@modern-js/main-doc 2.35.1 → 2.36.0
This diff represents the content of publicly available package versions that have been released to one of the supported registries. The information contained in this diff is provided for informational purposes only and reflects changes between package versions as they appear in their respective public registries.
- package/docs/en/apis/app/hooks/src/routes.mdx +1 -1
- package/docs/en/components/debug-app.mdx +1 -1
- package/docs/en/components/turtorials-example-list.mdx +2 -0
- package/docs/en/configure/app/source/entries.mdx +7 -6
- package/docs/en/guides/advanced-features/bff/sdk.mdx +119 -0
- package/docs/en/guides/advanced-features/rspack-start.mdx +1 -1
- package/docs/en/guides/advanced-features/ssr.mdx +17 -17
- package/docs/en/guides/basic-features/data/_category_.json +4 -0
- package/docs/en/guides/basic-features/{data-fetch.mdx → data/data-fetch.mdx} +35 -27
- package/docs/en/guides/basic-features/data/data-write.mdx +241 -0
- package/docs/en/guides/basic-features/routes.mdx +7 -7
- package/docs/en/guides/concept/entries.mdx +31 -30
- package/docs/en/guides/get-started/quick-start.mdx +1 -1
- package/docs/en/guides/topic-detail/framework-plugin/extend.mdx +0 -1
- package/docs/en/guides/topic-detail/framework-plugin/hook-list.mdx +0 -1
- package/docs/en/guides/topic-detail/framework-plugin/hook.mdx +1 -1
- package/docs/en/guides/topic-detail/framework-plugin/implement.mdx +1 -2
- package/docs/en/guides/topic-detail/framework-plugin/introduction.mdx +1 -1
- package/docs/en/guides/topic-detail/framework-plugin/lifecycle.mdx +1 -1
- package/docs/en/guides/topic-detail/framework-plugin/plugin-api.mdx +31 -11
- package/docs/en/guides/topic-detail/framework-plugin/relationship.mdx +2 -2
- package/docs/en/guides/topic-detail/generator/new/config.md +0 -5
- package/docs/en/guides/topic-detail/micro-frontend/c03-main-app.mdx +2 -2
- package/docs/en/tutorials/first-app/c05-loader.mdx +2 -2
- package/docs/en/tutorials/first-app/c06-model.mdx +4 -4
- package/docs/en/tutorials/first-app/c07-container.mdx +3 -3
- package/docs/en/tutorials/foundations/introduction.mdx +3 -2
- package/docs/zh/apis/app/hooks/src/routes.mdx +1 -1
- package/docs/zh/components/debug-app.mdx +1 -1
- package/docs/zh/components/micro-runtime-config.mdx +2 -2
- package/docs/zh/components/turtorials-example-list.mdx +2 -0
- package/docs/zh/configure/app/source/entries.mdx +7 -6
- package/docs/zh/guides/advanced-features/bff/sdk.mdx +119 -0
- package/docs/zh/guides/advanced-features/rspack-start.mdx +1 -1
- package/docs/zh/guides/advanced-features/ssr.mdx +16 -16
- package/docs/zh/guides/basic-features/data/_category_.json +4 -0
- package/docs/zh/guides/basic-features/{data-fetch.mdx → data/data-fetch.md} +31 -27
- package/docs/zh/guides/basic-features/data/data-write.mdx +236 -0
- package/docs/zh/guides/basic-features/routes.mdx +7 -7
- package/docs/zh/guides/concept/entries.mdx +34 -32
- package/docs/zh/guides/get-started/quick-start.mdx +1 -1
- package/docs/zh/guides/topic-detail/framework-plugin/extend.mdx +0 -1
- package/docs/zh/guides/topic-detail/framework-plugin/hook-list.mdx +0 -1
- package/docs/zh/guides/topic-detail/framework-plugin/hook.mdx +1 -1
- package/docs/zh/guides/topic-detail/framework-plugin/implement.mdx +0 -1
- package/docs/zh/guides/topic-detail/framework-plugin/introduction.mdx +1 -1
- package/docs/zh/guides/topic-detail/framework-plugin/lifecycle.mdx +1 -1
- package/docs/zh/guides/topic-detail/framework-plugin/plugin-api.mdx +31 -11
- package/docs/zh/guides/topic-detail/framework-plugin/relationship.mdx +1 -1
- package/docs/zh/guides/topic-detail/generator/new/config.md +0 -5
- package/docs/zh/guides/topic-detail/micro-frontend/c03-main-app.mdx +2 -2
- package/docs/zh/guides/topic-detail/monorepo/create-sub-project.mdx +0 -14
- package/docs/zh/guides/topic-detail/monorepo/sub-project-interface.mdx +7 -43
- package/docs/zh/tutorials/first-app/c05-loader.mdx +2 -2
- package/docs/zh/tutorials/first-app/c06-model.mdx +3 -3
- package/docs/zh/tutorials/first-app/c07-container.mdx +3 -3
- package/docs/zh/tutorials/foundations/introduction.mdx +3 -2
- package/package.json +7 -7
|
@@ -0,0 +1,236 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
---
|
|
2
|
+
title: 数据写入
|
|
3
|
+
sidebar_position: 4
|
|
4
|
+
---
|
|
5
|
+
|
|
6
|
+
# 数据写入
|
|
7
|
+
|
|
8
|
+
在 Data Loader 章节中,介绍了 Modern.js 获取数据的方式,你可能会遇到两个问题:
|
|
9
|
+
1. 如何更新 Data Loader 中的数据?
|
|
10
|
+
2. 如何将新的数据传递到服务器?
|
|
11
|
+
|
|
12
|
+
EdenX 对此的解决方案是 DataAction。
|
|
13
|
+
|
|
14
|
+
## 基本示例
|
|
15
|
+
|
|
16
|
+
Data Action 和 Data Loader 一样,也是基于约定式路由的,通过 Modern.js 的[约定式(嵌套)路由](/guides/basic-features/routes#约定式路由),每个路由组件(`layout.ts`,`page.ts` 或 `$.tsx`)可以有一个同名的 `data` 文件,`data` 文件中可以导出一个命名为 `action` 的函数。
|
|
17
|
+
```bash
|
|
18
|
+
.
|
|
19
|
+
└── routes
|
|
20
|
+
└── user
|
|
21
|
+
├── layout.tsx
|
|
22
|
+
└── layout.data.ts
|
|
23
|
+
```
|
|
24
|
+
在文件中定义以下代码:
|
|
25
|
+
```ts title="routes/user/layout.data.ts"
|
|
26
|
+
import type { ActionFunction } from '@modern-js/runtime/router';
|
|
27
|
+
|
|
28
|
+
export const action: ActionFunction = ({ request }) => {
|
|
29
|
+
const newUser = await request.json();
|
|
30
|
+
const name = newUser.name;
|
|
31
|
+
return updateUserProfile(name);
|
|
32
|
+
}
|
|
33
|
+
```
|
|
34
|
+
|
|
35
|
+
```tsx title="routes/user/layout.tsx"
|
|
36
|
+
import {
|
|
37
|
+
useFetcher,
|
|
38
|
+
useLoaderData,
|
|
39
|
+
useParams,
|
|
40
|
+
Outlet
|
|
41
|
+
} from '@modern-js/runtime/router';
|
|
42
|
+
|
|
43
|
+
export default () => {
|
|
44
|
+
const userInfo = useLoaderData();
|
|
45
|
+
const { submit } = useFetcher();
|
|
46
|
+
const editUser = () => {
|
|
47
|
+
const newUser = {
|
|
48
|
+
name: 'Modern.js'
|
|
49
|
+
}
|
|
50
|
+
return submit(newUser, {
|
|
51
|
+
method: 'post',
|
|
52
|
+
encType: 'application/json',
|
|
53
|
+
})
|
|
54
|
+
}
|
|
55
|
+
return (
|
|
56
|
+
<div>
|
|
57
|
+
<button onClick={editUser}>edit user</button>
|
|
58
|
+
<div className="user-profile">
|
|
59
|
+
{userInfo}
|
|
60
|
+
</div>
|
|
61
|
+
<Outlet context={userInfo}></Outlet>
|
|
62
|
+
</div>
|
|
63
|
+
)
|
|
64
|
+
}
|
|
65
|
+
```
|
|
66
|
+
|
|
67
|
+
这里当执行 submit 后,会触发定义的 action 函数;在 action 函数中,可以通过 request (request.json,request.formData)获取提交的数据,获取数据后,再发送数据到服务端。
|
|
68
|
+
|
|
69
|
+
而 action 函数执行完,会执行 loader 函数代码,并更新对应的数据和视图。
|
|
70
|
+
|
|
71
|
+
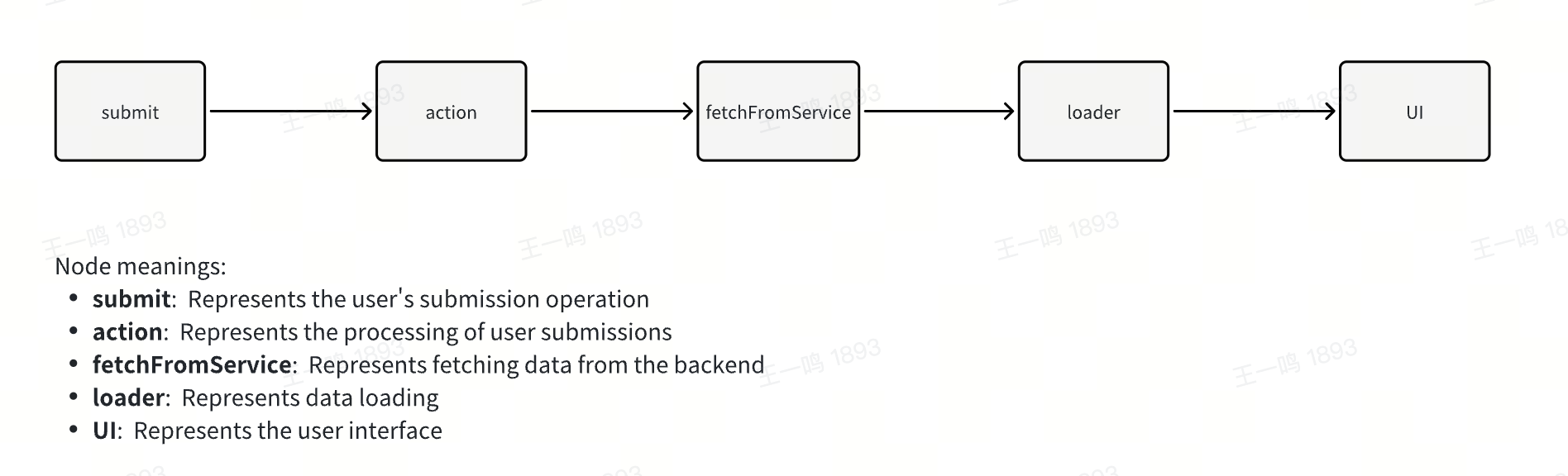
|
|
72
|
+
|
|
73
|
+
|
|
74
|
+
|
|
75
|
+
## 为什么要提供 Data Action
|
|
76
|
+
|
|
77
|
+
Modern.js 中提供 Data Action 主要是为了使 UI 和服务器的状态能保持同步,通过这种方式可以减少状态管理的负担,
|
|
78
|
+
传统的状态管理方式,会在客户端和远程分别持有状态:
|
|
79
|
+
|
|
80
|
+
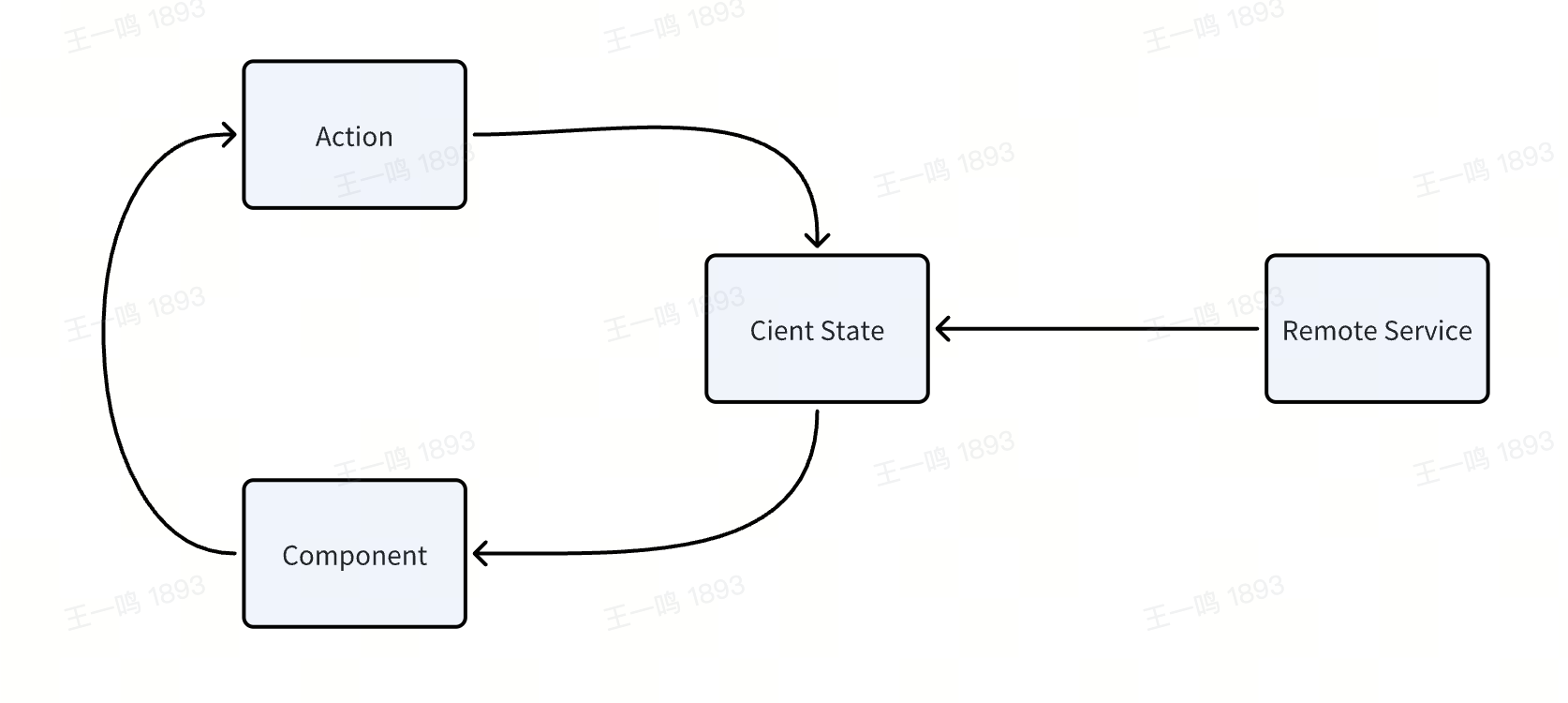
|
|
81
|
+
|
|
82
|
+
而在 Modern.js 中,我们希望通过 Loader 和 Action 帮助开发者自动的同步客户端和服务端的状态:
|
|
83
|
+
|
|
84
|
+
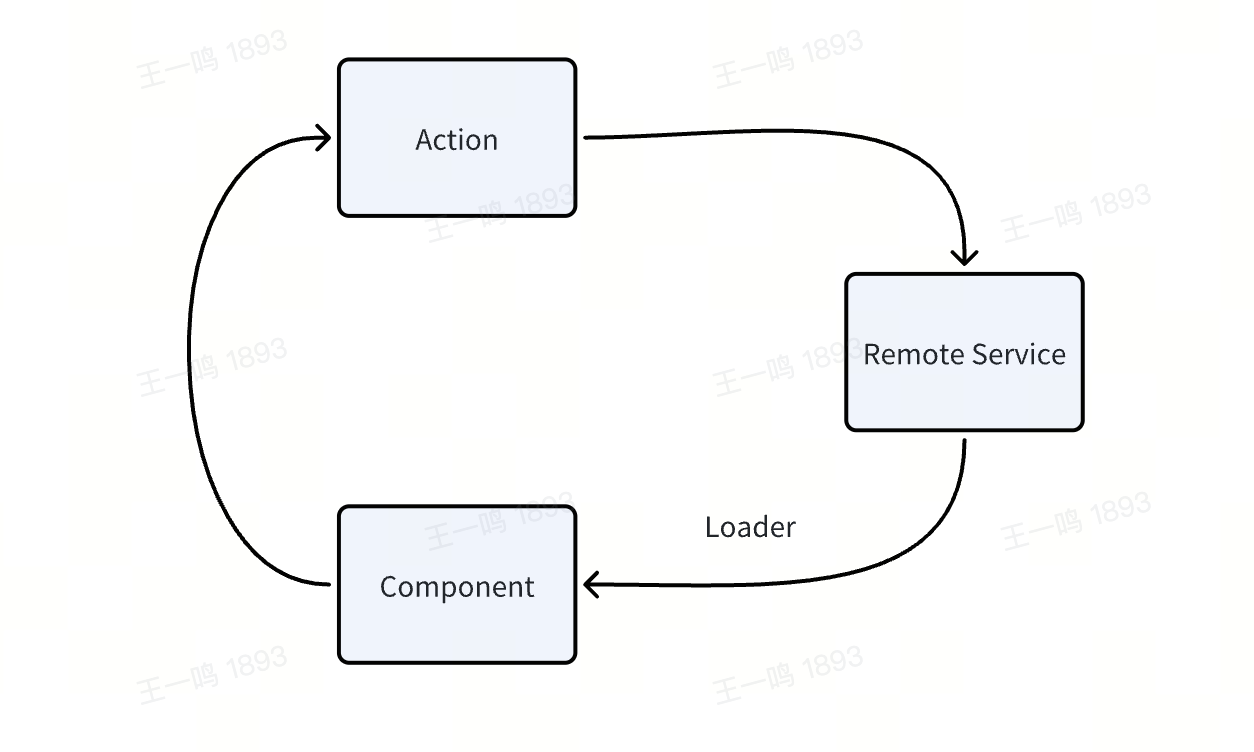
|
|
85
|
+
|
|
86
|
+
如果项目中组件共享的数据主要服务端的状态,则无需在项目引入客户端状态管理库,使用 Data Loader 请求数据,通过 [`useRouteLoaderData`](/guides/basic-features/data/data-fetch.md) 在子组件中共享数据,
|
|
87
|
+
通过 Data Actino 修改和同步服务端的状态。
|
|
88
|
+
|
|
89
|
+
|
|
90
|
+
|
|
91
|
+
## `action` 函数
|
|
92
|
+
|
|
93
|
+
与 `loader` 函数一样,`action` 函数有两个入参,`params` 和 `request`:
|
|
94
|
+
|
|
95
|
+
### `params`
|
|
96
|
+
|
|
97
|
+
当路由文件通过 `[]` 时,会作为[动态路由](/guides/basic-features/routes#动态路由),动态路由片段会作为参数传入 `action` 函数:
|
|
98
|
+
|
|
99
|
+
```tsx
|
|
100
|
+
// routes/user/[id]/page.data.ts
|
|
101
|
+
import { ActionFunctionArgs } from '@modern-js/runtime/router';
|
|
102
|
+
|
|
103
|
+
export const action = async ({ params }: ActionFunctionArgs) => {
|
|
104
|
+
const { id } = params;
|
|
105
|
+
const res = await fetch(`https://api/user/${id}`);
|
|
106
|
+
return res.json();
|
|
107
|
+
};
|
|
108
|
+
```
|
|
109
|
+
|
|
110
|
+
当访问 `/user/123` 时,`action` 函数的参数为 `{ params: { id: '123' } }`。
|
|
111
|
+
|
|
112
|
+
|
|
113
|
+
### `request`
|
|
114
|
+
|
|
115
|
+
`request` 是一个 [Fetch Request](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Request) 实例。
|
|
116
|
+
|
|
117
|
+
通过 `request`,可以在 action 函数中获取到客户端提交的数据,如 `request.json()`,`request.formData()`,`request.json()` 等,
|
|
118
|
+
具体应该使用哪个 API,请参考[数据类型](#数据类型)。
|
|
119
|
+
|
|
120
|
+
```tsx
|
|
121
|
+
// routes/user/[id]/page.data.ts
|
|
122
|
+
import { ActionFunctionArgs } from '@modern-js/runtime/router';
|
|
123
|
+
|
|
124
|
+
export const action = async ({ request }: ActionFunctionArgs) => {
|
|
125
|
+
const newUser = await request.json();
|
|
126
|
+
return updateUser(newUser);
|
|
127
|
+
};
|
|
128
|
+
```
|
|
129
|
+
|
|
130
|
+
### 返回值
|
|
131
|
+
|
|
132
|
+
`action` 函数的返回值可以是任何可序列化的内容,也可以是一个 [Fetch Response](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Response) 实例,
|
|
133
|
+
可以通过 [`useActionData`](https://reactrouter.com/en/main/hooks/use-action-data) 访问 response 中内容。
|
|
134
|
+
|
|
135
|
+
|
|
136
|
+
## useSubmit 和 useFetcher
|
|
137
|
+
|
|
138
|
+
### 区别
|
|
139
|
+
|
|
140
|
+
你可以通过 [`useSubmit`](https://reactrouter.com/en/main/hooks/use-submit) 或 [`useFetcher`](https://reactrouter.com/en/main/hooks/use-fetcher) 调用 action,它们的区别是通过
|
|
141
|
+
`useSubmit` 调用 action,会触发浏览器的导航,通过 `useFetcher` 则不会触发浏览器的导航。
|
|
142
|
+
|
|
143
|
+
useSubmit:
|
|
144
|
+
|
|
145
|
+
```ts
|
|
146
|
+
const submit = useSubmit();
|
|
147
|
+
submit(null, { method: "post", action: "/logout" });
|
|
148
|
+
```
|
|
149
|
+
|
|
150
|
+
useFetcher:
|
|
151
|
+
```ts
|
|
152
|
+
const { submit } = useFetcher();
|
|
153
|
+
submit(null, { method: "post", action: "/logout" });
|
|
154
|
+
```
|
|
155
|
+
|
|
156
|
+
`submit` 函数有两个入参,`method` 和 `action`,`method` 相当于表单提交时的 `method`,大部分写入数据的场景下,`method` 可以传入 `post`,
|
|
157
|
+
`action` 用来指定触发哪个路由组件的 `action`,如果未传入 `action` 入参,默认会触发当前路由组件的 action,即 `user/page.tsx` 组件或子组件中执行 submit,
|
|
158
|
+
会触发 `user/page.data.ts` 中定义的 action。
|
|
159
|
+
|
|
160
|
+
:::info
|
|
161
|
+
这两个 API 更多的信息可参考相关文档:
|
|
162
|
+
- [`useSubmit`](https://reactrouter.com/en/main/hooks/use-submit)
|
|
163
|
+
- [`useFetcher`](https://reactrouter.com/en/main/hooks/use-fetcher)
|
|
164
|
+
|
|
165
|
+
:::
|
|
166
|
+
|
|
167
|
+
|
|
168
|
+
### 数据类型
|
|
169
|
+
|
|
170
|
+
`submit` 函数的第一个入参,可以接受不同类型的值。
|
|
171
|
+
如 `FormData`:
|
|
172
|
+
```ts
|
|
173
|
+
let formData = new FormData();
|
|
174
|
+
formData.append("cheese", "gouda");
|
|
175
|
+
submit(formData);
|
|
176
|
+
// In the action, you can get the data by request.json
|
|
177
|
+
```
|
|
178
|
+
|
|
179
|
+
或 `URLSearchParams` 类型的值:
|
|
180
|
+
```ts
|
|
181
|
+
let searchParams = new URLSearchParams();
|
|
182
|
+
searchParams.append("cheese", "gouda");
|
|
183
|
+
submit(searchParams);
|
|
184
|
+
// In the action, you can get the data by request.json
|
|
185
|
+
```
|
|
186
|
+
|
|
187
|
+
或任意 `URLSearchParams` 构造函数可接受的值
|
|
188
|
+
```ts
|
|
189
|
+
submit("cheese=gouda&toasted=yes");
|
|
190
|
+
submit([
|
|
191
|
+
["cheese", "gouda"],
|
|
192
|
+
["toasted", "yes"],
|
|
193
|
+
]);
|
|
194
|
+
// In the action, you can get the data by request.json
|
|
195
|
+
```
|
|
196
|
+
|
|
197
|
+
默认情况下,如果 `submit` 函数中的第一个入参是一个对象,对应的数据会被 encode 为 `formData`:
|
|
198
|
+
|
|
199
|
+
```ts
|
|
200
|
+
submit(
|
|
201
|
+
{ key: "value" },
|
|
202
|
+
{
|
|
203
|
+
method: "post",
|
|
204
|
+
encType: "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
|
|
205
|
+
}
|
|
206
|
+
);
|
|
207
|
+
|
|
208
|
+
// In the action, you can get the data by request.formData
|
|
209
|
+
```
|
|
210
|
+
|
|
211
|
+
也可以指定为 json 编码:
|
|
212
|
+
|
|
213
|
+
```tsx
|
|
214
|
+
submit(
|
|
215
|
+
{ key: "value" },
|
|
216
|
+
{ method: "post", encType: "application/json" }
|
|
217
|
+
);
|
|
218
|
+
|
|
219
|
+
submit('{"key":"value"}', {
|
|
220
|
+
method: "post",
|
|
221
|
+
encType: "application/json",
|
|
222
|
+
});
|
|
223
|
+
|
|
224
|
+
// In the action, you can get the data by request.json
|
|
225
|
+
```
|
|
226
|
+
|
|
227
|
+
或提交纯文本:
|
|
228
|
+
```ts
|
|
229
|
+
submit("value", { method: "post", encType: "text/plain" });
|
|
230
|
+
// In the action, you can get the data by request.text
|
|
231
|
+
```
|
|
232
|
+
|
|
233
|
+
|
|
234
|
+
## CSR 和 SSR
|
|
235
|
+
|
|
236
|
+
与 Data Loader 一样,SSR 项目中,Data Action 是在服务端执行的(框架会自动发请求触发 Data Action),而在 CSR 项目中,Data Action 是在客户端执行的。
|
|
@@ -164,7 +164,7 @@ export const handle = {
|
|
|
164
164
|
|
|
165
165
|
```ts title="routes/layout.ts"
|
|
166
166
|
export default () => {
|
|
167
|
-
const matches = useMatches;
|
|
167
|
+
const matches = useMatches();
|
|
168
168
|
const breadcrumbs = matches.map(
|
|
169
169
|
matchedRoute => matchedRoute?.handle?.breadcrumbName,
|
|
170
170
|
);
|
|
@@ -189,7 +189,7 @@ export default () => {
|
|
|
189
189
|
|
|
190
190
|
在组件中,可以通过 [useParams](/apis/app/runtime/router/router#useparams) 获取对应命名的参数。
|
|
191
191
|
|
|
192
|
-
在 loader 中,params 会作为 [loader](/guides/basic-features/data-fetch#loader-函数) 的入参,通过 `params.xxx` 可以获取。
|
|
192
|
+
在 loader 中,params 会作为 [loader](/guides/basic-features/data/data-fetch#loader-函数) 的入参,通过 `params.xxx` 可以获取。
|
|
193
193
|
|
|
194
194
|
### 动态可选路由
|
|
195
195
|
|
|
@@ -209,7 +209,7 @@ export default () => {
|
|
|
209
209
|
|
|
210
210
|
在组件中,可以通过 [useParams](/apis/app/runtime/router/router#useparams) 获取对应命名的参数。
|
|
211
211
|
|
|
212
|
-
在 loader 中,params 会作为 [loader](/guides/basic-features/data-fetch#loader-函数) 的入参,通过 `params.xxx` 可以获取。
|
|
212
|
+
在 loader 中,params 会作为 [loader](/guides/basic-features/data/data-fetch#loader-函数) 的入参,通过 `params.xxx` 可以获取。
|
|
213
213
|
|
|
214
214
|
### 通配路由
|
|
215
215
|
|
|
@@ -352,12 +352,12 @@ Modern.js 建议必须有根 Layout 和根 Loading。
|
|
|
352
352
|
|
|
353
353
|
### 路由重定向
|
|
354
354
|
|
|
355
|
-
可以通过创建 [`Data Loader`](/guides/basic-features/data-fetch) 文件做路由的重定向,如有文件 `routes/user/page.tsx`,想对这个文件对应的路由做重定向,可以创建 `routes/user/page.
|
|
355
|
+
可以通过创建 [`Data Loader`](/guides/basic-features/data/data-fetch) 文件做路由的重定向,如有文件 `routes/user/page.tsx`,想对这个文件对应的路由做重定向,可以创建 `routes/user/page.data.ts` 文件:
|
|
356
356
|
|
|
357
|
-
```ts title="routes/user/page.
|
|
357
|
+
```ts title="routes/user/page.data.ts"
|
|
358
358
|
import { redirect } from '@modern-js/runtime/router';
|
|
359
359
|
|
|
360
|
-
export
|
|
360
|
+
export const loader () => {
|
|
361
361
|
const user = await getUser();
|
|
362
362
|
if (!user) {
|
|
363
363
|
return redirect('/login');
|
|
@@ -504,7 +504,7 @@ export const init = (context: RuntimeContext) => {
|
|
|
504
504
|
:::info
|
|
505
505
|
|
|
506
506
|
- 该功能目前仅在 Webpack 项目中支持,Rspack 项目暂不支持。
|
|
507
|
-
- 对数据的预加载目前只会预加载 SSR 项目中 [Data Loader](/guides/basic-features/data-fetch) 中返回的数据。
|
|
507
|
+
- 对数据的预加载目前只会预加载 SSR 项目中 [Data Loader](/guides/basic-features/data/data-fetch) 中返回的数据。
|
|
508
508
|
|
|
509
509
|
:::
|
|
510
510
|
|
|
@@ -6,9 +6,9 @@ sidebar_position: 1
|
|
|
6
6
|
|
|
7
7
|
通过本章节,你可以了解到 Modern.js 中的入口约定,以及如何自定义入口。
|
|
8
8
|
|
|
9
|
-
##
|
|
9
|
+
## 什么是入口
|
|
10
10
|
|
|
11
|
-
|
|
11
|
+
**入口(Entry)指的是一个页面的起始模块。**
|
|
12
12
|
|
|
13
13
|
在 Modern.js 项目中,每一个入口对应一个独立的页面,也对应一条服务端路由。默认情况下,Modern.js 会基于目录约定来自动确定页面的入口,同时也支持通过配置项来自定义入口。
|
|
14
14
|
|
|
@@ -56,7 +56,7 @@ Modern.js 初始化的项目是单入口的(SPA),项目结构如下:
|
|
|
56
56
|
|
|
57
57
|
原本的入口代码被移动到了和 `package.json` 中 `name` 同名的目录下,并创建了 `new-entry` 入口目录。
|
|
58
58
|
|
|
59
|
-
|
|
59
|
+
你可以执行 `pnpm run dev` 启动开发服务,此时可以看到新增了一条名为 `/new-entry` 的路由,并且原有页面的路由并未发生变化。
|
|
60
60
|
|
|
61
61
|
:::tip
|
|
62
62
|
Modern.js 会将与 `package.json` 文件中 `name` 字段同名的入口作为主入口,主入口的路由为 `/`,其他入口的路由为 `/{entryName}`。
|
|
@@ -76,7 +76,8 @@ import EntryMode from '@site-docs/components/entry-mode.mdx';
|
|
|
76
76
|
默认情况下,Modern.js 启动项目前会对 `src/` 下的文件进行扫描,识别入口,并生成对应的服务端路由。
|
|
77
77
|
|
|
78
78
|
:::tip
|
|
79
|
-
|
|
79
|
+
- 你可以通过 [source.entriesDir](/configure/app/source/entries-dir) 修改页面入口的识别目录。
|
|
80
|
+
- 如果你需要自定义入口,请参考 [自定义入口](#自定义入口)。
|
|
80
81
|
|
|
81
82
|
:::
|
|
82
83
|
|
|
@@ -98,7 +99,7 @@ import EntryMode from '@site-docs/components/entry-mode.mdx';
|
|
|
98
99
|
|
|
99
100
|
### 框架模式入口
|
|
100
101
|
|
|
101
|
-
|
|
102
|
+
框架模式指的是需要使用 Modern.js 的框架能力,例如嵌套路由、SSR、一体化调用等。这类入口约定下,开发者定义的入口并不是真正的编译入口。Modern.js 在启动时会生成一个封装过的入口,可以在 `node_modules/.modern/[entryName]/index.js` 找到真正的入口。
|
|
102
103
|
|
|
103
104
|
#### 约定式路由
|
|
104
105
|
|
|
@@ -146,7 +147,7 @@ export default (App: React.ComponentType, bootstrap: () => void) => {
|
|
|
146
147
|
// do something before bootstrap...
|
|
147
148
|
initSomething().then(() => {
|
|
148
149
|
bootstrap();
|
|
149
|
-
})
|
|
150
|
+
});
|
|
150
151
|
};
|
|
151
152
|
```
|
|
152
153
|
|
|
@@ -170,7 +171,9 @@ function render() {
|
|
|
170
171
|
// runtime 的插件参数...
|
|
171
172
|
})(App);
|
|
172
173
|
if (IS_BROWSER) {
|
|
173
|
-
customBootstrap(AppWrapper, () =>
|
|
174
|
+
customBootstrap(AppWrapper, () =>
|
|
175
|
+
bootstrap(AppWrapper, MOUNT_ID, root, ReactDOM),
|
|
176
|
+
);
|
|
174
177
|
}
|
|
175
178
|
return AppWrapper;
|
|
176
179
|
}
|
|
@@ -182,9 +185,11 @@ export default AppWrapper;
|
|
|
182
185
|
|
|
183
186
|
### 构建模式入口
|
|
184
187
|
|
|
185
|
-
|
|
188
|
+
构建模式指的是不使用 Modern.js 自动生成的入口,而是完全由开发者自行定义页面的入口。
|
|
186
189
|
|
|
187
|
-
|
|
190
|
+
当入口目录中存在 `index.[jt]sx`,并且没有通过 `export default` 导出函数时,这类文件就会被识别为 webpack 或 Rspack 的 entry 模块。
|
|
191
|
+
|
|
192
|
+
此时 Modern.js 不会自动生成入口代码,因此需要你自行将组件挂载到 DOM 节点上,例如:
|
|
188
193
|
|
|
189
194
|
```js title=src/index.jsx
|
|
190
195
|
import React from 'react';
|
|
@@ -194,42 +199,39 @@ import App from './App';
|
|
|
194
199
|
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('root'));
|
|
195
200
|
```
|
|
196
201
|
|
|
197
|
-
Modern.js
|
|
202
|
+
这种方式等价于开启 Modern.js 的 [source.entries.disableMount](/configure/app/source/entries) 选项。当你使用这种方式时,**将无法使用 Modern.js 框架的运行时能力**,比如 modern.config.js 文件中的 `runtime` 配置将不会再生效。
|
|
198
203
|
|
|
199
|
-
##
|
|
204
|
+
## 自定义入口
|
|
200
205
|
|
|
201
|
-
|
|
206
|
+
在某些情况下,你可能需要自定义入口配置,而不是使用 Modern.js 提供的入口约定。
|
|
202
207
|
|
|
203
|
-
|
|
208
|
+
比如你需要将一个非 Modern.js 项目迁移到 Modern.js,它并不是按照 Modern.js 的目录结构来搭建的。如果你要将它改成 Modern.js 约定的目录结构,可能会存在一定的迁移成本。这种情况下,你就可以使用自定义入口。
|
|
204
209
|
|
|
205
|
-
|
|
206
|
-
export default defineConfig({
|
|
207
|
-
source: {
|
|
208
|
-
entries: {
|
|
209
|
-
// 指定一个名称为 entry_customize 的新入口
|
|
210
|
-
entry_customize: './src/home/test/index.ts',
|
|
211
|
-
},
|
|
212
|
-
// 禁用默认入口扫描
|
|
213
|
-
disableDefaultEntries: true,
|
|
214
|
-
},
|
|
215
|
-
});
|
|
216
|
-
```
|
|
210
|
+
Modern.js 提供了以下配置项,你可以在 [modern.config.ts](/configure/app/usage) 中配置它们:
|
|
217
211
|
|
|
218
|
-
|
|
212
|
+
- [source.entries](/configure/app/source/entries):用于设置自定义的入口对象。
|
|
213
|
+
- [source.disableDefaultEntries](/configure/app/source/disable-default-entries):用于关闭 Modern.js 默认的入口扫描行为。当你使用自定义入口时,项目的部分结构可能会恰巧命中 Modern.js 约定的目录结构,但你可能不希望 Modern.js 为你自动生成入口配置,开启该选项可以避免这个问题。
|
|
219
214
|
|
|
220
|
-
|
|
215
|
+
### 示例
|
|
221
216
|
|
|
222
|
-
|
|
217
|
+
下面是一个自定义入口的例子,你也可以查看相关配置项的文档来了解更多用法。
|
|
223
218
|
|
|
224
219
|
```ts title="modern.config.ts"
|
|
225
220
|
export default defineConfig({
|
|
226
221
|
source: {
|
|
222
|
+
entries: {
|
|
223
|
+
// 指定一个名为 'my-entry' 的入口
|
|
224
|
+
'my-entry': {
|
|
225
|
+
// 入口模块的路径
|
|
226
|
+
entry: './src/my-page/index.tsx',
|
|
227
|
+
// 关闭 Modern.js 自动生成入口代码的行为
|
|
228
|
+
disableMount: true,
|
|
229
|
+
},
|
|
230
|
+
},
|
|
231
|
+
// 禁用入口扫描行为
|
|
227
232
|
disableDefaultEntries: true,
|
|
228
233
|
},
|
|
229
234
|
});
|
|
230
235
|
```
|
|
231
236
|
|
|
232
|
-
|
|
233
|
-
详细用法请查看 [source.entries](/configure/app/source/entries) 和 [source.disableDefaultEntries](/configure/app/source/disable-default-entries)。
|
|
234
|
-
|
|
235
|
-
:::
|
|
237
|
+
注意,当你开启 `disableMount` 时,**将无法使用 Modern.js 框架的运行时能力**,比如 modern.config.ts 文件中的 `runtime` 配置将不会再生效。
|
|
@@ -1,5 +1,4 @@
|
|
|
1
1
|
---
|
|
2
|
-
title: 插件 API
|
|
3
2
|
sidebar_position: 6
|
|
4
3
|
---
|
|
5
4
|
|
|
@@ -79,26 +78,43 @@ interface NormalizedConfig {
|
|
|
79
78
|
const useAppContext: () => IAppContext;
|
|
80
79
|
|
|
81
80
|
interface IAppContext {
|
|
81
|
+
/** 当前项目的根目录 */
|
|
82
82
|
appDirectory: string;
|
|
83
|
+
/** 源代码目录 */
|
|
84
|
+
srcDirectory: string;
|
|
85
|
+
/** 构建产出输出目录 */
|
|
86
|
+
distDirectory: string;
|
|
87
|
+
/** 公共模块目录 */
|
|
88
|
+
sharedDirectory: string;
|
|
89
|
+
/** 框架临时文件输出目录 */
|
|
90
|
+
internalDirectory: string;
|
|
91
|
+
/** node_modules 目录 */
|
|
92
|
+
nodeModulesDirectory: string;
|
|
93
|
+
/** 配置文件路径 */
|
|
83
94
|
configFile: string | false;
|
|
95
|
+
/** 当前机器的 IPv4 地址 */
|
|
84
96
|
ip?: string;
|
|
97
|
+
/** 开发服务器的端口号 */
|
|
85
98
|
port?: number;
|
|
86
|
-
|
|
99
|
+
/** 当前项目 package.json 的 name */
|
|
87
100
|
packageName: string;
|
|
88
|
-
|
|
89
|
-
|
|
90
|
-
|
|
91
|
-
internalDirectory: string;
|
|
92
|
-
plugins: {
|
|
93
|
-
cli?: any;
|
|
94
|
-
server?: any;
|
|
95
|
-
}[];
|
|
101
|
+
/** 当前注册的插件 */
|
|
102
|
+
plugins: any[];
|
|
103
|
+
/** 页面入口信息 */
|
|
96
104
|
entrypoints: Entrypoint[];
|
|
105
|
+
/** 服务端路由信息 */
|
|
97
106
|
serverRoutes: ServerRoute[];
|
|
98
|
-
|
|
107
|
+
/** 当前项目类型 */
|
|
108
|
+
toolsType?: 'app-tools' | 'module-tools' | 'monorepo-tools';
|
|
109
|
+
/** 当前使用的打包工具类型 */
|
|
110
|
+
bundlerType?: 'webpack' | 'rspack' | 'esbuild';
|
|
99
111
|
}
|
|
100
112
|
```
|
|
101
113
|
|
|
114
|
+
:::tip
|
|
115
|
+
AppContext 中的部分字段是动态设置的,会随着程序的运行而变化。因此,当插件在不同的时机读取字段时,可能会获取到不同的值。
|
|
116
|
+
:::
|
|
117
|
+
|
|
102
118
|
### useHookRunners
|
|
103
119
|
|
|
104
120
|
用于获取 Hooks 的执行器,并触发特定的 Hook 执行。
|
|
@@ -116,3 +132,7 @@ export const myPlugin = (): CliPlugin => ({
|
|
|
116
132
|
},
|
|
117
133
|
});
|
|
118
134
|
```
|
|
135
|
+
|
|
136
|
+
:::tip
|
|
137
|
+
请尽量避免执行框架内置的 hooks,否则可能会导致框架内部的运行逻辑出错。
|
|
138
|
+
:::
|
|
@@ -44,12 +44,12 @@ defineConfig(App, {
|
|
|
44
44
|
return [
|
|
45
45
|
{
|
|
46
46
|
name: 'Table',
|
|
47
|
-
entry: 'http://localhost:
|
|
47
|
+
entry: 'http://localhost:8081',
|
|
48
48
|
// activeWhen: '/table'
|
|
49
49
|
},
|
|
50
50
|
{
|
|
51
51
|
name: 'Dashboard',
|
|
52
|
-
entry: 'http://localhost:
|
|
52
|
+
entry: 'http://localhost:8082',
|
|
53
53
|
// activeWhen: '/dashboard'
|
|
54
54
|
},
|
|
55
55
|
];
|
|
@@ -29,23 +29,9 @@ pnpm run new
|
|
|
29
29
|
```
|
|
30
30
|
? 请选择你想创建的工程类型 (Use arrow keys)
|
|
31
31
|
❯ Web 应用
|
|
32
|
-
Web 应用(测试)
|
|
33
32
|
Npm 模块
|
|
34
|
-
Npm 模块(内部)
|
|
35
33
|
```
|
|
36
34
|
|
|
37
|
-
:::info
|
|
38
|
-
「应用」与「应用(测试)」都是「应用」类型的项目,区别是「应用」类型的子项目会创建在 `./apps` 目录下,而 「应用(测试)」类型的子项目会创建在 `./examples` 目录下。
|
|
39
|
-
|
|
40
|
-
:::
|
|
41
|
-
|
|
42
|
-
:::info
|
|
43
|
-
「模块」与「模块(内部)」都是「模块」类型的项目,区别之一是「模块」类型的子项目会创建在 `./packages` 目录下,而「模块(内部)」类型的子项目会创建在 `./features` 目录下。
|
|
44
|
-
|
|
45
|
-
对于「模块」类型的子项目允许被发布到外部(例如 npm),而对于「模块(内部)」的子项目则可以在应用项目中直接使用其源码(该特性是「模块」项目不具备的,应用项目对于「模块(内部)」子项目做了特殊处理),因此这类子项目不需要发布到外部。
|
|
46
|
-
|
|
47
|
-
:::
|
|
48
|
-
|
|
49
35
|
然后根据不同的需求选择对应的类型项目选项,选择之后便开始出现对应子项目类型的问题和选项。例如选择「应用」后会出现:
|
|
50
36
|
|
|
51
37
|
```
|