
|
|
29
|
+
def insert_many_points(self, points: Iterable[Point]) -> int: ...
|
|
30
|
+
def insert_many(self, items: Iterable[Tuple[Point, Any]]) -> int: ...
|
|
31
|
+
def attach(self, id: int, obj: Any) -> None: ...
|
|
32
|
+
|
|
33
|
+
# Deletions
|
|
34
|
+
def delete(self, id: int, xy: Point) -> bool: ...
|
|
35
|
+
def delete_by_object(self, obj: Any) -> bool: ...
|
|
36
|
+
|
|
37
|
+
# Queries
|
|
38
|
+
@overload
|
|
39
|
+
def query(
|
|
40
|
+
self, rect: Bounds, *, as_items: _Literal[False] = ...
|
|
41
|
+
) -> List[Tuple[int, float, float]]: ...
|
|
42
|
+
@overload
|
|
43
|
+
def query(self, rect: Bounds, *, as_items: _Literal[True]) -> List[Item]: ...
|
|
44
|
+
@overload
|
|
45
|
+
def nearest_neighbor(
|
|
46
|
+
self, xy: Point, *, as_item: _Literal[False] = ...
|
|
47
|
+
) -> Optional[Tuple[int, float, float]]: ...
|
|
48
|
+
@overload
|
|
49
|
+
def nearest_neighbor(
|
|
50
|
+
self, xy: Point, *, as_item: _Literal[True]
|
|
51
|
+
) -> Optional[Item]: ...
|
|
52
|
+
@overload
|
|
53
|
+
def nearest_neighbors(
|
|
54
|
+
self, xy: Point, k: int, *, as_items: _Literal[False] = ...
|
|
55
|
+
) -> List[Tuple[int, float, float]]: ...
|
|
56
|
+
@overload
|
|
57
|
+
def nearest_neighbors(
|
|
58
|
+
self, xy: Point, k: int, *, as_items: _Literal[True]
|
|
59
|
+
) -> List[Item]: ...
|
|
60
|
+
|
|
61
|
+
# Misc
|
|
62
|
+
def get(self, id: int) -> Any | None: ...
|
|
63
|
+
def get_all_rectangles(self) -> List[Bounds]: ...
|
|
64
|
+
def get_all_objects(self) -> List[Any]: ...
|
|
65
|
+
def get_all_items(self) -> List[Item]: ...
|
|
66
|
+
def count_items(self) -> int: ...
|
|
67
|
+
def __len__(self) -> int: ...
|
fastquadtree/_bimap.py
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
# _bimap.py
|
|
2
|
+
from __future__ import annotations
|
|
3
|
+
from typing import Any, Iterable, Iterator, Tuple, Optional
|
|
4
|
+
|
|
5
|
+
from ._item import Item
|
|
6
|
+
|
|
7
|
+
|
|
8
|
+
class BiMap:
|
|
9
|
+
"""
|
|
10
|
+
Bidirectional map to the same Item:
|
|
11
|
+
id -> Item
|
|
12
|
+
obj -> Item (uses object identity)
|
|
13
|
+
|
|
14
|
+
Rules:
|
|
15
|
+
- One-to-one: an id maps to exactly one Item, and an object maps to exactly one Item.
|
|
16
|
+
- add(item): inserts or replaces both sides so they point to 'item'.
|
|
17
|
+
- If item.obj is None, only id -> Item is stored.
|
|
18
|
+
"""
|
|
19
|
+
|
|
20
|
+
__slots__ = ("_id_to_item", "_objid_to_item")
|
|
21
|
+
|
|
22
|
+
def __init__(self, items: Iterable[Item] | None = None) -> None:
|
|
23
|
+
self._id_to_item: dict[int, Item] = {}
|
|
24
|
+
self._objid_to_item: dict[int, Item] = {}
|
|
25
|
+
if items:
|
|
26
|
+
for it in items:
|
|
27
|
+
self.add(it)
|
|
28
|
+
|
|
29
|
+
# - core -
|
|
30
|
+
|
|
31
|
+
def add(self, item: Item) -> None:
|
|
32
|
+
"""
|
|
33
|
+
Insert or replace mapping for this Item.
|
|
34
|
+
Handles conflicts so that both id and obj point to this exact Item.
|
|
35
|
+
"""
|
|
36
|
+
id_ = item.id
|
|
37
|
+
obj = item.obj
|
|
38
|
+
|
|
39
|
+
# Unlink any old item currently bound to this id
|
|
40
|
+
old = self._id_to_item.get(id_)
|
|
41
|
+
if old is not None and old is not item:
|
|
42
|
+
old_obj = old.obj
|
|
43
|
+
if old_obj is not None:
|
|
44
|
+
self._objid_to_item.pop(id(old_obj), None)
|
|
45
|
+
|
|
46
|
+
# Unlink any old item currently bound to this obj
|
|
47
|
+
if obj is not None:
|
|
48
|
+
prev = self._objid_to_item.get(id(obj))
|
|
49
|
+
if prev is not None and prev is not item:
|
|
50
|
+
self._id_to_item.pop(prev.id, None)
|
|
51
|
+
|
|
52
|
+
# Link new
|
|
53
|
+
self._id_to_item[id_] = item
|
|
54
|
+
if obj is not None:
|
|
55
|
+
self._objid_to_item[id(obj)] = item
|
|
56
|
+
|
|
57
|
+
def by_id(self, id_: int) -> Optional[Item]:
|
|
58
|
+
return self._id_to_item.get(id_)
|
|
59
|
+
|
|
60
|
+
def by_obj(self, obj: Any) -> Optional[Item]:
|
|
61
|
+
return self._objid_to_item.get(id(obj))
|
|
62
|
+
|
|
63
|
+
def pop_id(self, id_: int) -> Optional[Item]:
|
|
64
|
+
it = self._id_to_item.pop(id_, None)
|
|
65
|
+
if it is not None:
|
|
66
|
+
obj = it.obj
|
|
67
|
+
if obj is not None:
|
|
68
|
+
self._objid_to_item.pop(id(obj), None)
|
|
69
|
+
return it
|
|
70
|
+
|
|
71
|
+
def pop_obj(self, obj: Any) -> Optional[Item]:
|
|
72
|
+
it = self._objid_to_item.pop(id(obj), None)
|
|
73
|
+
if it is not None:
|
|
74
|
+
self._id_to_item.pop(it.id, None)
|
|
75
|
+
return it
|
|
76
|
+
|
|
77
|
+
def pop_item(self, item: Item) -> Optional[Item]:
|
|
78
|
+
"""
|
|
79
|
+
Remove this exact Item if present on either side.
|
|
80
|
+
"""
|
|
81
|
+
removed = None
|
|
82
|
+
# Remove by id first
|
|
83
|
+
if self._id_to_item.get(item.id) is item:
|
|
84
|
+
removed = self._id_to_item.pop(item.id)
|
|
85
|
+
# Remove by obj side
|
|
86
|
+
obj = item.obj
|
|
87
|
+
if obj is not None and self._objid_to_item.get(id(obj)) is item:
|
|
88
|
+
self._objid_to_item.pop(id(obj), None)
|
|
89
|
+
removed = removed or item
|
|
90
|
+
return removed
|
|
91
|
+
|
|
92
|
+
# - convenience -
|
|
93
|
+
|
|
94
|
+
def __len__(self) -> int:
|
|
95
|
+
return len(self._id_to_item)
|
|
96
|
+
|
|
97
|
+
def clear(self) -> None:
|
|
98
|
+
self._id_to_item.clear()
|
|
99
|
+
self._objid_to_item.clear()
|
|
100
|
+
|
|
101
|
+
def contains_id(self, id_: int) -> bool:
|
|
102
|
+
return id_ in self._id_to_item
|
|
103
|
+
|
|
104
|
+
def contains_obj(self, obj: Any) -> bool:
|
|
105
|
+
return id(obj) in self._objid_to_item
|
|
106
|
+
|
|
107
|
+
def items_by_id(self) -> Iterator[Tuple[int, Item]]:
|
|
108
|
+
return iter(self._id_to_item.items())
|
|
109
|
+
|
|
110
|
+
def items(self) -> Iterator[Item]:
|
|
111
|
+
return iter(self._id_to_item.values())
|
fastquadtree/_item.py
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
# item.py
|
|
2
|
+
from __future__ import annotations
|
|
3
|
+
from typing import Any
|
|
4
|
+
|
|
5
|
+
|
|
6
|
+
class Item:
|
|
7
|
+
"""
|
|
8
|
+
Lightweight view of an index entry.
|
|
9
|
+
|
|
10
|
+
Attributes:
|
|
11
|
+
id: Integer identifier.
|
|
12
|
+
x: X coordinate.
|
|
13
|
+
y: Y coordinate.
|
|
14
|
+
obj: The attached Python object if available, else None.
|
|
15
|
+
"""
|
|
16
|
+
|
|
17
|
+
__slots__ = ("id", "x", "y", "obj")
|
|
18
|
+
|
|
19
|
+
def __init__(self, id: int, x: float, y: float, obj: Any | None = None):
|
|
20
|
+
self.id = id
|
|
21
|
+
self.x = x
|
|
22
|
+
self.y = y
|
|
23
|
+
self.obj = obj
|
|
Binary file
|
fastquadtree/py.typed
ADDED
|
File without changes
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,288 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
Metadata-Version: 2.4
|
|
2
|
+
Name: fastquadtree
|
|
3
|
+
Version: 0.4.0
|
|
4
|
+
Classifier: Programming Language :: Python :: 3
|
|
5
|
+
Classifier: Programming Language :: Python :: 3 :: Only
|
|
6
|
+
Classifier: Programming Language :: Rust
|
|
7
|
+
Classifier: Programming Language :: Python :: Implementation :: CPython
|
|
8
|
+
Classifier: Operating System :: OS Independent
|
|
9
|
+
Classifier: Topic :: Scientific/Engineering
|
|
10
|
+
Classifier: Topic :: Scientific/Engineering :: Information Analysis
|
|
11
|
+
Classifier: Topic :: Software Development :: Libraries
|
|
12
|
+
Classifier: Typing :: Typed
|
|
13
|
+
Classifier: License :: OSI Approved :: MIT License
|
|
14
|
+
License-File: LICENSE
|
|
15
|
+
Summary: Rust-accelerated quadtree for Python with fast inserts, range queries, and k-NN search.
|
|
16
|
+
Keywords: quadtree,spatial-index,geometry,rust,pyo3,nearest-neighbor,k-nn
|
|
17
|
+
Author: Ethan Anderson
|
|
18
|
+
Requires-Python: >=3.8
|
|
19
|
+
Description-Content-Type: text/markdown
|
|
20
|
+
Project-URL: Homepage, https://github.com/Elan456/fastquadtree
|
|
21
|
+
Project-URL: Repository, https://github.com/Elan456/fastquadtree
|
|
22
|
+
Project-URL: Issues, https://github.com/Elan456/fastquadtree/issues
|
|
23
|
+
|
|
24
|
+
# fastquadtree
|
|
25
|
+
|
|
26
|
+
[](https://pepy.tech/projects/fastquadtree)
|
|
27
|
+
|
|
28
|
+
|
|
29
|
+
|
|
30
|
+
|
|
31
|
+
Rust-optimized quadtree with a simple Python API.
|
|
32
|
+
|
|
33
|
+
- Python package: **`fastquadtree`**
|
|
34
|
+
- Python ≥ 3.8
|
|
35
|
+
- Import path: `from fastquadtree import QuadTree`
|
|
36
|
+
|
|
37
|
+
## Install
|
|
38
|
+
|
|
39
|
+
```bash
|
|
40
|
+
pip install fastquadtree
|
|
41
|
+
````
|
|
42
|
+
|
|
43
|
+
If you are developing locally:
|
|
44
|
+
|
|
45
|
+
```bash
|
|
46
|
+
# optimized dev install
|
|
47
|
+
maturin develop --release
|
|
48
|
+
```
|
|
49
|
+
|
|
50
|
+
## Quickstart
|
|
51
|
+
|
|
52
|
+
```python
|
|
53
|
+
from fastquadtree import QuadTree
|
|
54
|
+
|
|
55
|
+
# Bounds are (min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y)
|
|
56
|
+
qt = QuadTree(bounds=(0, 0, 1000, 1000), capacity=20) # max_depth is optional
|
|
57
|
+
|
|
58
|
+
# Insert points with auto ids
|
|
59
|
+
id1 = qt.insert((10, 10))
|
|
60
|
+
id2 = qt.insert((200, 300))
|
|
61
|
+
id3 = qt.insert((999, 500), id=42) # you can supply your own id
|
|
62
|
+
|
|
63
|
+
# Axis-aligned rectangle query
|
|
64
|
+
hits = qt.query((0, 0, 250, 350)) # returns [(id, x, y), ...] by default
|
|
65
|
+
print(hits) # e.g. [(1, 10.0, 10.0), (2, 200.0, 300.0)]
|
|
66
|
+
|
|
67
|
+
# Nearest neighbor
|
|
68
|
+
best = qt.nearest_neighbor((210, 310)) # -> (id, x, y) or None
|
|
69
|
+
print(best)
|
|
70
|
+
|
|
71
|
+
# k-nearest neighbors
|
|
72
|
+
top3 = qt.nearest_neighbors((210, 310), 3)
|
|
73
|
+
print(top3) # list of up to 3 (id, x, y) tuples
|
|
74
|
+
|
|
75
|
+
# Delete items by ID and location
|
|
76
|
+
deleted = qt.delete(id2, (200, 300)) # True if found and deleted
|
|
77
|
+
print(f"Deleted: {deleted}")
|
|
78
|
+
print(f"Remaining items: {qt.count_items()}")
|
|
79
|
+
|
|
80
|
+
# For object tracking with track_objects=True
|
|
81
|
+
qt_tracked = QuadTree((0, 0, 1000, 1000), capacity=4, track_objects=True)
|
|
82
|
+
player1 = {"name": "Alice", "score": 100}
|
|
83
|
+
player2 = {"name": "Bob", "score": 200}
|
|
84
|
+
|
|
85
|
+
id1 = qt_tracked.insert((50, 50), obj=player1)
|
|
86
|
+
id2 = qt_tracked.insert((150, 150), obj=player2)
|
|
87
|
+
|
|
88
|
+
# Delete by object reference (O(1) lookup!)
|
|
89
|
+
deleted = qt_tracked.delete_by_object(player1, (50, 50))
|
|
90
|
+
print(f"Deleted player: {deleted}") # True
|
|
91
|
+
```
|
|
92
|
+
|
|
93
|
+
### Working with Python objects
|
|
94
|
+
|
|
95
|
+
You can keep the tree pure and manage your own id → object map, or let the wrapper manage it.
|
|
96
|
+
|
|
97
|
+
**Option A: Manage your own map**
|
|
98
|
+
|
|
99
|
+
```python
|
|
100
|
+
from fastquadtree import QuadTree
|
|
101
|
+
|
|
102
|
+
qt = QuadTree((0, 0, 1000, 1000), capacity=16)
|
|
103
|
+
objects: dict[int, object] = {}
|
|
104
|
+
|
|
105
|
+
def add(obj) -> int:
|
|
106
|
+
obj_id = qt.insert(obj.position) # auto id
|
|
107
|
+
objects[obj_id] = obj
|
|
108
|
+
return obj_id
|
|
109
|
+
|
|
110
|
+
# Later, resolve ids back to objects
|
|
111
|
+
ids = [obj_id for (obj_id, x, y) in qt.query((100, 100, 300, 300))]
|
|
112
|
+
selected = [objects[i] for i in ids]
|
|
113
|
+
```
|
|
114
|
+
|
|
115
|
+
**Option B: Ask the wrapper to track objects**
|
|
116
|
+
|
|
117
|
+
```python
|
|
118
|
+
from fastquadtree import QuadTree
|
|
119
|
+
|
|
120
|
+
qt = QuadTree((0, 0, 1000, 1000), capacity=16, track_objects=True)
|
|
121
|
+
|
|
122
|
+
# Store the object alongside the point
|
|
123
|
+
qt.insert((25, 40), obj={"name": "apple"})
|
|
124
|
+
|
|
125
|
+
# Ask for Item objects so you can access .obj lazily
|
|
126
|
+
items = qt.query((0, 0, 100, 100), as_items=True)
|
|
127
|
+
for it in items:
|
|
128
|
+
print(it.id, it.x, it.y, it.obj)
|
|
129
|
+
```
|
|
130
|
+
|
|
131
|
+
You can also attach or replace an object later:
|
|
132
|
+
|
|
133
|
+
```python
|
|
134
|
+
qt.attach(123, my_object) # binds object to id 123
|
|
135
|
+
```
|
|
136
|
+
|
|
137
|
+
## API
|
|
138
|
+
|
|
139
|
+
### `QuadTree(bounds, capacity, *, max_depth=None, track_objects=False, start_id=1)`
|
|
140
|
+
|
|
141
|
+
* `bounds` — tuple `(min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y)` defines the 2D area covered by the quadtree
|
|
142
|
+
* `capacity` — max number of points kept in a leaf before splitting
|
|
143
|
+
* `max_depth` — optional depth cap. If omitted, the tree can keep splitting as needed
|
|
144
|
+
* `track_objects` — if `True`, the wrapper maintains an id → object map for convenience.
|
|
145
|
+
* `start_id` — starting value for auto-assigned ids
|
|
146
|
+
|
|
147
|
+
### Core Methods
|
|
148
|
+
|
|
149
|
+
Full docs are in the docstrings of the [Python Shim](pysrc/fastquadtree/__init__.py)
|
|
150
|
+
|
|
151
|
+
- `insert(xy, *, id=None, obj=None) -> int`
|
|
152
|
+
|
|
153
|
+
- `insert_many_points(points) -> int`
|
|
154
|
+
|
|
155
|
+
- `query(rect, *, as_items=False) -> list`
|
|
156
|
+
|
|
157
|
+
- `nearest_neighbor(xy, *, as_item=False) -> (id, x, y) | Item | None`
|
|
158
|
+
|
|
159
|
+
- `nearest_neighbors(xy, k, *, as_items=False) -> list`
|
|
160
|
+
|
|
161
|
+
- `delete(id, xy) -> bool`
|
|
162
|
+
|
|
163
|
+
- `delete_by_object(obj) -> bool (requires track_objects=True)`
|
|
164
|
+
|
|
165
|
+
- `attach(id, obj) -> None (requires track_objects=True)`
|
|
166
|
+
|
|
167
|
+
- `count_items() -> int`
|
|
168
|
+
|
|
169
|
+
- `get(id) -> object | None`
|
|
170
|
+
|
|
171
|
+
- `get_all_rectangles() -> list[tuple] (for visualization)`
|
|
172
|
+
|
|
173
|
+
### `Item` (returned when `as_items=True`)
|
|
174
|
+
|
|
175
|
+
* Attributes: `id`, `x`, `y`, and a lazy `obj` property
|
|
176
|
+
* Accessing `obj` performs a dictionary lookup only if tracking is enabled
|
|
177
|
+
|
|
178
|
+
### Geometric conventions
|
|
179
|
+
|
|
180
|
+
* Rectangles are `(min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y)`.
|
|
181
|
+
* Containment rule is closed on the min edge and open on the max edge
|
|
182
|
+
`(x >= min_x and x < max_x and y >= min_y and y < max_y)`.
|
|
183
|
+
This only matters for points exactly on edges.
|
|
184
|
+
|
|
185
|
+
## Performance tips
|
|
186
|
+
|
|
187
|
+
* Choose `capacity` so that leaves keep a small batch of points. Typical values are 8 to 64.
|
|
188
|
+
* If your data is very skewed, set a `max_depth` to prevent long chains.
|
|
189
|
+
* For fastest local runs, use `maturin develop --release`.
|
|
190
|
+
* The wrapper keeps Python overhead low: raw tuple results by default, `Item` wrappers only when requested.
|
|
191
|
+
|
|
192
|
+
## Benchmarks
|
|
193
|
+
|
|
194
|
+
fastquadtree outperforms all other quadtree python packages (at least all the ones I could find and install via pip.)
|
|
195
|
+
|
|
196
|
+
### Library comparison
|
|
197
|
+
|
|
198
|
+
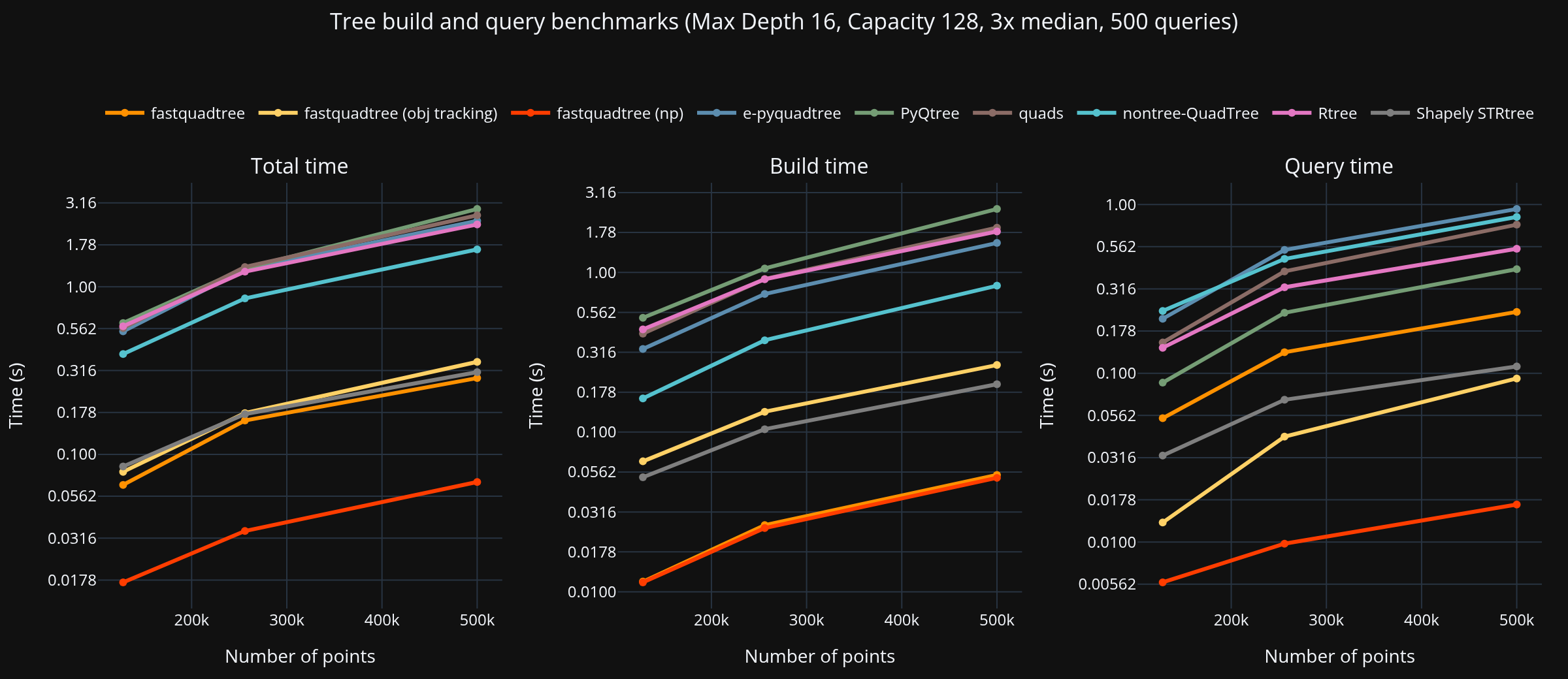
|
|
199
|
+
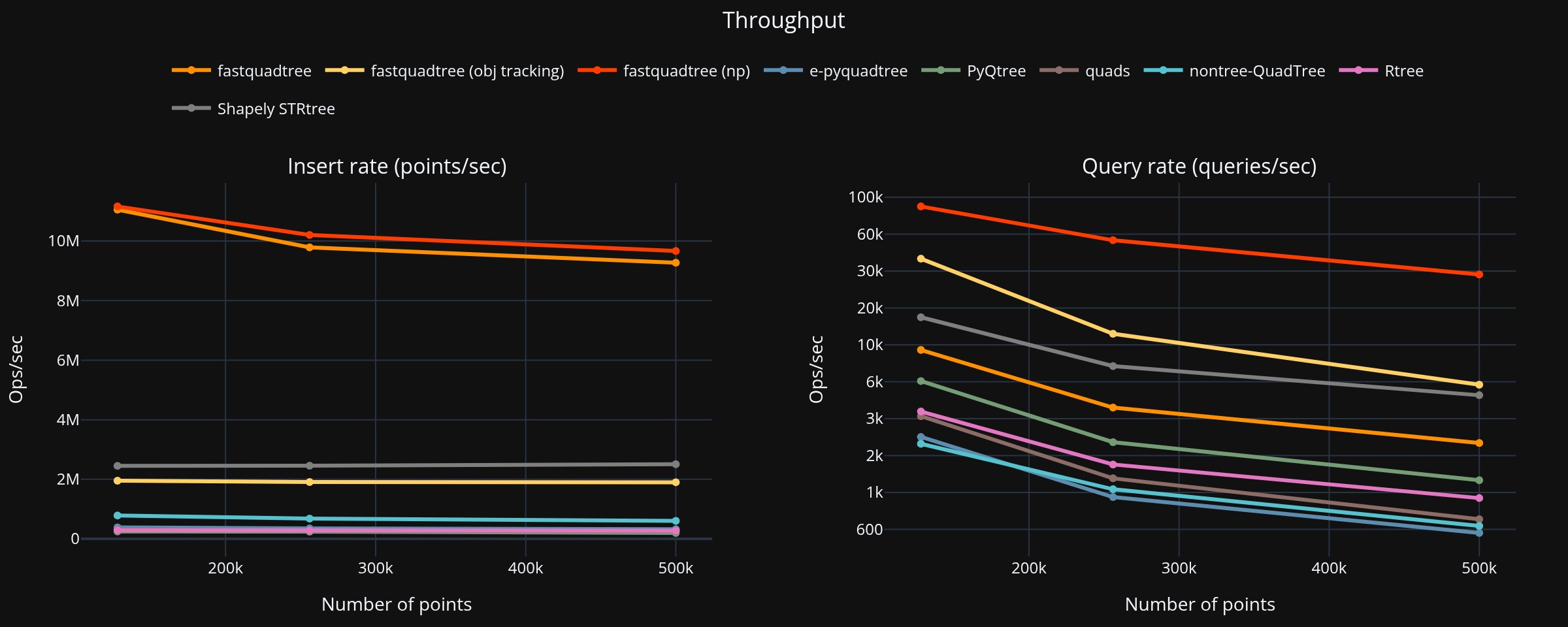
|
|
200
|
+
|
|
201
|
+
### Summary (largest dataset, PyQtree baseline)
|
|
202
|
+
- Points: **500,000**, Queries: **500**
|
|
203
|
+
- Fastest total: **fastquadtree** at **2.207 s**
|
|
204
|
+
|
|
205
|
+
| Library | Build (s) | Query (s) | Total (s) | Speed vs PyQtree |
|
|
206
|
+
|---|---:|---:|---:|---:|
|
|
207
|
+
| fastquadtree | 0.321 | 1.885 | 2.207 | 4.27× |
|
|
208
|
+
| Rtree | 1.718 | 4.376 | 6.095 | 1.55× |
|
|
209
|
+
| nontree-QuadTree | 1.617 | 7.643 | 9.260 | 1.02× |
|
|
210
|
+
| PyQtree | 4.349 | 5.082 | 9.431 | 1.00× |
|
|
211
|
+
| quads | 3.874 | 9.058 | 12.932 | 0.73× |
|
|
212
|
+
| e-pyquadtree | 2.732 | 10.598 | 13.330 | 0.71× |
|
|
213
|
+
| Brute force | 0.019 | 19.986 | 20.005 | 0.47× |
|
|
214
|
+
|
|
215
|
+
### Native vs Shim
|
|
216
|
+
|
|
217
|
+
**Setup**
|
|
218
|
+
- Points: 500,000
|
|
219
|
+
- Queries: 500
|
|
220
|
+
- Repeats: 5
|
|
221
|
+
|
|
222
|
+
**Timing (seconds)**
|
|
223
|
+
|
|
224
|
+
| Variant | Build | Query | Total |
|
|
225
|
+
|---|---:|---:|---:|
|
|
226
|
+
| Native | 0.483 | 4.380 | 4.863 |
|
|
227
|
+
| Shim (no map) | 0.668 | 4.167 | 4.835 |
|
|
228
|
+
| Shim (track+objs) | 1.153 | 4.458 | 5.610 |
|
|
229
|
+
|
|
230
|
+
**Overhead vs Native**
|
|
231
|
+
|
|
232
|
+
- No map: build 1.38x, query 0.95x, total 0.99x
|
|
233
|
+
- Track + objs: build 2.39x, query 1.02x, total 1.15x
|
|
234
|
+
|
|
235
|
+
### Run benchmarks
|
|
236
|
+
To run the benchmarks yourself, first install the dependencies:
|
|
237
|
+
|
|
238
|
+
```bash
|
|
239
|
+
pip install -r benchmarks/requirements.txt
|
|
240
|
+
```
|
|
241
|
+
|
|
242
|
+
Then run:
|
|
243
|
+
|
|
244
|
+
```bash
|
|
245
|
+
python benchmarks/cross_library_bench.py
|
|
246
|
+
python benchmarks/benchmark_native_vs_shim.py
|
|
247
|
+
```
|
|
248
|
+
|
|
249
|
+
## Run Visualizer
|
|
250
|
+
A visualizer is included to help you understand how the quadtree subdivides space.
|
|
251
|
+
|
|
252
|
+
```bash
|
|
253
|
+
pip install -r interactive/requirements.txt
|
|
254
|
+
python interactive/interactive_v2.py
|
|
255
|
+
```
|
|
256
|
+
|
|
257
|
+
Check the CLI arguments for the cross-library benchmark in `benchmarks/quadtree_bench/main.py`.
|
|
258
|
+
|
|
259
|
+
## FAQ
|
|
260
|
+
|
|
261
|
+
**What happens if I insert the same id more than once?**
|
|
262
|
+
Allowed. For k-nearest, duplicates are de-duplicated by id. For range queries you will see every inserted point.
|
|
263
|
+
|
|
264
|
+
**Can I delete items from the quadtree?**
|
|
265
|
+
Yes! Use `delete(id, xy)` to remove specific items. You must provide both the ID and exact location for precise deletion. This handles cases where multiple items exist at the same location. If you're using `track_objects=True`, you can also use `delete_by_object(obj, xy)` for convenient object-based deletion with O(1) lookup. The tree automatically merges nodes when item counts drop below capacity.
|
|
266
|
+
|
|
267
|
+
**Can I store rectangles or circles?**
|
|
268
|
+
The core stores points. To index objects with extent, insert whatever representative point you choose. For rectangles you can insert centers or build an AABB tree separately.
|
|
269
|
+
|
|
270
|
+
**Threading**
|
|
271
|
+
Use one tree per thread if you need heavy parallel inserts from Python.
|
|
272
|
+
|
|
273
|
+
## License
|
|
274
|
+
|
|
275
|
+
MIT. See `LICENSE`.
|
|
276
|
+
|
|
277
|
+
## Acknowledgments
|
|
278
|
+
|
|
279
|
+
* Python libraries compared: [PyQtree], [e-pyquadtree], [Rtree], [nontree], [quads]
|
|
280
|
+
* Built with [PyO3] and [maturin]
|
|
281
|
+
|
|
282
|
+
[PyQtree]: https://pypi.org/project/pyqtree/
|
|
283
|
+
[e-pyquadtree]: https://pypi.org/project/e-pyquadtree/
|
|
284
|
+
[PyO3]: https://pyo3.rs/
|
|
285
|
+
[maturin]: https://www.maturin.rs/
|
|
286
|
+
[Rtree]: https://pypi.org/project/Rtree/
|
|
287
|
+
[nontree]: https://pypi.org/project/nontree/
|
|
288
|
+
[quads]: https://pypi.org/project/quads/
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
fastquadtree-0.4.0.dist-info/METADATA,sha256=3t-XheiR-GXWFVWY0zHsbmZCqmxP9RgzQ2a8MHh4gD8,9331
|
|
2
|
+
fastquadtree-0.4.0.dist-info/WHEEL,sha256=2A3mFKbbStZmBBWlvTTYUEM089PovEhjpJwyy5qmAeE,146
|
|
3
|
+
fastquadtree-0.4.0.dist-info/licenses/LICENSE,sha256=pRuvcuqIMtEUBMgvP1Bc4fOHydzeuA61c6DQoQ1pb1w,1071
|
|
4
|
+
fastquadtree/__init__.py,sha256=fAHXmWTWeZFEPE2WSWhL1Hyt0QCaCZt84AXNdyLWwY0,12264
|
|
5
|
+
fastquadtree/__init__.pyi,sha256=rNR03KUZxjWKz0ZezzatYHdhQX85EBFOAVH-qoHKhws,2099
|
|
6
|
+
fastquadtree/_bimap.py,sha256=xQ1Y91sWQcI0OL_uNwEP41WLKVlDqKYmYI3Vnj_Jdss,3415
|
|
7
|
+
fastquadtree/_item.py,sha256=Sk3oFVOOx0o83mJVHhAaN7WJzAvIy3SEGPtOeOYiCWo,503
|
|
8
|
+
fastquadtree/_native.abi3.so,sha256=BTXQEO5qaMpi5Zj44tN1WOOICLjXOXshggZbGkP4tso,915328
|
|
9
|
+
fastquadtree/py.typed,sha256=47DEQpj8HBSa-_TImW-5JCeuQeRkm5NMpJWZG3hSuFU,0
|
|
10
|
+
fastquadtree-0.4.0.dist-info/RECORD,,
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
MIT License
|
|
2
|
+
|
|
3
|
+
Copyright (c) 2025 Ethan Anderson
|
|
4
|
+
|
|
5
|
+
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
|
6
|
+
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
|
7
|
+
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
|
8
|
+
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
|
9
|
+
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
|
10
|
+
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
|
11
|
+
|
|
12
|
+
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
|
13
|
+
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
|
14
|
+
|
|
15
|
+
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
|
16
|
+
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
|
17
|
+
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
|
18
|
+
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
|
19
|
+
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
|
20
|
+
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
|
|
21
|
+
SOFTWARE.
|