@op-engineering/op-sqlite 1.0.0
This diff represents the content of publicly available package versions that have been released to one of the supported registries. The information contained in this diff is provided for informational purposes only and reflects changes between package versions as they appear in their respective public registries.
- package/LICENSE +7 -0
- package/README.md +274 -0
- package/android/.project +17 -0
- package/android/.settings/org.eclipse.buildship.core.prefs +13 -0
- package/android/CMakeLists.txt +57 -0
- package/android/build.gradle +127 -0
- package/android/cpp-adapter.cpp +42 -0
- package/android/gradle.properties +4 -0
- package/android/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml +4 -0
- package/android/src/main/java/com/op/sqlite/OPSQLiteBridge.java +29 -0
- package/android/src/main/java/com/op/sqlite/OPSQLiteModule.java +46 -0
- package/android/src/main/java/com/op/sqlite/OPSQLitePackage.java +26 -0
- package/cpp/DynamicHostObject.cpp +30 -0
- package/cpp/DynamicHostObject.h +30 -0
- package/cpp/ThreadPool.cpp +95 -0
- package/cpp/ThreadPool.h +46 -0
- package/cpp/bindings.cpp +430 -0
- package/cpp/bindings.h +13 -0
- package/cpp/bridge.cpp +502 -0
- package/cpp/bridge.h +34 -0
- package/cpp/logs.h +38 -0
- package/cpp/macros.h +16 -0
- package/cpp/sqlbatchexecutor.cpp +94 -0
- package/cpp/sqlbatchexecutor.h +28 -0
- package/cpp/sqlite3.c +252611 -0
- package/cpp/sqlite3.h +13257 -0
- package/cpp/utils.cpp +218 -0
- package/cpp/utils.h +55 -0
- package/ios/OPSQLite.h +8 -0
- package/ios/OPSQLite.mm +63 -0
- package/ios/OPSQLite.xcodeproj/project.pbxproj +275 -0
- package/lib/commonjs/index.js +190 -0
- package/lib/commonjs/index.js.map +1 -0
- package/lib/module/index.js +183 -0
- package/lib/module/index.js.map +1 -0
- package/lib/typescript/index.d.ts +108 -0
- package/op-sqlite.podspec +39 -0
- package/package.json +79 -0
- package/src/index.ts +374 -0
package/LICENSE
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
Copyright 2021 Oscar Franco
|
|
2
|
+
|
|
3
|
+
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
|
4
|
+
|
|
5
|
+
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
|
6
|
+
|
|
7
|
+
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
|
package/README.md
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,274 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+

|
|
2
|
+
|
|
3
|
+
<div align="center">
|
|
4
|
+
<pre align="center">
|
|
5
|
+
yarn add @op-engineering/op-sqlite
|
|
6
|
+
npx pod-install</pre>
|
|
7
|
+
<br />
|
|
8
|
+
</div>
|
|
9
|
+
<br />
|
|
10
|
+
|
|
11
|
+
OP SQLite embeds the latest version of SQLite and provides a low-level (JSI-backed) API to execute SQL queries.
|
|
12
|
+
|
|
13
|
+
**Current SQLite version: 3.44.0**
|
|
14
|
+
|
|
15
|
+
Created by [@ospfranco](https://twitter.com/ospfranco). Also created `react-native-quick-sqlite`, this is the next version. You can expect a new version once Static Hermes is out.
|
|
16
|
+
|
|
17
|
+
**Please consider Sponsoring**, none of this work is for free. I pay for it with my time and knowledge. If you are a company in need of help with your React Native/React apps feel free to reach out. I also do a lot of C++ and nowadays Rust.
|
|
18
|
+
|
|
19
|
+
## Known issues
|
|
20
|
+
|
|
21
|
+
[ArrayBuffer support is commented out right now](https://github.com/OP-Engineering/op-sqlite/blob/main/cpp/bridge.cpp#L247). I will get to it in the next days or feel free to submit a PR.
|
|
22
|
+
|
|
23
|
+
## Benchmarks
|
|
24
|
+
|
|
25
|
+
You can find the [benchmarking code in the example app](https://github.com/OP-Engineering/op-sqlite/blob/main/example/src/Database.ts#L44). Loading a 300k record database:
|
|
26
|
+
|
|
27
|
+
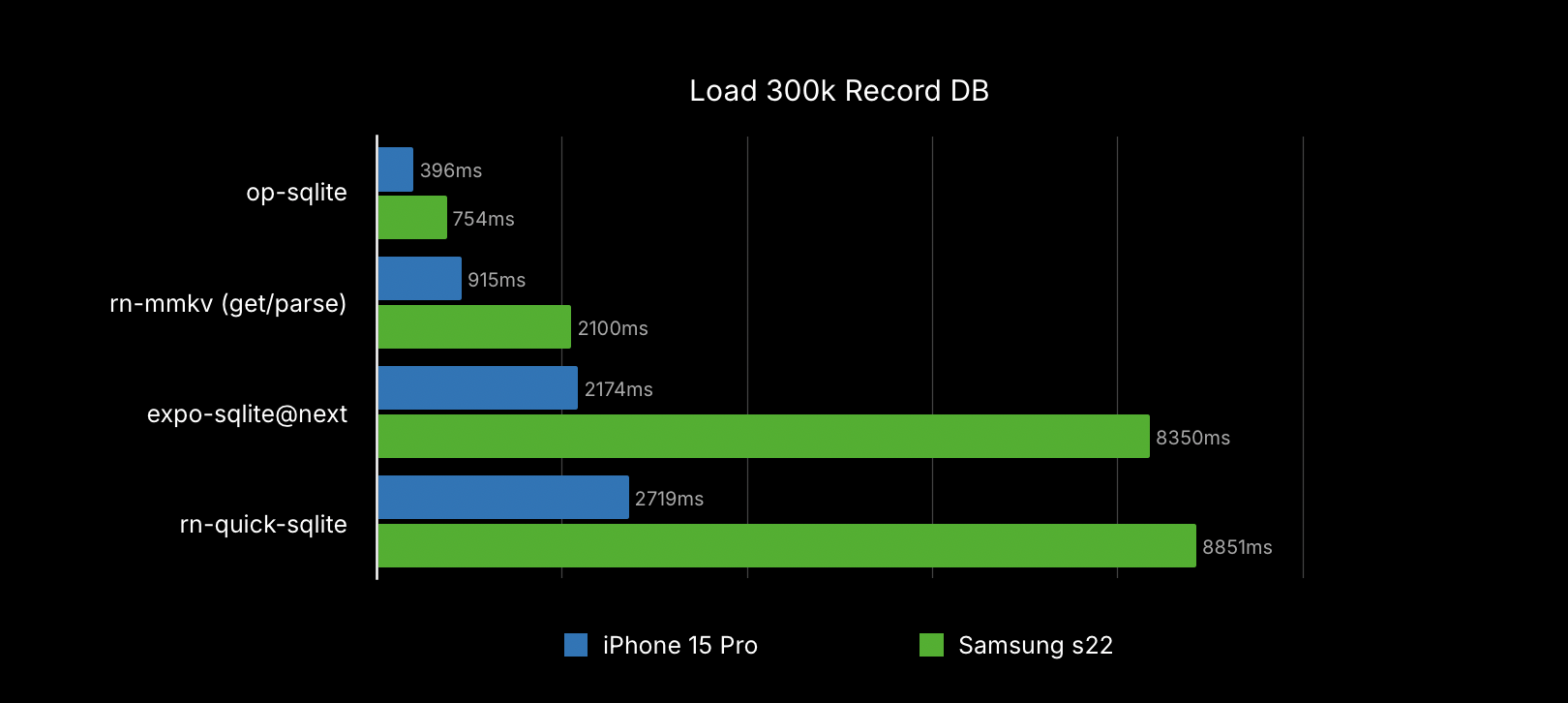
|
|
28
|
+
|
|
29
|
+
# DB Paths
|
|
30
|
+
|
|
31
|
+
The library creates/opens databases by appending the passed name plus, the [library directory on iOS](https://github.com/OP-Engineering/op-sqlite/blob/main/ios/OPSQLite.mm#L51) and the [database directory on Android](https://github.com/OP-Engineering/op-sqlite/blob/main/android/src/main/java/com/op/sqlite/OPSQLiteBridge.java#L18). If you are migrating from `react-native-quick-sqlite` you will have to move your library using one of the many react-native fs libraries.
|
|
32
|
+
|
|
33
|
+
If you have an existing database file you want to load you can navigate from these directories using dot notation. e.g.:
|
|
34
|
+
|
|
35
|
+
```ts
|
|
36
|
+
const largeDb = open({
|
|
37
|
+
name: 'largeDB',
|
|
38
|
+
location: '../files/databases',
|
|
39
|
+
});
|
|
40
|
+
```
|
|
41
|
+
|
|
42
|
+
Note that on iOS the file system is sand-boxed, so you cannot access files/directories outside your app bundle directories.
|
|
43
|
+
|
|
44
|
+
## API
|
|
45
|
+
|
|
46
|
+
```typescript
|
|
47
|
+
import {open} from '@op-engineering/op-sqlite'
|
|
48
|
+
|
|
49
|
+
const db = open('myDb.sqlite')
|
|
50
|
+
|
|
51
|
+
// The db object contains the following methods:
|
|
52
|
+
db = {
|
|
53
|
+
close: () => void,
|
|
54
|
+
delete: () => void,
|
|
55
|
+
attach: (dbNameToAttach: string, alias: string, location?: string) => void,
|
|
56
|
+
detach: (alias: string) => void,
|
|
57
|
+
transaction: (fn: (tx: Transaction) => void) => Promise<void>,
|
|
58
|
+
execute: (query: string, params?: any[]) => QueryResult,
|
|
59
|
+
executeAsync: (
|
|
60
|
+
query: string,
|
|
61
|
+
params?: any[]
|
|
62
|
+
) => Promise<QueryResult>,
|
|
63
|
+
executeBatch: (commands: SQLBatchParams[]) => BatchQueryResult,
|
|
64
|
+
executeBatchAsync: (commands: SQLBatchParams[]) => Promise<BatchQueryResult>,
|
|
65
|
+
loadFile: (location: string) => Promise<FileLoadResult>
|
|
66
|
+
}
|
|
67
|
+
```
|
|
68
|
+
|
|
69
|
+
### Simple queries
|
|
70
|
+
|
|
71
|
+
The basic query is **synchronous**, it will block rendering on large operations, further below you will find async versions.
|
|
72
|
+
|
|
73
|
+
```typescript
|
|
74
|
+
import { open } from '@op-engineering/op-sqlite';
|
|
75
|
+
|
|
76
|
+
try {
|
|
77
|
+
const db = open('myDb.sqlite');
|
|
78
|
+
|
|
79
|
+
let { rows } = db.execute('SELECT somevalue FROM sometable');
|
|
80
|
+
|
|
81
|
+
rows.forEach((row) => {
|
|
82
|
+
console.log(row);
|
|
83
|
+
});
|
|
84
|
+
|
|
85
|
+
let { rowsAffected } = await db.executeAsync(
|
|
86
|
+
'UPDATE sometable SET somecolumn = ? where somekey = ?',
|
|
87
|
+
[0, 1]
|
|
88
|
+
);
|
|
89
|
+
|
|
90
|
+
console.log(`Update affected ${rowsAffected} rows`);
|
|
91
|
+
} catch (e) {
|
|
92
|
+
console.error('Something went wrong executing SQL commands:', e.message);
|
|
93
|
+
}
|
|
94
|
+
```
|
|
95
|
+
|
|
96
|
+
### Transactions
|
|
97
|
+
|
|
98
|
+
Throwing an error inside the callback will ROLLBACK the transaction.
|
|
99
|
+
|
|
100
|
+
If you want to execute a large set of commands as fast as possible you should use the `executeBatch` method, it wraps all the commands in a transaction and has less overhead.
|
|
101
|
+
|
|
102
|
+
```typescript
|
|
103
|
+
await db.transaction('myDatabase', (tx) => {
|
|
104
|
+
const { status } = tx.execute(
|
|
105
|
+
'UPDATE sometable SET somecolumn = ? where somekey = ?',
|
|
106
|
+
[0, 1]
|
|
107
|
+
);
|
|
108
|
+
|
|
109
|
+
// offload from JS thread
|
|
110
|
+
await tx.executeAsync = tx.executeAsync(
|
|
111
|
+
'UPDATE sometable SET somecolumn = ? where somekey = ?',
|
|
112
|
+
[0, 1]
|
|
113
|
+
);
|
|
114
|
+
|
|
115
|
+
// Any uncatched error ROLLBACK transaction
|
|
116
|
+
throw new Error('Random Error!');
|
|
117
|
+
|
|
118
|
+
// You can manually commit or rollback
|
|
119
|
+
tx.commit();
|
|
120
|
+
// or
|
|
121
|
+
tx.rollback();
|
|
122
|
+
});
|
|
123
|
+
```
|
|
124
|
+
|
|
125
|
+
### Batch operation
|
|
126
|
+
|
|
127
|
+
Batch execution allows the transactional execution of a set of commands
|
|
128
|
+
|
|
129
|
+
```typescript
|
|
130
|
+
const commands = [
|
|
131
|
+
['CREATE TABLE TEST (id integer)'],
|
|
132
|
+
['INSERT INTO TEST (id) VALUES (?)', [1]],
|
|
133
|
+
[('INSERT INTO TEST (id) VALUES (?)', [2])],
|
|
134
|
+
[('INSERT INTO TEST (id) VALUES (?)', [[3], [4], [5], [6]])],
|
|
135
|
+
];
|
|
136
|
+
|
|
137
|
+
const res = db.executeSqlBatch('myDatabase', commands);
|
|
138
|
+
|
|
139
|
+
console.log(`Batch affected ${result.rowsAffected} rows`);
|
|
140
|
+
```
|
|
141
|
+
|
|
142
|
+
### Dynamic Column Metadata
|
|
143
|
+
|
|
144
|
+
In some scenarios, dynamic applications may need to get some metadata information about the returned result set.
|
|
145
|
+
|
|
146
|
+
This can be done by testing the returned data directly, but in some cases may not be enough, for example when data is stored outside
|
|
147
|
+
SQLite datatypes. When fetching data directly from tables or views linked to table columns, SQLite can identify the table declared types:
|
|
148
|
+
|
|
149
|
+
```typescript
|
|
150
|
+
let { metadata } = db.executeSql(
|
|
151
|
+
'myDatabase',
|
|
152
|
+
'SELECT int_column_1, bol_column_2 FROM sometable'
|
|
153
|
+
);
|
|
154
|
+
|
|
155
|
+
metadata.forEach((column) => {
|
|
156
|
+
// Output:
|
|
157
|
+
// int_column_1 - INTEGER
|
|
158
|
+
// bol_column_2 - BOOLEAN
|
|
159
|
+
console.log(`${column.name} - ${column.type}`);
|
|
160
|
+
});
|
|
161
|
+
```
|
|
162
|
+
|
|
163
|
+
### Async operations
|
|
164
|
+
|
|
165
|
+
You might have too much SQL to process and it will cause your application to freeze. There are async versions for some of the operations. This will offload the SQLite processing to a different thread.
|
|
166
|
+
|
|
167
|
+
```ts
|
|
168
|
+
db.executeAsync(
|
|
169
|
+
'myDatabase',
|
|
170
|
+
'SELECT * FROM "User";',
|
|
171
|
+
[]).then(({rows}) => {
|
|
172
|
+
console.log('users', rows);
|
|
173
|
+
})
|
|
174
|
+
);
|
|
175
|
+
```
|
|
176
|
+
|
|
177
|
+
### Attach or Detach other databases
|
|
178
|
+
|
|
179
|
+
SQLite supports attaching or detaching other database files into your main database connection through an alias.
|
|
180
|
+
You can do any operation you like on this attached database like JOIN results across tables in different schemas, or update data or objects.
|
|
181
|
+
These databases can have different configurations, like journal modes, and cache settings.
|
|
182
|
+
|
|
183
|
+
You can, at any moment, detach a database that you don't need anymore. You don't need to detach an attached database before closing your connection. Closing the main connection will detach any attached databases.
|
|
184
|
+
|
|
185
|
+
SQLite has a limit for attached databases: A default of 10, and a global max of 125
|
|
186
|
+
|
|
187
|
+
References: [Attach](https://www.sqlite.org/lang_attach.html) - [Detach](https://www.sqlite.org/lang_detach.html)
|
|
188
|
+
|
|
189
|
+
```ts
|
|
190
|
+
db.attach('mainDatabase', 'statistics', 'stats', '../databases');
|
|
191
|
+
|
|
192
|
+
const res = db.executeSql(
|
|
193
|
+
'mainDatabase',
|
|
194
|
+
'SELECT * FROM some_table_from_mainschema a INNER JOIN stats.some_table b on a.id_column = b.id_column'
|
|
195
|
+
);
|
|
196
|
+
|
|
197
|
+
// You can detach databases at any moment
|
|
198
|
+
db.detach('mainDatabase', 'stats');
|
|
199
|
+
if (!detachResult.status) {
|
|
200
|
+
// Database de-attached
|
|
201
|
+
}
|
|
202
|
+
```
|
|
203
|
+
|
|
204
|
+
### Loading SQL Dump Files
|
|
205
|
+
|
|
206
|
+
If you have a plain SQL file, you can load it directly, with low memory consumption.
|
|
207
|
+
|
|
208
|
+
```typescript
|
|
209
|
+
const { rowsAffected, commands } = db.loadFile(
|
|
210
|
+
'myDatabase',
|
|
211
|
+
'/absolute/path/to/file.sql'
|
|
212
|
+
);
|
|
213
|
+
```
|
|
214
|
+
|
|
215
|
+
Or use the async version which will load the file in another native thread
|
|
216
|
+
|
|
217
|
+
```typescript
|
|
218
|
+
db.loadFileAsync('myDatabase', '/absolute/path/to/file.sql').then((res) => {
|
|
219
|
+
const { rowsAffected, commands } = res;
|
|
220
|
+
});
|
|
221
|
+
```
|
|
222
|
+
|
|
223
|
+
## Use built-in SQLite
|
|
224
|
+
|
|
225
|
+
On iOS you can use the embedded SQLite, when running `pod-install` add an environment flag:
|
|
226
|
+
|
|
227
|
+
```
|
|
228
|
+
OP_SQLITE_USE_PHONE_VERSION=1 npx pod-install
|
|
229
|
+
```
|
|
230
|
+
|
|
231
|
+
On Android, it is not possible to link the OS SQLite. It is also a bad idea due to vendor changes, old android bugs, etc. Unfortunately, this means this library will add some megabytes to your app size.
|
|
232
|
+
|
|
233
|
+
## Enable compile-time options
|
|
234
|
+
|
|
235
|
+
By specifying pre-processor flags, you can enable optional features like FTS5, Geopoly, etc.
|
|
236
|
+
|
|
237
|
+
### iOS
|
|
238
|
+
|
|
239
|
+
Add a `post_install` block to your `<PROJECT_ROOT>/ios/Podfile` like so:
|
|
240
|
+
|
|
241
|
+
```ruby
|
|
242
|
+
post_install do |installer|
|
|
243
|
+
installer.pods_project.targets.each do |target|
|
|
244
|
+
if target.name == "op-sqlite" then
|
|
245
|
+
target.build_configurations.each do |config|
|
|
246
|
+
config.build_settings['GCC_PREPROCESSOR_DEFINITIONS'] << 'SQLITE_ENABLE_FTS5=1'
|
|
247
|
+
end
|
|
248
|
+
end
|
|
249
|
+
end
|
|
250
|
+
end
|
|
251
|
+
```
|
|
252
|
+
|
|
253
|
+
Replace the `<SQLITE_FLAGS>` part with the flags you want to add.
|
|
254
|
+
For example, you could add `SQLITE_ENABLE_FTS5=1` to `GCC_PREPROCESSOR_DEFINITIONS` to enable FTS5 in the iOS project.
|
|
255
|
+
|
|
256
|
+
### Android
|
|
257
|
+
|
|
258
|
+
You can specify flags via `<PROJECT_ROOT>/android/gradle.properties` like so:
|
|
259
|
+
|
|
260
|
+
```
|
|
261
|
+
OPSQLiteFlags="<SQLITE_FLAGS>"
|
|
262
|
+
```
|
|
263
|
+
|
|
264
|
+
## Additional configuration
|
|
265
|
+
|
|
266
|
+
### App groups (iOS only)
|
|
267
|
+
|
|
268
|
+
On iOS, the SQLite database can be placed in an app group, in order to make it accessible from other apps in that app group. E.g. for sharing capabilities.
|
|
269
|
+
|
|
270
|
+
To use an app group, add the app group ID as the value for the `OPSQLite_AppGroup` key in your project's `Info.plist` file. You'll also need to configure the app group in your project settings. (Xcode -> Project Settings -> Signing & Capabilities -> Add Capability -> App Groups)
|
|
271
|
+
|
|
272
|
+
## License
|
|
273
|
+
|
|
274
|
+
MIT License.
|
package/android/.project
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
|
|
2
|
+
<projectDescription>
|
|
3
|
+
<name>android_</name>
|
|
4
|
+
<comment>Project android_ created by Buildship.</comment>
|
|
5
|
+
<projects>
|
|
6
|
+
</projects>
|
|
7
|
+
<buildSpec>
|
|
8
|
+
<buildCommand>
|
|
9
|
+
<name>org.eclipse.buildship.core.gradleprojectbuilder</name>
|
|
10
|
+
<arguments>
|
|
11
|
+
</arguments>
|
|
12
|
+
</buildCommand>
|
|
13
|
+
</buildSpec>
|
|
14
|
+
<natures>
|
|
15
|
+
<nature>org.eclipse.buildship.core.gradleprojectnature</nature>
|
|
16
|
+
</natures>
|
|
17
|
+
</projectDescription>
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
arguments=
|
|
2
|
+
auto.sync=false
|
|
3
|
+
build.scans.enabled=false
|
|
4
|
+
connection.gradle.distribution=GRADLE_DISTRIBUTION(VERSION(6.0))
|
|
5
|
+
connection.project.dir=
|
|
6
|
+
eclipse.preferences.version=1
|
|
7
|
+
gradle.user.home=
|
|
8
|
+
java.home=/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_144.jdk/Contents/Home
|
|
9
|
+
jvm.arguments=
|
|
10
|
+
offline.mode=false
|
|
11
|
+
override.workspace.settings=true
|
|
12
|
+
show.console.view=true
|
|
13
|
+
show.executions.view=true
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
project(OPSQLite)
|
|
2
|
+
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.9.0)
|
|
3
|
+
|
|
4
|
+
set (PACKAGE_NAME "op-sqlite")
|
|
5
|
+
set (CMAKE_VERBOSE_MAKEFILE ON)
|
|
6
|
+
set (CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)
|
|
7
|
+
set (BUILD_DIR ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/build)
|
|
8
|
+
|
|
9
|
+
include_directories(
|
|
10
|
+
../cpp
|
|
11
|
+
)
|
|
12
|
+
|
|
13
|
+
add_definitions(
|
|
14
|
+
${SQLITE_FLAGS}
|
|
15
|
+
)
|
|
16
|
+
|
|
17
|
+
add_library(
|
|
18
|
+
${PACKAGE_NAME}
|
|
19
|
+
SHARED
|
|
20
|
+
../cpp/bridge.cpp
|
|
21
|
+
../cpp/bridge.h
|
|
22
|
+
../cpp/bindings.cpp
|
|
23
|
+
../cpp/bindings.h
|
|
24
|
+
../cpp/sqlite3.h
|
|
25
|
+
../cpp/sqlite3.c
|
|
26
|
+
../cpp/utils.h
|
|
27
|
+
../cpp/utils.cpp
|
|
28
|
+
../cpp/ThreadPool.h
|
|
29
|
+
../cpp/ThreadPool.cpp
|
|
30
|
+
../cpp/sqlbatchexecutor.h
|
|
31
|
+
../cpp/sqlbatchexecutor.cpp
|
|
32
|
+
../cpp/DynamicHostObject.cpp
|
|
33
|
+
../cpp/DynamicHostObject.h
|
|
34
|
+
../cpp/macros.h
|
|
35
|
+
cpp-adapter.cpp
|
|
36
|
+
)
|
|
37
|
+
|
|
38
|
+
set_target_properties(
|
|
39
|
+
${PACKAGE_NAME} PROPERTIES
|
|
40
|
+
CXX_STANDARD 17
|
|
41
|
+
CXX_EXTENSIONS OFF
|
|
42
|
+
POSITION_INDEPENDENT_CODE ON
|
|
43
|
+
)
|
|
44
|
+
|
|
45
|
+
find_package(ReactAndroid REQUIRED CONFIG)
|
|
46
|
+
find_package(fbjni REQUIRED CONFIG)
|
|
47
|
+
find_library(LOG_LIB log)
|
|
48
|
+
|
|
49
|
+
target_link_libraries(
|
|
50
|
+
${PACKAGE_NAME}
|
|
51
|
+
${LOG_LIB}
|
|
52
|
+
fbjni::fbjni
|
|
53
|
+
ReactAndroid::jsi
|
|
54
|
+
ReactAndroid::turbomodulejsijni
|
|
55
|
+
ReactAndroid::react_nativemodule_core
|
|
56
|
+
android
|
|
57
|
+
)
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
import java.nio.file.Paths
|
|
2
|
+
|
|
3
|
+
buildscript {
|
|
4
|
+
repositories {
|
|
5
|
+
maven {
|
|
6
|
+
url "https://plugins.gradle.org/m2/"
|
|
7
|
+
}
|
|
8
|
+
mavenCentral()
|
|
9
|
+
google()
|
|
10
|
+
}
|
|
11
|
+
|
|
12
|
+
dependencies {
|
|
13
|
+
classpath("com.android.tools.build:gradle:7.2.2")
|
|
14
|
+
}
|
|
15
|
+
}
|
|
16
|
+
|
|
17
|
+
def resolveBuildType() {
|
|
18
|
+
Gradle gradle = getGradle()
|
|
19
|
+
String tskReqStr = gradle.getStartParameter().getTaskRequests()['args'].toString()
|
|
20
|
+
|
|
21
|
+
return tskReqStr.contains('Release') ? 'release' : 'debug'
|
|
22
|
+
}
|
|
23
|
+
|
|
24
|
+
def isNewArchitectureEnabled() {
|
|
25
|
+
// - Set `newArchEnabled` to true inside the `gradle.properties` file
|
|
26
|
+
return project.hasProperty("newArchEnabled") && project.newArchEnabled == "true"
|
|
27
|
+
}
|
|
28
|
+
|
|
29
|
+
def SQLITE_FLAGS = rootProject.properties['OPSQLiteFlags']
|
|
30
|
+
|
|
31
|
+
apply plugin: 'com.android.library'
|
|
32
|
+
|
|
33
|
+
def safeExtGet(prop, fallback) {
|
|
34
|
+
rootProject.ext.has(prop) ? rootProject.ext.get(prop) : fallback
|
|
35
|
+
}
|
|
36
|
+
|
|
37
|
+
def reactNativeArchitectures() {
|
|
38
|
+
def value = project.getProperties().get("reactNativeArchitectures")
|
|
39
|
+
return value ? value.split(",") : ["armeabi-v7a", "x86", "x86_64", "arm64-v8a"]
|
|
40
|
+
}
|
|
41
|
+
|
|
42
|
+
def USE_HERMES = rootProject.ext.hermesEnabled
|
|
43
|
+
|
|
44
|
+
repositories {
|
|
45
|
+
mavenCentral()
|
|
46
|
+
}
|
|
47
|
+
|
|
48
|
+
android {
|
|
49
|
+
|
|
50
|
+
compileSdkVersion safeExtGet("compileSdkVersion", 28)
|
|
51
|
+
|
|
52
|
+
// Used to override the NDK path/version on internal CI or by allowing
|
|
53
|
+
// users to customize the NDK path/version from their root project (e.g. for M1 support)
|
|
54
|
+
if (rootProject.hasProperty("ndkPath")) {
|
|
55
|
+
ndkPath rootProject.ext.ndkPath
|
|
56
|
+
}
|
|
57
|
+
if (rootProject.hasProperty("ndkVersion")) {
|
|
58
|
+
ndkVersion rootProject.ext.ndkVersion
|
|
59
|
+
}
|
|
60
|
+
|
|
61
|
+
buildFeatures {
|
|
62
|
+
prefab true
|
|
63
|
+
}
|
|
64
|
+
|
|
65
|
+
defaultConfig {
|
|
66
|
+
minSdkVersion 21
|
|
67
|
+
targetSdkVersion safeExtGet('targetSdkVersion', 28)
|
|
68
|
+
versionCode 1
|
|
69
|
+
versionName "1.0"
|
|
70
|
+
|
|
71
|
+
externalNativeBuild {
|
|
72
|
+
cmake {
|
|
73
|
+
cppFlags "-O2", "-fexceptions", "-frtti", "-std=c++1y", "-DONANDROID"
|
|
74
|
+
abiFilters 'x86', 'x86_64', 'armeabi-v7a', 'arm64-v8a'
|
|
75
|
+
arguments '-DANDROID_STL=c++_shared',
|
|
76
|
+
"-DSQLITE_FLAGS='${SQLITE_FLAGS ? SQLITE_FLAGS : ''}'",
|
|
77
|
+
"-DUSE_HERMES=${USE_HERMES}"
|
|
78
|
+
abiFilters (*reactNativeArchitectures())
|
|
79
|
+
}
|
|
80
|
+
}
|
|
81
|
+
|
|
82
|
+
packagingOptions {
|
|
83
|
+
doNotStrip resolveBuildType() == 'debug' ? "**/**/*.so" : ''
|
|
84
|
+
excludes = [
|
|
85
|
+
"META-INF",
|
|
86
|
+
"META-INF/**",
|
|
87
|
+
"**/libjsi.so",
|
|
88
|
+
"**/libreact_nativemodule_core.so",
|
|
89
|
+
"**/libturbomodulejsijni.so",
|
|
90
|
+
"**/libc++_shared.so",
|
|
91
|
+
"**/libfbjni.so"
|
|
92
|
+
]
|
|
93
|
+
}
|
|
94
|
+
|
|
95
|
+
}
|
|
96
|
+
|
|
97
|
+
compileOptions {
|
|
98
|
+
sourceCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
|
|
99
|
+
targetCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
|
|
100
|
+
}
|
|
101
|
+
|
|
102
|
+
externalNativeBuild {
|
|
103
|
+
cmake {
|
|
104
|
+
path "CMakeLists.txt"
|
|
105
|
+
}
|
|
106
|
+
}
|
|
107
|
+
}
|
|
108
|
+
|
|
109
|
+
dependencies {
|
|
110
|
+
//noinspection GradleDynamicVersion
|
|
111
|
+
implementation 'com.facebook.react:react-android:+'
|
|
112
|
+
}
|
|
113
|
+
|
|
114
|
+
// Resolves "LOCAL_SRC_FILES points to a missing file, Check that libfb.so exists or that its path is correct".
|
|
115
|
+
tasks.whenTaskAdded { task ->
|
|
116
|
+
if (task.name.contains("configureCMakeDebug")) {
|
|
117
|
+
rootProject.getTasksByName("packageReactNdkDebugLibs", true).forEach {
|
|
118
|
+
task.dependsOn(it)
|
|
119
|
+
}
|
|
120
|
+
}
|
|
121
|
+
// We want to add a dependency for both configureCMakeRelease and configureCMakeRelWithDebInfo
|
|
122
|
+
if (task.name.contains("configureCMakeRel")) {
|
|
123
|
+
rootProject.getTasksByName("packageReactNdkReleaseLibs", true).forEach {
|
|
124
|
+
task.dependsOn(it)
|
|
125
|
+
}
|
|
126
|
+
}
|
|
127
|
+
}
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
#include "bindings.h"
|
|
2
|
+
#include "logs.h"
|
|
3
|
+
#include <ReactCommon/CallInvokerHolder.h>
|
|
4
|
+
#include <fbjni/fbjni.h>
|
|
5
|
+
#include <jni.h>
|
|
6
|
+
#include <jsi/jsi.h>
|
|
7
|
+
#include <typeinfo>
|
|
8
|
+
|
|
9
|
+
struct OPSQLiteBridge : jni::JavaClass<OPSQLiteBridge> {
|
|
10
|
+
static constexpr auto kJavaDescriptor =
|
|
11
|
+
"Lcom/op/sqlite/OPSQLiteBridge;";
|
|
12
|
+
|
|
13
|
+
static void registerNatives() {
|
|
14
|
+
javaClassStatic()->registerNatives(
|
|
15
|
+
{// initialization for JSI
|
|
16
|
+
makeNativeMethod("installNativeJsi",
|
|
17
|
+
OPSQLiteBridge::installNativeJsi),
|
|
18
|
+
makeNativeMethod("clearStateNativeJsi",
|
|
19
|
+
OPSQLiteBridge::clearStateNativeJsi)
|
|
20
|
+
});
|
|
21
|
+
}
|
|
22
|
+
|
|
23
|
+
private:
|
|
24
|
+
static void installNativeJsi(
|
|
25
|
+
jni::alias_ref<jni::JObject> thiz, jlong jsiRuntimePtr,
|
|
26
|
+
jni::alias_ref<react::CallInvokerHolder::javaobject> jsCallInvokerHolder,
|
|
27
|
+
jni::alias_ref<jni::JString> docPath) {
|
|
28
|
+
auto jsiRuntime = reinterpret_cast<jsi::Runtime *>(jsiRuntimePtr);
|
|
29
|
+
auto jsCallInvoker = jsCallInvokerHolder->cthis()->getCallInvoker();
|
|
30
|
+
std::string docPathString = docPath->toStdString();
|
|
31
|
+
|
|
32
|
+
osp::install(*jsiRuntime, jsCallInvoker, docPathString.c_str());
|
|
33
|
+
}
|
|
34
|
+
|
|
35
|
+
static void clearStateNativeJsi(jni::alias_ref<jni::JObject> thiz) {
|
|
36
|
+
osp::clearState();
|
|
37
|
+
}
|
|
38
|
+
};
|
|
39
|
+
|
|
40
|
+
JNIEXPORT jint JNI_OnLoad(JavaVM *vm, void *) {
|
|
41
|
+
return jni::initialize(vm, [] { OPSQLiteBridge::registerNatives(); });
|
|
42
|
+
}
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
package com.op.sqlite;
|
|
2
|
+
|
|
3
|
+
import android.util.Log;
|
|
4
|
+
|
|
5
|
+
import com.facebook.react.bridge.ReactApplicationContext;
|
|
6
|
+
import com.facebook.react.bridge.ReactContext;
|
|
7
|
+
import com.facebook.react.turbomodule.core.CallInvokerHolderImpl;
|
|
8
|
+
|
|
9
|
+
public class OPSQLiteBridge {
|
|
10
|
+
private native void installNativeJsi(long jsContextNativePointer, CallInvokerHolderImpl jsCallInvokerHolder, String docPath);
|
|
11
|
+
private native void clearStateNativeJsi();
|
|
12
|
+
public static final OPSQLiteBridge instance = new OPSQLiteBridge();
|
|
13
|
+
|
|
14
|
+
public void install(ReactContext context) {
|
|
15
|
+
long jsContextPointer = context.getJavaScriptContextHolder().get();
|
|
16
|
+
CallInvokerHolderImpl jsCallInvokerHolder = (CallInvokerHolderImpl)context.getCatalystInstance().getJSCallInvokerHolder();
|
|
17
|
+
// Trick to get the base database path
|
|
18
|
+
final String dbPath = context.getDatabasePath("defaultDatabase").getAbsolutePath().replace("defaultDatabase", "");
|
|
19
|
+
installNativeJsi(
|
|
20
|
+
jsContextPointer,
|
|
21
|
+
jsCallInvokerHolder,
|
|
22
|
+
dbPath
|
|
23
|
+
);
|
|
24
|
+
}
|
|
25
|
+
|
|
26
|
+
public void clearState() {
|
|
27
|
+
clearStateNativeJsi();
|
|
28
|
+
}
|
|
29
|
+
}
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
package com.op.sqlite;
|
|
2
|
+
|
|
3
|
+
import androidx.annotation.NonNull;
|
|
4
|
+
import android.util.Log;
|
|
5
|
+
|
|
6
|
+
import com.facebook.jni.HybridData;
|
|
7
|
+
import com.facebook.jni.annotations.DoNotStrip;
|
|
8
|
+
import com.facebook.react.bridge.ReactApplicationContext;
|
|
9
|
+
import com.facebook.react.bridge.ReactContextBaseJavaModule;
|
|
10
|
+
import com.facebook.react.bridge.ReactMethod;
|
|
11
|
+
import com.facebook.react.turbomodule.core.CallInvokerHolderImpl;
|
|
12
|
+
|
|
13
|
+
class OPSQLiteModule extends ReactContextBaseJavaModule {
|
|
14
|
+
public static final String NAME = "OPSQLite";
|
|
15
|
+
|
|
16
|
+
public OPSQLiteModule(ReactApplicationContext context) {
|
|
17
|
+
super(context);
|
|
18
|
+
}
|
|
19
|
+
|
|
20
|
+
@NonNull
|
|
21
|
+
@Override
|
|
22
|
+
public String getName() {
|
|
23
|
+
return NAME;
|
|
24
|
+
}
|
|
25
|
+
|
|
26
|
+
@ReactMethod(isBlockingSynchronousMethod = true)
|
|
27
|
+
public boolean install() {
|
|
28
|
+
try {
|
|
29
|
+
System.loadLibrary("op-sqlite");
|
|
30
|
+
OPSQLiteBridge.instance.install(getReactApplicationContext());
|
|
31
|
+
return true;
|
|
32
|
+
} catch (Exception exception) {
|
|
33
|
+
Log.e(NAME, "Failed to install JSI Bindings!", exception);
|
|
34
|
+
return false;
|
|
35
|
+
}
|
|
36
|
+
}
|
|
37
|
+
|
|
38
|
+
@Override
|
|
39
|
+
public void onCatalystInstanceDestroy() {
|
|
40
|
+
try {
|
|
41
|
+
OPSQLiteBridge.instance.clearState();
|
|
42
|
+
} catch (Exception exception) {
|
|
43
|
+
Log.e(NAME, "Failed to clear state!", exception);
|
|
44
|
+
}
|
|
45
|
+
}
|
|
46
|
+
}
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
package com.op.sqlite;
|
|
2
|
+
|
|
3
|
+
import androidx.annotation.NonNull;
|
|
4
|
+
|
|
5
|
+
import com.facebook.react.ReactPackage;
|
|
6
|
+
import com.facebook.react.bridge.NativeModule;
|
|
7
|
+
import com.facebook.react.bridge.ReactApplicationContext;
|
|
8
|
+
import com.facebook.react.uimanager.ViewManager;
|
|
9
|
+
|
|
10
|
+
import java.util.Collections;
|
|
11
|
+
import java.util.List;
|
|
12
|
+
|
|
13
|
+
|
|
14
|
+
public class OPSQLitePackage implements ReactPackage {
|
|
15
|
+
@NonNull
|
|
16
|
+
@Override
|
|
17
|
+
public List<NativeModule> createNativeModules(@NonNull ReactApplicationContext reactContext) {
|
|
18
|
+
return Collections.singletonList(new OPSQLiteModule(reactContext));
|
|
19
|
+
}
|
|
20
|
+
|
|
21
|
+
@NonNull
|
|
22
|
+
@Override
|
|
23
|
+
public List<ViewManager> createViewManagers(@NonNull ReactApplicationContext reactContext) {
|
|
24
|
+
return Collections.emptyList();
|
|
25
|
+
}
|
|
26
|
+
}
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
#include "DynamicHostObject.h"
|
|
2
|
+
#include "utils.h"
|
|
3
|
+
#include <iostream>
|
|
4
|
+
|
|
5
|
+
namespace osp {
|
|
6
|
+
|
|
7
|
+
namespace jsi = facebook::jsi;
|
|
8
|
+
|
|
9
|
+
std::vector<jsi::PropNameID> DynamicHostObject::getPropertyNames(jsi::Runtime &rt) {
|
|
10
|
+
std::vector<jsi::PropNameID> keys;
|
|
11
|
+
|
|
12
|
+
for (auto field : fields) {
|
|
13
|
+
keys.push_back(jsi::PropNameID::forAscii(rt, field.first));
|
|
14
|
+
}
|
|
15
|
+
|
|
16
|
+
return keys;
|
|
17
|
+
}
|
|
18
|
+
|
|
19
|
+
jsi::Value DynamicHostObject::get(jsi::Runtime &rt, const jsi::PropNameID &propNameID) {
|
|
20
|
+
auto name = propNameID.utf8(rt);
|
|
21
|
+
|
|
22
|
+
if(fields.find(name) == fields.end()) {
|
|
23
|
+
return {};
|
|
24
|
+
} else {
|
|
25
|
+
std::any val = fields[name];
|
|
26
|
+
return toJSI(rt, val);
|
|
27
|
+
}
|
|
28
|
+
}
|
|
29
|
+
|
|
30
|
+
}
|