mathpack 0.4.1 → 0.4.2
This diff represents the content of publicly available package versions that have been released to one of the supported registries. The information contained in this diff is provided for informational purposes only and reflects changes between package versions as they appear in their respective public registries.
- checksums.yaml +4 -4
- data/README.md +39 -8
- data/lib/mathpack/approximation.rb +3 -3
- data/lib/mathpack/integration.rb +5 -12
- data/lib/mathpack/io.rb +13 -0
- data/lib/mathpack/sle.rb +4 -3
- data/lib/mathpack/statistics.rb +30 -21
- data/lib/mathpack/version.rb +1 -1
- data/lib/mathpack.rb +1 -0
- data/spec/approximation_spec.rb +2 -2
- data/spec/sle_spec.rb +15 -1
- data/spec/statistics_spec.rb +21 -13
- metadata +3 -2
checksums.yaml
CHANGED
|
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
|
|
1
1
|
---
|
|
2
2
|
SHA1:
|
|
3
|
-
metadata.gz:
|
|
4
|
-
data.tar.gz:
|
|
3
|
+
metadata.gz: 111c0ff1891e4a3c36c9b93e8f76c6e95e6d3daa
|
|
4
|
+
data.tar.gz: 3356428babcbf1b7031dc7dfbd4c03a397dc565c
|
|
5
5
|
SHA512:
|
|
6
|
-
metadata.gz:
|
|
7
|
-
data.tar.gz:
|
|
6
|
+
metadata.gz: 4f04c1e83d260b0376c79b7899092d878b8f5f3b9dedcc40963a931ca0a5b200a8770598164429678fb2d02d1af14d4d99569a4000c633ced33882f617e2fa6d
|
|
7
|
+
data.tar.gz: 39e0707d6eabb22509488221178fe14322d391934a248e8092ddef5050d0a1902755cba9af1698a01d1146046ad489c457b2b82ac2e82f75ae508df6444865d8
|
data/README.md
CHANGED
|
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ Gem `mathpack` allows to count statistical functions through `Statistics` class,
|
|
|
34
34
|
- **empirical_cdf** - returns *empirical distribution function* value in some point
|
|
35
35
|
- **empirical_pdf** - returns *empirical probability density function* value in some point
|
|
36
36
|
- **print_empirical_cdf_to_csv** - allows to print empirical_cdf line chart values to `.csv` file with name *filename*
|
|
37
|
-
- **
|
|
37
|
+
- **print_empirical_pdf_to_csv** - allows to print empirical_pdf line chart values to `.csv` file with name *filename*
|
|
38
38
|
- **trend** - returns trend polynom
|
|
39
39
|
|
|
40
40
|
### Usage
|
|
@@ -43,7 +43,7 @@ stat = Mathpack::Statistics.new([1, 2, 5, 6])
|
|
|
43
43
|
stat.number() #=> 4
|
|
44
44
|
stat.mean() #=> 3.5
|
|
45
45
|
stat.variance() #=> 4.25
|
|
46
|
-
stat.kurtosis() #=> 1.
|
|
46
|
+
stat.kurtosis() #=> -1.778546712802768
|
|
47
47
|
stat.skewness() #=> 0.0
|
|
48
48
|
stat.min() #=> 1
|
|
49
49
|
stat.max() #=> 6
|
|
@@ -117,23 +117,54 @@ manage with this problem using `Approximation` module. This module uses least sq
|
|
|
117
117
|
### Usage
|
|
118
118
|
```ruby
|
|
119
119
|
# Function to print polynom having it's coefficients
|
|
120
|
-
Mathpack::Approximation
|
|
120
|
+
Mathpack::Approximation.print_polynom([1, -2, 1]) #=> x^2 - 2*x + 1
|
|
121
121
|
|
|
122
122
|
# Function to generate nodes for approximation. Only choose start value, end value and step
|
|
123
|
-
x = Mathpack::Approximation
|
|
123
|
+
x = Mathpack::Approximation.generate_nodes(from: 0, to: 10, step: 0.25)
|
|
124
124
|
#=> [0, 0.25, ..., 10]
|
|
125
125
|
|
|
126
126
|
# Function that approximate given function by polynom with power polynom_power in approximation nodes x and returns coefficients of approximating polynom
|
|
127
|
-
result = Mathpack::Approximation
|
|
127
|
+
result = Mathpack::Approximation.approximate_by_polynom(x: x, polynom_power: 5){ |x| Math.sin(x) }
|
|
128
128
|
#=> [0.0008009744982571882, -0.030619986086758588, 0.3805927651948083, -1.8481035413353888, 2.985465287759307, -0.3873066069630569]
|
|
129
129
|
|
|
130
130
|
# May be you want to print this polynom, let's call print_polynom function
|
|
131
|
-
Mathpack::Approximation
|
|
131
|
+
Mathpack::Approximation.print_polynom(result)
|
|
132
132
|
#=> 0.0008009744982571882*x^5 - 0.030619986086758588*x^4 + 0.3805927651948083*x^3 - 1.8481035413353888*x^2 + 2.985465287759307*x - 0.3873066069630569
|
|
133
133
|
|
|
134
134
|
# If you have a table of values, where x - array of arguement values and f - array of function values, call approximate by polynom function with parameter f instead of block
|
|
135
|
-
result = Mathpack::Approximation
|
|
136
|
-
Mathpack::Approximation
|
|
135
|
+
result = Mathpack::Approximation.approximate_by_polynom(x: [1, 2, 3], f: [1, 4, 9], polynom_power: 2) #=> [1, 0, 0]
|
|
136
|
+
Mathpack::Approximation.print_polynom(result) #=> x^2
|
|
137
|
+
```
|
|
138
|
+
|
|
139
|
+
## Integration
|
|
140
|
+
`Integration` module has method `integrate`, which is used to integrate numericality various functions.
|
|
141
|
+
|
|
142
|
+
### Usage
|
|
143
|
+
Let you have the following integral:
|
|
144
|
+
|
|
145
|
+
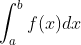
|
|
146
|
+
|
|
147
|
+
Where *a* can be finite or equal to 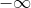, and *b* can be finite or equal to 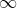. To find value of integral you should call **integrate** method of Integration module.
|
|
148
|
+
```ruby
|
|
149
|
+
Mathpack::Integration.integrate(from: a, to: b){ |x| f(x) }
|
|
150
|
+
```
|
|
151
|
+
Let's demostrate some examples of Integration module practical usage:
|
|
152
|
+
```ruby
|
|
153
|
+
Mathpack::Integration.integrate(from: 0, to: 3.6){ |x| Math.sin(x) / x } #=> 1.8219481156495034
|
|
154
|
+
Mathpack::Integration.integrate(from: 0, to: Float::INFINITY){ |x| Math.exp(-x) / (x + 1) } #=> 0.5963473623136091
|
|
155
|
+
Mathpack::Integration.integrate(from: -Float::INFINITY, to: Float::INFINITY){ |x| Math.exp(-x**2) * Math.cos(x) } #=> 1.3803884100161075
|
|
156
|
+
```
|
|
157
|
+
|
|
158
|
+
## IO
|
|
159
|
+
|
|
160
|
+
`IO` module allows to output complex data
|
|
161
|
+
|
|
162
|
+
### Usage
|
|
163
|
+
|
|
164
|
+
If you have table function, represented by argument array and function values array, you should use
|
|
165
|
+
`print_table_function`, that prints your data to `.csv` file.
|
|
166
|
+
```ruby
|
|
167
|
+
Mathpack::IO.print_table_function(filename: 'table.csv', x: [1, 2, 3], y: [2, 4, 6], labels: { x: 'x', y: 'f(x)'}
|
|
137
168
|
```
|
|
138
169
|
|
|
139
170
|
## Contributing
|
|
@@ -57,11 +57,11 @@ module Mathpack
|
|
|
57
57
|
nodes = []
|
|
58
58
|
i = 0
|
|
59
59
|
loop do
|
|
60
|
-
nodes << params[:
|
|
60
|
+
nodes << params[:from] + i * params[:step]
|
|
61
61
|
i += 1
|
|
62
|
-
break if params[:
|
|
62
|
+
break if params[:from] + i * params[:step] > params[:to]
|
|
63
63
|
end
|
|
64
|
-
nodes << params[:
|
|
64
|
+
nodes << params[:to] if nodes.last != params[:to]
|
|
65
65
|
nodes
|
|
66
66
|
end
|
|
67
67
|
|
data/lib/mathpack/integration.rb
CHANGED
|
@@ -5,7 +5,10 @@ module Mathpack
|
|
|
5
5
|
|
|
6
6
|
def self.integrate(params = {}, &f)
|
|
7
7
|
if params[:from] == -Float::INFINITY && params[:to] == Float::INFINITY
|
|
8
|
-
result =
|
|
8
|
+
result = solve_oi(-INTEGRATION_LIMIT, INTEGRATION_LIMIT, &f)
|
|
9
|
+
g = ->(x) { f.call(-x) }
|
|
10
|
+
result += solve_ni_1(INTEGRATION_LIMIT, &g)
|
|
11
|
+
result += solve_ni_1(INTEGRATION_LIMIT, &f)
|
|
9
12
|
elsif params[:to] == Float::INFINITY || params[:from] == -Float::INFINITY
|
|
10
13
|
if params[:from] == -Float::INFINITY
|
|
11
14
|
params[:from] = -params[:to]
|
|
@@ -29,7 +32,7 @@ module Mathpack
|
|
|
29
32
|
|
|
30
33
|
def self.solve_oi(from, to, &f)
|
|
31
34
|
result = 0.0
|
|
32
|
-
nodes = Mathpack::Approximation.generate_nodes(
|
|
35
|
+
nodes = Mathpack::Approximation.generate_nodes(from: from, to: to, step: STEP)
|
|
33
36
|
for i in 0...nodes.length - 1 do
|
|
34
37
|
result += basic_integrate(nodes[i], nodes[i + 1], &f)
|
|
35
38
|
end
|
|
@@ -46,15 +49,5 @@ module Mathpack
|
|
|
46
49
|
end
|
|
47
50
|
result
|
|
48
51
|
end
|
|
49
|
-
|
|
50
|
-
def self.solve_ni_2(&f)
|
|
51
|
-
result = 0.0
|
|
52
|
-
coefficients_array = [0.004530009906, 0.1570673203, 0.7246295952, 0.7246295952, 0.1570673203, 0.004530009906]
|
|
53
|
-
nodes_array = [-2.3506049737, -1.3358490740, -0.4360774119, 0.4360774119, 1.3358490740, 2.3506049737]
|
|
54
|
-
nodes_array.each_index do |i|
|
|
55
|
-
result += coefficients_array[i] * Math.exp(nodes_array[i]**2) * f.call(nodes_array[i])
|
|
56
|
-
end
|
|
57
|
-
result
|
|
58
|
-
end
|
|
59
52
|
end
|
|
60
53
|
end
|
data/lib/mathpack/io.rb
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
module Mathpack
|
|
2
|
+
module IO
|
|
3
|
+
def self.print_table_function(params = {})
|
|
4
|
+
fail 'Arrays length dismatch' if params[:x].length != params[:y].length
|
|
5
|
+
File.open(params[:filename] || 'table_function.csv', 'w+') do |file|
|
|
6
|
+
file.write("#{params[:labels][:x]};#{params[:labels][:y]}\n") if params[:labels] && params[:labels][:x] && params[:labels][:y]
|
|
7
|
+
params[:x].each_index do |i|
|
|
8
|
+
file.write("#{params[:x][i]};#{params[:y][i]}\n")
|
|
9
|
+
end
|
|
10
|
+
end
|
|
11
|
+
end
|
|
12
|
+
end
|
|
13
|
+
end
|
data/lib/mathpack/sle.rb
CHANGED
|
@@ -6,11 +6,12 @@ module Mathpack
|
|
|
6
6
|
|
|
7
7
|
def self.solve(params)
|
|
8
8
|
type = params[:f].class
|
|
9
|
-
@matrix = params[:matrix].
|
|
10
|
-
@f = params[:f].
|
|
9
|
+
@matrix = Marshal.load(Marshal.dump(params[:matrix])).to_a
|
|
10
|
+
@f = params[:f].to_a.flatten
|
|
11
|
+
fail 'Incorrect size of array or vector' unless @matrix.length == @matrix.first.length && @matrix.length == @f.length
|
|
11
12
|
@number = @f.length
|
|
12
13
|
@x = Array.new(@number) { |i| i + 1 }
|
|
13
|
-
fail '
|
|
14
|
+
fail 'Matrix is singular' unless solve_direct
|
|
14
15
|
type == Matrix ? Matrix.row_vector(solve_reverse) : solve_reverse
|
|
15
16
|
end
|
|
16
17
|
|
data/lib/mathpack/statistics.rb
CHANGED
|
@@ -2,6 +2,7 @@ module Mathpack
|
|
|
2
2
|
class Statistics
|
|
3
3
|
def initialize(series)
|
|
4
4
|
@series = series
|
|
5
|
+
@data_set, @frequency = parse_series(series)
|
|
5
6
|
end
|
|
6
7
|
|
|
7
8
|
def number
|
|
@@ -21,27 +22,31 @@ module Mathpack
|
|
|
21
22
|
end
|
|
22
23
|
|
|
23
24
|
def kurtosis
|
|
24
|
-
central_moment(4) / variance**2
|
|
25
|
+
central_moment(4) / variance**2 - 3.0
|
|
25
26
|
end
|
|
26
27
|
|
|
27
28
|
def max
|
|
28
|
-
@
|
|
29
|
+
@data_set.max
|
|
29
30
|
end
|
|
30
31
|
|
|
31
32
|
def min
|
|
32
|
-
@
|
|
33
|
+
@data_set.min
|
|
33
34
|
end
|
|
34
35
|
|
|
35
36
|
def raw_moment(power)
|
|
36
37
|
raw_moment = 0.0
|
|
37
|
-
@
|
|
38
|
+
@data_set.each_index do |i|
|
|
39
|
+
raw_moment += @frequency[i] * @data_set[i]**power
|
|
40
|
+
end
|
|
38
41
|
raw_moment / number
|
|
39
42
|
end
|
|
40
43
|
|
|
41
44
|
def central_moment(power)
|
|
42
45
|
central_moment = 0.0
|
|
43
46
|
m = mean
|
|
44
|
-
@
|
|
47
|
+
@data_set.each_index do |i|
|
|
48
|
+
central_moment += @frequency[i] * (@data_set[i] - m)**power
|
|
49
|
+
end
|
|
45
50
|
central_moment / number
|
|
46
51
|
end
|
|
47
52
|
|
|
@@ -53,14 +58,9 @@ module Mathpack
|
|
|
53
58
|
|
|
54
59
|
def print_empirical_cdf_to_csv(filename)
|
|
55
60
|
step = 0.5 * (max - min) / number
|
|
56
|
-
|
|
57
|
-
|
|
58
|
-
|
|
59
|
-
file.write("#{val};")
|
|
60
|
-
file.write("#{empirical_cdf(val)}\n")
|
|
61
|
-
val += step
|
|
62
|
-
end
|
|
63
|
-
end
|
|
61
|
+
nodes = Mathpack::Approximation.generate_nodes(from: min - step, to: max + step, step: step)
|
|
62
|
+
values = nodes.map { |x| empirical_cdf(x) }
|
|
63
|
+
Mathpack::IO.print_table_function(filename: filename, x: nodes, y: values)
|
|
64
64
|
end
|
|
65
65
|
|
|
66
66
|
def empirical_pdf(x)
|
|
@@ -72,14 +72,9 @@ module Mathpack
|
|
|
72
72
|
|
|
73
73
|
def print_empirical_pdf_to_csv(filename)
|
|
74
74
|
step = 0.5 * (max - min) / number
|
|
75
|
-
|
|
76
|
-
|
|
77
|
-
|
|
78
|
-
file.write("#{val};")
|
|
79
|
-
file.write("#{empirical_pdf(val)}\n")
|
|
80
|
-
val += step
|
|
81
|
-
end
|
|
82
|
-
end
|
|
75
|
+
nodes = Mathpack::Approximation.generate_nodes(from: min - 10 * step, to: max + 10 * step, step: step)
|
|
76
|
+
values = nodes.map { |x| empirical_pdf(x) }
|
|
77
|
+
Mathpack::IO.print_table_function(filename: filename, x: nodes, y: values)
|
|
83
78
|
end
|
|
84
79
|
|
|
85
80
|
def trend(params = {})
|
|
@@ -93,5 +88,19 @@ module Mathpack
|
|
|
93
88
|
def heaviside(x)
|
|
94
89
|
x <= 0 ? 0 : 1
|
|
95
90
|
end
|
|
91
|
+
|
|
92
|
+
def parse_series(series)
|
|
93
|
+
data_set = []
|
|
94
|
+
frequency = []
|
|
95
|
+
series.each do |element|
|
|
96
|
+
if data_set.include? element
|
|
97
|
+
frequency[data_set.index(element)] += 1
|
|
98
|
+
else
|
|
99
|
+
data_set << element
|
|
100
|
+
frequency[data_set.index(element)] = 1
|
|
101
|
+
end
|
|
102
|
+
end
|
|
103
|
+
[data_set, frequency]
|
|
104
|
+
end
|
|
96
105
|
end
|
|
97
106
|
end
|
data/lib/mathpack/version.rb
CHANGED
data/lib/mathpack.rb
CHANGED
data/spec/approximation_spec.rb
CHANGED
|
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ describe 'Approximation' do
|
|
|
5
5
|
let(:x_start) { 0.0 }
|
|
6
6
|
let(:x_end) { 10.0 }
|
|
7
7
|
let(:step) { 0.25 }
|
|
8
|
-
let(:nodes) { Mathpack::Approximation.generate_nodes(
|
|
8
|
+
let(:nodes) { Mathpack::Approximation.generate_nodes(from: x_start, to: x_end, step: step) }
|
|
9
9
|
let(:values) { Mathpack::Approximation.fill_f(nodes){ |val| val**2 } }
|
|
10
10
|
|
|
11
11
|
it 'should generate nodes' do
|
|
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ describe 'Approximation' do
|
|
|
15
15
|
end
|
|
16
16
|
|
|
17
17
|
it 'should generate correct nodes' do
|
|
18
|
-
nodes = Mathpack::Approximation.generate_nodes(
|
|
18
|
+
nodes = Mathpack::Approximation.generate_nodes(from: 0, to: 1, step: 0.001)
|
|
19
19
|
expect(nodes.last).to eq(1.0)
|
|
20
20
|
end
|
|
21
21
|
|
data/spec/sle_spec.rb
CHANGED
|
@@ -12,12 +12,26 @@ describe 'SLE' do
|
|
|
12
12
|
expect(Mathpack::SLE.solve(matrix: a, f: b)).to eq([-1.0, 2.0, 4.0])
|
|
13
13
|
end
|
|
14
14
|
|
|
15
|
-
it 'should raise error' do
|
|
15
|
+
it 'should raise error when matrix is singular' do
|
|
16
16
|
expect { Mathpack::SLE.solve(matrix: unsolved, f: b) }.to raise_error
|
|
17
17
|
end
|
|
18
18
|
|
|
19
|
+
it 'should raise error when matrix has incorrect size' do
|
|
20
|
+
b << 1
|
|
21
|
+
expect { Mathpack::SLE.solve(matrix: a, f: b) }.to raise_error
|
|
22
|
+
b.pop
|
|
23
|
+
a << [1, 2, 3, 4]
|
|
24
|
+
expect { Mathpack::SLE.solve(matrix: a, f: b) }.to raise_error
|
|
25
|
+
end
|
|
26
|
+
|
|
19
27
|
it 'should return vector if matrix class is given' do
|
|
20
28
|
expect(Mathpack::SLE.solve(matrix: matrix_a, f: vector_b)).to eq(Matrix.row_vector [-1.0, 2.0, 4.0])
|
|
21
29
|
end
|
|
30
|
+
|
|
31
|
+
it 'should not change source data' do
|
|
32
|
+
Mathpack::SLE.solve(matrix: a, f: b)
|
|
33
|
+
expect(a).to eq([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [3, 5, 2]])
|
|
34
|
+
expect(b).to eq([15, 30, 15])
|
|
35
|
+
end
|
|
22
36
|
end
|
|
23
37
|
end
|
data/spec/statistics_spec.rb
CHANGED
|
@@ -3,35 +3,43 @@ describe 'Statistics' do
|
|
|
3
3
|
|
|
4
4
|
describe '#calculate statistics functions' do
|
|
5
5
|
|
|
6
|
-
let(:data)
|
|
6
|
+
let(:data) do
|
|
7
|
+
array = []
|
|
8
|
+
array << [0]*50
|
|
9
|
+
array << [1]*35
|
|
10
|
+
array << [2]*10
|
|
11
|
+
array << [3]*4
|
|
12
|
+
array << [4]*1
|
|
13
|
+
array.flatten
|
|
14
|
+
end
|
|
7
15
|
let(:stat) { Mathpack::Statistics.new(data) }
|
|
8
16
|
|
|
9
17
|
it 'should calculate number of elements' do
|
|
10
|
-
expect(stat.number).to eq(
|
|
18
|
+
expect(stat.number).to eq(100)
|
|
11
19
|
end
|
|
12
20
|
|
|
13
21
|
it 'should calculate mean' do
|
|
14
|
-
expect(stat.mean).to eq(
|
|
22
|
+
expect(stat.mean).to eq(0.71)
|
|
15
23
|
end
|
|
16
24
|
|
|
17
25
|
it 'should calculate variance' do
|
|
18
|
-
expect(stat.variance).to eq(
|
|
26
|
+
expect(stat.variance).to eq(0.7659)
|
|
19
27
|
end
|
|
20
28
|
|
|
21
29
|
it 'should calculate skewness' do
|
|
22
|
-
expect(stat.skewness).to eq(
|
|
30
|
+
expect(stat.skewness).to eq(1.3139557526940238)
|
|
23
31
|
end
|
|
24
32
|
|
|
25
33
|
it 'should calculate kurtosis' do
|
|
26
|
-
expect(stat.kurtosis).to eq(1.
|
|
34
|
+
expect(stat.kurtosis).to eq(1.5654257435282322)
|
|
27
35
|
end
|
|
28
36
|
|
|
29
37
|
it 'should calculate the minimal element' do
|
|
30
|
-
expect(stat.min).to eq(
|
|
38
|
+
expect(stat.min).to eq(0)
|
|
31
39
|
end
|
|
32
40
|
|
|
33
41
|
it 'should calculate the maximal element' do
|
|
34
|
-
expect(stat.max).to eq(
|
|
42
|
+
expect(stat.max).to eq(4)
|
|
35
43
|
end
|
|
36
44
|
|
|
37
45
|
it 'should calculate first raw moment equal to mean' do
|
|
@@ -43,25 +51,25 @@ describe 'Statistics' do
|
|
|
43
51
|
end
|
|
44
52
|
|
|
45
53
|
it 'should calculate raw moments' do
|
|
46
|
-
expect(stat.raw_moment(3)).to eq(
|
|
54
|
+
expect(stat.raw_moment(3)).to eq(2.87)
|
|
47
55
|
end
|
|
48
56
|
|
|
49
57
|
it 'should calculate central moments' do
|
|
50
|
-
expect(stat.central_moment(5)).to eq(
|
|
58
|
+
expect(stat.central_moment(5)).to eq(6.641392040400001)
|
|
51
59
|
end
|
|
52
60
|
|
|
53
61
|
it 'should calculate empirical cdf values in points' do
|
|
54
62
|
expect(stat.empirical_cdf(stat.min - 0.1)).to eq(0.0)
|
|
55
63
|
expect(stat.empirical_cdf(stat.max + 0.1)).to eq(1.0)
|
|
56
|
-
expect(stat.empirical_cdf(stat.mean)).to eq(0.
|
|
64
|
+
expect(stat.empirical_cdf(stat.mean)).to eq(0.5)
|
|
57
65
|
end
|
|
58
66
|
|
|
59
67
|
it 'should calculate empirical pdf values in points' do
|
|
60
|
-
expect(stat.empirical_pdf(stat.mean)).to eq(0.
|
|
68
|
+
expect(stat.empirical_pdf(stat.mean)).to eq( 0.4308095750697591)
|
|
61
69
|
end
|
|
62
70
|
|
|
63
71
|
it 'should find trend' do
|
|
64
|
-
expect(stat.trend(polynom_power: 2)).to eq('0.
|
|
72
|
+
expect(stat.trend(polynom_power: 2)).to eq('0.00042531864230840915*x^2 - 0.016860573212183233*x + 0.12239332096475111')
|
|
65
73
|
end
|
|
66
74
|
end
|
|
67
75
|
end
|
metadata
CHANGED
|
@@ -1,14 +1,14 @@
|
|
|
1
1
|
--- !ruby/object:Gem::Specification
|
|
2
2
|
name: mathpack
|
|
3
3
|
version: !ruby/object:Gem::Version
|
|
4
|
-
version: 0.4.
|
|
4
|
+
version: 0.4.2
|
|
5
5
|
platform: ruby
|
|
6
6
|
authors:
|
|
7
7
|
- maxmilan
|
|
8
8
|
autorequire:
|
|
9
9
|
bindir: bin
|
|
10
10
|
cert_chain: []
|
|
11
|
-
date: 2015-
|
|
11
|
+
date: 2015-03-07 00:00:00.000000000 Z
|
|
12
12
|
dependencies:
|
|
13
13
|
- !ruby/object:Gem::Dependency
|
|
14
14
|
name: bundler
|
|
@@ -55,6 +55,7 @@ files:
|
|
|
55
55
|
- lib/mathpack/approximation.rb
|
|
56
56
|
- lib/mathpack/equation.rb
|
|
57
57
|
- lib/mathpack/integration.rb
|
|
58
|
+
- lib/mathpack/io.rb
|
|
58
59
|
- lib/mathpack/sle.rb
|
|
59
60
|
- lib/mathpack/statistics.rb
|
|
60
61
|
- lib/mathpack/version.rb
|