aws-lex-conversation 6.1.0 → 6.4.0
Sign up to get free protection for your applications and to get access to all the features.
- checksums.yaml +4 -4
- data/.rubocop.yml +2 -0
- data/CHANGELOG.md +36 -1
- data/README.md +224 -56
- data/aws-lex-conversation.gemspec +2 -1
- data/lib/aws/lex/conversation/base.rb +5 -0
- data/lib/aws/lex/conversation/response/elicit_slot.rb +3 -2
- data/lib/aws/lex/conversation/simulator.rb +28 -0
- data/lib/aws/lex/conversation/slot/elicitation.rb +3 -5
- data/lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/checkpoint.rb +22 -0
- data/lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/dialog_action.rb +3 -1
- data/lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/event.rb +5 -1
- data/lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/message.rb +5 -0
- data/lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/proposed_next_state.rb +21 -0
- data/lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/slot.rb +1 -1
- data/lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/slot_elicitation_style.rb +17 -0
- data/lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/transcription/resolved_context.rb +17 -0
- data/lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/transcription.rb +24 -0
- data/lib/aws/lex/conversation/version.rb +1 -1
- data/lib/aws/lex/conversation.rb +26 -5
- metadata +10 -5
checksums.yaml
CHANGED
|
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
|
|
1
1
|
---
|
|
2
2
|
SHA256:
|
|
3
|
-
metadata.gz:
|
|
4
|
-
data.tar.gz:
|
|
3
|
+
metadata.gz: 61c4edf66e617becb5f2c7aa3611e32c7eeef58ab2cb9533f1816abcaf675ab8
|
|
4
|
+
data.tar.gz: 485e85d4c07d25527752e2451e99c02af1eae808dfd9e048efa147a8042d76aa
|
|
5
5
|
SHA512:
|
|
6
|
-
metadata.gz:
|
|
7
|
-
data.tar.gz:
|
|
6
|
+
metadata.gz: 03f8814a82e0f6cea94033ef13d4f59ade4bb74a1cee26fe554151bff1b0785f32f0c3aef17e2a2293a1c71dd4442679ee516a9d16bd1bc94069e0e00dccfb3f
|
|
7
|
+
data.tar.gz: 360cb550a21e90e6063722c676071ed59d083e6a03eb44281f2517b79b8e2a70ccfeb435ad0df4b37b1c46a8e6e9e4258505622b6396f3168a140eb9e2998524
|
data/.rubocop.yml
CHANGED
data/CHANGELOG.md
CHANGED
|
@@ -1,11 +1,45 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
# 6.4.0 - Feb 10, 2022
|
|
2
|
+
|
|
3
|
+
* Add support for the new protocol properties of `proposedNextState` and `transcriptions`. This enables support for [transcription confidence scores](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lexv2/latest/dg/using-transcript-confidence-scores.html).
|
|
4
|
+
* Expose the following methods on `Aws::Lex::Conversation` instances:
|
|
5
|
+
- `proposed_next_state?`: Returns `true` if a `proposedNextState` value is present or `false` otherwise.
|
|
6
|
+
- `proposed_next_state`: Returns an `Aws::Lex::Conversation::Type::ProposedNextState` instance. May return `nil`.
|
|
7
|
+
- `transcriptions`: Returns an array of `Aws::Lex::Conversation::Type::Transcription` instances. Defaults to a empty array if the `transcriptions` property is not present.
|
|
8
|
+
* Make the `content_type` attribute in the constructor for `Aws::Lex::Conversation::Type::Message` default to `PlainText` when not present.
|
|
9
|
+
|
|
10
|
+
# 6.3.0 - Nov 22, 2021
|
|
11
|
+
|
|
12
|
+
* Add support for the recently added `slotElicitationStyle` property when generating an `ElicitSlot` repsonse ([documentation](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lexv2/latest/dg/using-spelling.html)).
|
|
13
|
+
|
|
14
|
+
You can generate an `ElicitSlot` response now with an optional `slot_elicitation_style` property to allow for spelling support:
|
|
15
|
+
|
|
16
|
+
```ruby
|
|
17
|
+
conversation.elicit_slot(
|
|
18
|
+
slot_to_elicit: 'LastName',
|
|
19
|
+
slot_elicitation_style: 'SpellByWord' # one of Default, SpellByLetter, or SpellByWord
|
|
20
|
+
)
|
|
21
|
+
```
|
|
22
|
+
|
|
23
|
+
# 6.2.0 - Sept 28, 2021
|
|
24
|
+
|
|
25
|
+
* Add a `Aws::Lex::Conversation#restore_from!` method that accepts a checkpoint parameter. This method modifies the underlying conversation state to match the data from the saved checkpoint.
|
|
26
|
+
* Make the `dialog_action_type` parameter on `Aws::Lex::Conversation#checkpoint!` default to `Delegate` if not specified as a developer convenience.
|
|
27
|
+
* Allow developers to pass an optional `intent` override parameter on `Aws::Lex::Conversation#checkpoint!` for convenience.
|
|
28
|
+
* Update the README with advanced examples for the conversation stash and checkpoints.
|
|
29
|
+
|
|
30
|
+
# 6.1.1 - Sept 22, 2021
|
|
31
|
+
|
|
32
|
+
* renamed `maximum_elicitations` to `max_retries` and made it backwards compatible to make the param name clear, by default this value is zero, allowing each slot to elicit only once
|
|
33
|
+
|
|
1
34
|
# 6.1.0 - Sept 7, 2021
|
|
35
|
+
|
|
2
36
|
Added helper methods for clearing active contexts
|
|
37
|
+
|
|
3
38
|
```ruby
|
|
4
39
|
conversation.clear_context!(name: 'test') # clears this specific active context
|
|
5
40
|
conversation.clear_all_contexts! # clears all current active contexts
|
|
6
41
|
```
|
|
7
42
|
|
|
8
|
-
|
|
9
43
|
# 6.0.0 - Sept 7, 2021
|
|
10
44
|
|
|
11
45
|
* **breaking change** - Modify `Aws::Lex::Conversation::Type::Base#computed_property` to accept a block instead of a callable argument. This is an internal class and should not require any application-level changes.
|
|
@@ -63,6 +97,7 @@ it 'creates an event' do
|
|
|
63
97
|
expect(event).to include_session_values(username: 'jane.doe')
|
|
64
98
|
end
|
|
65
99
|
```
|
|
100
|
+
|
|
66
101
|
* Add a few convenience methods to `Aws::Lex::Conversation` instances for dealing with active contexts:
|
|
67
102
|
- `#active_context(name:)`:
|
|
68
103
|
|
data/README.md
CHANGED
|
@@ -1,19 +1,15 @@
|
|
|
1
|
-
# Aws::Lex::Conversation
|
|
1
|
+
# `Aws::Lex::Conversation`
|
|
2
2
|
|
|
3
|
-
|
|
3
|
+
Building a chatbot with [AWS Lex](https://aws.amazon.com/lex/) is really fun! Unfortunately implementing your bot's behaviour with the [Lex/Lambda event protocol](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lexv2/latest/dg/lambda.html) is less fun.
|
|
4
4
|
|
|
5
|
-
|
|
5
|
+
But don't worry - we've done the hard work for you!
|
|
6
6
|
|
|
7
|
-
|
|
8
|
-
|
|
9
|
-
### Lex V1
|
|
10
|
-
|
|
11
|
-
Version 3.x is the last major version of this gem that will support Lex V1.
|
|
7
|
+
`Aws::Lex::Conversation` makes it simple to build dynamic, conversational chatbots with AWS Lex and AWS Lambda!
|
|
12
8
|
|
|
13
|
-
|
|
9
|
+
## Installation
|
|
14
10
|
|
|
15
11
|
```ruby
|
|
16
|
-
gem 'aws-lex-conversation'
|
|
12
|
+
gem 'aws-lex-conversation'
|
|
17
13
|
```
|
|
18
14
|
|
|
19
15
|
And then execute:
|
|
@@ -22,96 +18,162 @@ And then execute:
|
|
|
22
18
|
bundle install
|
|
23
19
|
```
|
|
24
20
|
|
|
25
|
-
|
|
21
|
+
**Please Note:** This library currently supports [AWS Lex Version 2](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lexv2/latest/dg/lambda.html). If you're looking for Lex V1 support, lock `aws-lex-conversation` to `~> 3.0` in your `Gemfile`.
|
|
22
|
+
|
|
23
|
+
## Core Concepts
|
|
24
|
+
|
|
25
|
+
### The Conversation Instance
|
|
26
26
|
|
|
27
|
-
|
|
27
|
+
Instances of `Aws::Lex::Conversation` wrap the Lex input/output event format and make it easy to manage conversation dialog.
|
|
28
28
|
|
|
29
|
-
|
|
29
|
+
Imagine you have a `ButlerBot` configured with a `ServeBreakfast` intent and `BreakfastFood` slot.
|
|
30
|
+
|
|
31
|
+
The backing lambda handler for your bot might look something like:
|
|
30
32
|
|
|
31
33
|
```ruby
|
|
32
|
-
|
|
34
|
+
require "aws-lex-conversation"
|
|
35
|
+
|
|
36
|
+
def lambda_handler(event:, context:)
|
|
37
|
+
# The conversation instance validates and wraps the Lex input event
|
|
38
|
+
conversation = Aws::Lex::Conversation.new(event: event, context: context)
|
|
39
|
+
|
|
40
|
+
# Return a Close dialog action to our Lex bot and end the conversation
|
|
41
|
+
conversation.close(
|
|
42
|
+
fulfillment_state: "Fulfilled",
|
|
43
|
+
messages: [
|
|
44
|
+
# We can construct response messages using wrapper classes.
|
|
45
|
+
Aws::Lex::Conversation::Type::Message.new(
|
|
46
|
+
content: "Hi - I'm a 🤖!"
|
|
47
|
+
),
|
|
48
|
+
# Or we can pass a Hash that directly maps to the Lex response format
|
|
49
|
+
{
|
|
50
|
+
content: "Your intent is: #{conversation.intent_name}",
|
|
51
|
+
contentType: "PlainText"
|
|
52
|
+
},
|
|
53
|
+
{
|
|
54
|
+
content: "Here's your #{conversation.slots[:BreakfastFood].value}!",
|
|
55
|
+
contentType: "PlainText"
|
|
56
|
+
}
|
|
57
|
+
]
|
|
58
|
+
)
|
|
59
|
+
end
|
|
33
60
|
```
|
|
34
61
|
|
|
35
|
-
|
|
62
|
+
This lambda handler would generate the following dialog:
|
|
36
63
|
|
|
37
|
-
|
|
38
|
-
|
|
64
|
+
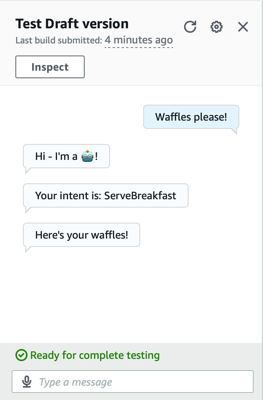
|
|
65
|
+
|
|
66
|
+
All data from the Lex input event is exposed via the `lex` attribute. By convention, the `lex` attribute directly translates input event attributes from `camelCase` to `snake_case`.
|
|
67
|
+
|
|
68
|
+
We also provide some helpers to help manage the conversation. For example:
|
|
69
|
+
|
|
70
|
+
```ruby
|
|
71
|
+
# returns true if the lambda function was invoked as a DialogCodeHook
|
|
72
|
+
conversation.lex.invocation_source.dialog_code_hook?
|
|
73
|
+
|
|
74
|
+
# returns true if the InputMode is Speech
|
|
75
|
+
conversation.lex.input_mode.speech?
|
|
76
|
+
|
|
77
|
+
# you can easily set or retrieve a session values
|
|
78
|
+
conversation.session[:name] = "Jane"
|
|
79
|
+
conversation.session[:name] # => "Jane"
|
|
80
|
+
|
|
81
|
+
# dealing with slot data is simple
|
|
82
|
+
conversation.slots[:BreakfastFood].filled? # returns true if a slot value is present
|
|
83
|
+
conversation.slots[:Hometown].blank? # returns true if a slot value is nil/empty
|
|
84
|
+
conversation.slots[:FirstName].value # => "John"
|
|
39
85
|
```
|
|
40
86
|
|
|
41
|
-
|
|
87
|
+
### The Handler Chain
|
|
88
|
+
|
|
89
|
+
Conversational dialog gets complex quickly! Conversation instances include a handler chain that can help manage this complexity.
|
|
42
90
|
|
|
43
|
-
|
|
91
|
+
Each handler in the chain defines the prerequisites necessary for the handler to generate a response.
|
|
44
92
|
|
|
45
|
-
|
|
93
|
+
You can configure the handler chain as follows:
|
|
46
94
|
|
|
47
95
|
```ruby
|
|
48
|
-
def
|
|
96
|
+
def lambda_handler(event:, context:)
|
|
49
97
|
conversation = Aws::Lex::Conversation.new(event: event, context: context)
|
|
50
98
|
|
|
51
|
-
# define a chain of your own Handler classes
|
|
52
99
|
conversation.handlers = [
|
|
100
|
+
# You need to define custom handler classes yourself
|
|
101
|
+
{ handler: ServeBreakfast },
|
|
102
|
+
{ handler: FallbackIntent },
|
|
103
|
+
# We offer a few "built in" handlers
|
|
53
104
|
{
|
|
54
105
|
handler: Aws::Lex::Conversation::Handler::Delegate,
|
|
55
106
|
options: {
|
|
56
|
-
|
|
107
|
+
# If we get this far, always return a Delegate action
|
|
108
|
+
respond_on: ->(_) { true }
|
|
57
109
|
}
|
|
58
110
|
}
|
|
59
111
|
]
|
|
60
112
|
|
|
61
|
-
#
|
|
113
|
+
# The respond method will execute each handler sequentially and return a Lex response
|
|
62
114
|
conversation.respond
|
|
63
115
|
end
|
|
64
116
|
```
|
|
65
117
|
|
|
66
|
-
|
|
118
|
+
### Writing Your Own Handler
|
|
119
|
+
|
|
120
|
+
Generally, custom behaviour in your flow is achieved by defining your own handler class. Handler classes must:
|
|
67
121
|
|
|
68
122
|
1. Inherit from `Aws::Lex::Conversation::Handler::Base`.
|
|
69
123
|
2. Define a `will_respond?(conversation)` method that returns a boolean value.
|
|
70
124
|
3. Define a `response(conversation)` method to return final response to Lex. This method is called if `will_respond?` returns `true`.
|
|
71
125
|
|
|
72
|
-
|
|
126
|
+
Handlers in the chain are invoked sequentially in the order defined.
|
|
73
127
|
|
|
74
|
-
The first handler that returns `true` for the `will_respond?` method will provide the final Lex response action.
|
|
128
|
+
The first handler in the chain that returns `true` for the `will_respond?` method will provide the final Lex response action.
|
|
75
129
|
|
|
76
|
-
|
|
130
|
+
Here's an example for the `ServeBreakfast` and `FallbackIntent` handlers above:
|
|
77
131
|
|
|
78
132
|
```ruby
|
|
79
|
-
class
|
|
133
|
+
class ServeBreakfast < Aws::Lex::Conversation::Handler::Base
|
|
80
134
|
def will_respond?(conversation)
|
|
81
|
-
conversation.
|
|
82
|
-
conversation.
|
|
83
|
-
conversation.slots[:name].filled? # our expected slot value is set
|
|
135
|
+
conversation.intent_name == "ServeBreakfast" &&
|
|
136
|
+
conversation.slots[:BreakfastFood].filled?
|
|
84
137
|
end
|
|
85
138
|
|
|
86
139
|
def response(conversation)
|
|
87
|
-
|
|
88
|
-
|
|
89
|
-
|
|
90
|
-
# will be normalized to a value that complies with the Lex response format.
|
|
91
|
-
#
|
|
92
|
-
# You can also specify raw values for the response:
|
|
93
|
-
#
|
|
94
|
-
# conversation.close(
|
|
95
|
-
# fulfillment_state: 'Fulfilled',
|
|
96
|
-
# messages: [{ content: "Hello, #{name}!", contentType: 'PlainText' }]
|
|
97
|
-
# )
|
|
98
|
-
#
|
|
140
|
+
food = conversation.slots[:BreakfastFood].value
|
|
141
|
+
emoji = food == "waffle" ? "🧇" : "🥓"
|
|
142
|
+
|
|
99
143
|
conversation.close(
|
|
100
|
-
fulfillment_state:
|
|
144
|
+
fulfillment_state: "Fulfilled",
|
|
101
145
|
messages: [
|
|
102
|
-
|
|
103
|
-
content: "
|
|
104
|
-
|
|
105
|
-
|
|
146
|
+
{
|
|
147
|
+
content: "Here's your #{emoji}!",
|
|
148
|
+
contentType: "PlainText"
|
|
149
|
+
}
|
|
150
|
+
]
|
|
151
|
+
)
|
|
152
|
+
end
|
|
153
|
+
end
|
|
154
|
+
|
|
155
|
+
class FallbackIntent < Aws::Lex::Conversation::Handler::Base
|
|
156
|
+
def will_respond?(conversation)
|
|
157
|
+
conversation.intent_name == "FallbackIntent"
|
|
158
|
+
end
|
|
159
|
+
|
|
160
|
+
def response(conversation)
|
|
161
|
+
conversation.close(
|
|
162
|
+
fulfillment_state: 'Failed',
|
|
163
|
+
messages: [
|
|
164
|
+
{
|
|
165
|
+
content: "Sorry - I'm not sure what you said!",
|
|
166
|
+
contentType: "PlainText"
|
|
167
|
+
}
|
|
106
168
|
]
|
|
107
169
|
)
|
|
108
170
|
end
|
|
109
171
|
end
|
|
110
172
|
```
|
|
111
173
|
|
|
112
|
-
|
|
174
|
+
### Built-In Handlers
|
|
113
175
|
|
|
114
|
-
|
|
176
|
+
#### `Aws::Lex::Conversation::Handler::Echo`
|
|
115
177
|
|
|
116
178
|
This handler simply returns a close response with a message that matches the `inputTranscript` property of the input event.
|
|
117
179
|
|
|
@@ -140,7 +202,7 @@ conversation.handlers = [
|
|
|
140
202
|
conversation.respond # => { dialogAction: { type: 'Close' } ... }
|
|
141
203
|
```
|
|
142
204
|
|
|
143
|
-
|
|
205
|
+
#### `Aws::Lex::Conversation::Handler::Delegate`
|
|
144
206
|
|
|
145
207
|
This handler returns a `Delegate` response to the Lex bot (i.e. "do the next bot action").
|
|
146
208
|
|
|
@@ -163,7 +225,7 @@ conversation.handlers = [
|
|
|
163
225
|
conversation.respond # => { dialogAction: { type: 'Delegate' } }
|
|
164
226
|
```
|
|
165
227
|
|
|
166
|
-
|
|
228
|
+
#### `Aws::Lex::Conversation::Handler::SlotResolution`
|
|
167
229
|
|
|
168
230
|
This handler will set all slot values equal to their top resolution in the input event. The handler then calls the next handler in the chain for a response.
|
|
169
231
|
|
|
@@ -191,6 +253,114 @@ conversation.handlers = [
|
|
|
191
253
|
conversation.respond # => { dialogAction: { type: 'Delegate' } }
|
|
192
254
|
```
|
|
193
255
|
|
|
256
|
+
## Advanced Concepts
|
|
257
|
+
|
|
258
|
+
This library provides a few constructs to help manage complex interactions:
|
|
259
|
+
|
|
260
|
+
### Data Stash
|
|
261
|
+
|
|
262
|
+
`Aws::Lex::Conversation` instances implement a `stash` method that can be used to store temporary data within a single invocation.
|
|
263
|
+
|
|
264
|
+
A conversation's stashed data will not be persisted between multiple invocations of your lambda function.
|
|
265
|
+
|
|
266
|
+
The conversation stash is a great spot to store deserialized data from the session, or invocation-specific state that needs to be shared between handler classes.
|
|
267
|
+
|
|
268
|
+
This example illustrates how the stash can be used to store deserialized data from the session:
|
|
269
|
+
|
|
270
|
+
```ruby
|
|
271
|
+
# given we have JSON-serialized data in as a persisted session value
|
|
272
|
+
conversation.session[:user_data] = '{"name":"Jane","id":1234,"email":"test@example.com"}'
|
|
273
|
+
# we can deserialize the data into a Hash that we store in the conversation stash
|
|
274
|
+
conversation.stash[:user] = JSON.parse(conversation.session[:user_data])
|
|
275
|
+
# later on we can reference our stashed data (within the same invocation)
|
|
276
|
+
conversation.stash[:user] # => {"name"=>"Jane", "id"=>1234, "email"=>"test@example.com"}
|
|
277
|
+
```
|
|
278
|
+
|
|
279
|
+
### Checkpoints
|
|
280
|
+
|
|
281
|
+
A conversation may transition between many different topics as the interaction progresses. This type of state transition can be easily handled with checkpoints.
|
|
282
|
+
|
|
283
|
+
When a checkpoint is created, all intent and slot data is encoded and stored into a `checkpoints` session value. This data persists between invocations, and is not removed until the checkpoint is restored.
|
|
284
|
+
|
|
285
|
+
You can create a checkpoint as follows:
|
|
286
|
+
|
|
287
|
+
```ruby
|
|
288
|
+
# we're ready to fulfill the OrderFlowers intent, but we want to elicit another intent first
|
|
289
|
+
conversation.checkpoint!(
|
|
290
|
+
label: 'order_flowers',
|
|
291
|
+
dialog_action_type: 'Close' # defaults to 'Delegate' if not specified
|
|
292
|
+
)
|
|
293
|
+
conversation.elicit_intent(
|
|
294
|
+
messages: [
|
|
295
|
+
{
|
|
296
|
+
content: 'Thanks! Before I place your order, is there anything else I can help with?',
|
|
297
|
+
contentType: 'PlainText'
|
|
298
|
+
}
|
|
299
|
+
]
|
|
300
|
+
)
|
|
301
|
+
```
|
|
302
|
+
|
|
303
|
+
You can restore the checkpoint in one of two ways:
|
|
304
|
+
|
|
305
|
+
```ruby
|
|
306
|
+
# in a future invocation, we can fetch an instance of the checkpoint and easily
|
|
307
|
+
# restore the conversation to the previous state
|
|
308
|
+
checkpoint = conversation.checkpoint(label: 'order_flowers')
|
|
309
|
+
checkpoint.restore!(
|
|
310
|
+
fulfillment_state: 'Fulfilled',
|
|
311
|
+
messages: [
|
|
312
|
+
{
|
|
313
|
+
content: 'Okay, your flowers have been ordered! Thanks!',
|
|
314
|
+
contentType: 'PlainText'
|
|
315
|
+
}
|
|
316
|
+
]
|
|
317
|
+
) # => our response object to Lex is returned
|
|
318
|
+
```
|
|
319
|
+
|
|
320
|
+
It's also possible to restore state from a checkpoint and utilize the conversation's handler chain:
|
|
321
|
+
|
|
322
|
+
```ruby
|
|
323
|
+
class AnotherIntent < Aws::Lex::Conversation::Handler::Base
|
|
324
|
+
def will_respond?(conversation)
|
|
325
|
+
conversation.intent_name == 'AnotherIntent' &&
|
|
326
|
+
conversation.checkpoint?(label: 'order_flowers')
|
|
327
|
+
end
|
|
328
|
+
|
|
329
|
+
def response(conversation)
|
|
330
|
+
checkpoint = conversation.checkpoint(label: 'order_flowers')
|
|
331
|
+
# replace the conversation's current resolved intent/slot data with the saved checkpoint data
|
|
332
|
+
conversation.restore_from!(checkpoint)
|
|
333
|
+
# call the next handler in the chain to produce a response
|
|
334
|
+
successor.handle(conversation)
|
|
335
|
+
end
|
|
336
|
+
end
|
|
337
|
+
|
|
338
|
+
class OrderFlowers < Aws::Lex::Conversation::Handler::Base
|
|
339
|
+
def will_respond?(conversation)
|
|
340
|
+
conversation.intent_name == 'OrderFlowers'
|
|
341
|
+
end
|
|
342
|
+
|
|
343
|
+
def response(conversation)
|
|
344
|
+
conversation.close(
|
|
345
|
+
fulfillment_state: 'Fulfilled',
|
|
346
|
+
messages: [
|
|
347
|
+
{
|
|
348
|
+
content: 'Okay, your flowers have been ordered! Thanks!',
|
|
349
|
+
contentType: 'PlainText'
|
|
350
|
+
}
|
|
351
|
+
]
|
|
352
|
+
)
|
|
353
|
+
end
|
|
354
|
+
end
|
|
355
|
+
|
|
356
|
+
conversation = Aws::Lex::Conversation.new(event: event, context: context)
|
|
357
|
+
conversation.handlers = [
|
|
358
|
+
{ handler: AnotherIntent },
|
|
359
|
+
{ handler: OrderFlowers }
|
|
360
|
+
]
|
|
361
|
+
conversation.respond # => returns a Lex response object
|
|
362
|
+
```
|
|
363
|
+
|
|
194
364
|
## Test Helpers
|
|
195
365
|
|
|
196
366
|
This library provides convenience methods to make testing easy! You can use the test helpers as follows:
|
|
@@ -251,8 +421,6 @@ end
|
|
|
251
421
|
|
|
252
422
|
After checking out the repo, run `bin/setup` to install dependencies. Then, run `rake spec` to run the tests. You can also run `bin/console` for an interactive prompt that will allow you to experiment.
|
|
253
423
|
|
|
254
|
-
To install this gem onto your local machine, run `bundle exec rake install`. To release a new version, update the version number in `version.rb`, and then run `bundle exec rake release`, which will create a git tag for the version, push git commits and tags, and push the `.gem` file to [rubygems.org](https://rubygems.org).
|
|
255
|
-
|
|
256
424
|
## Contributing
|
|
257
425
|
|
|
258
426
|
Bug reports and pull requests are welcome on GitHub at https://github.com/amaabca/aws-lex-conversation. This project is intended to be a safe, welcoming space for collaboration, and contributors are expected to adhere to the [code of conduct](https://github.com/amaabca/aws-lex-conversation/blob/master/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md).
|
|
@@ -263,4 +431,4 @@ The gem is available as open source under the terms of the [MIT License](https:/
|
|
|
263
431
|
|
|
264
432
|
## Code of Conduct
|
|
265
433
|
|
|
266
|
-
Everyone interacting in the Aws::Lex::Conversation project's codebases, issue trackers, chat rooms and mailing lists is expected to follow the [code of conduct](https://github.com/amaabca/aws-lex-conversation/blob/master/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md).
|
|
434
|
+
Everyone interacting in the `Aws::Lex::Conversation` project's codebases, issue trackers, chat rooms and mailing lists is expected to follow the [code of conduct](https://github.com/amaabca/aws-lex-conversation/blob/master/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md).
|
|
@@ -26,9 +26,10 @@ Gem::Specification.new do |spec|
|
|
|
26
26
|
spec.license = 'MIT'
|
|
27
27
|
spec.required_ruby_version = Gem::Requirement.new('>= 2.3.0')
|
|
28
28
|
spec.metadata['homepage_uri'] = spec.homepage
|
|
29
|
+
spec.metadata['rubygems_mfa_required'] = 'true'
|
|
29
30
|
|
|
30
31
|
spec.files = Dir.chdir(File.expand_path(__dir__)) do
|
|
31
|
-
`git ls-files -z`.split("\x0").reject { |f| f.match(%r{^(test|spec|features)/}) }
|
|
32
|
+
`git ls-files -z`.split("\x0").reject { |f| f.match(%r{^(test|spec|features|data)/}) }
|
|
32
33
|
end
|
|
33
34
|
|
|
34
35
|
spec.bindir = 'exe'
|
|
@@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
|
|
|
1
1
|
# frozen_string_literal: true
|
|
2
2
|
|
|
3
3
|
require 'base64'
|
|
4
|
+
require 'forwardable'
|
|
4
5
|
require 'json'
|
|
5
6
|
require 'shrink/wrap'
|
|
6
7
|
|
|
@@ -25,6 +26,7 @@ require_relative 'type/sentiment_score'
|
|
|
25
26
|
require_relative 'type/sentiment_response'
|
|
26
27
|
require_relative 'type/invocation_source'
|
|
27
28
|
require_relative 'type/dialog_action_type'
|
|
29
|
+
require_relative 'type/slot_elicitation_style'
|
|
28
30
|
require_relative 'type/dialog_action'
|
|
29
31
|
require_relative 'type/confirmation_state'
|
|
30
32
|
require_relative 'type/fulfillment_state'
|
|
@@ -35,11 +37,14 @@ require_relative 'type/slot_value'
|
|
|
35
37
|
require_relative 'type/slot'
|
|
36
38
|
require_relative 'type/context'
|
|
37
39
|
require_relative 'type/intent'
|
|
40
|
+
require_relative 'type/proposed_next_state'
|
|
38
41
|
require_relative 'type/checkpoint'
|
|
39
42
|
require_relative 'type/session_attributes'
|
|
40
43
|
require_relative 'type/session_state'
|
|
41
44
|
require_relative 'type/interpretation'
|
|
42
45
|
require_relative 'type/bot'
|
|
46
|
+
require_relative 'type/transcription/resolved_context'
|
|
47
|
+
require_relative 'type/transcription'
|
|
43
48
|
require_relative 'type/response_card/button'
|
|
44
49
|
require_relative 'type/response_card'
|
|
45
50
|
require_relative 'type/message/content_type'
|
|
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ module Aws
|
|
|
5
5
|
class Conversation
|
|
6
6
|
module Response
|
|
7
7
|
class ElicitSlot < Base
|
|
8
|
-
attr_accessor :slot_to_elicit
|
|
8
|
+
attr_accessor :slot_to_elicit, :slot_elicitation_style
|
|
9
9
|
|
|
10
10
|
def initialize(opts = {})
|
|
11
11
|
super
|
|
@@ -16,7 +16,8 @@ module Aws
|
|
|
16
16
|
def dialog_action
|
|
17
17
|
Aws::Lex::Conversation::Type::DialogAction.shrink_wrap(
|
|
18
18
|
type: 'ElicitSlot',
|
|
19
|
-
slotToElicit: slot_to_elicit
|
|
19
|
+
slotToElicit: slot_to_elicit,
|
|
20
|
+
slotElicitationStyle: slot_elicitation_style
|
|
20
21
|
)
|
|
21
22
|
end
|
|
22
23
|
end
|
|
@@ -120,13 +120,41 @@ module Aws
|
|
|
120
120
|
self
|
|
121
121
|
end
|
|
122
122
|
|
|
123
|
+
def proposed_next_state(opts = {})
|
|
124
|
+
data = {
|
|
125
|
+
dialogAction: lex_attributes(opts.fetch(:dialog_action)),
|
|
126
|
+
intent: lex_attributes(opts.fetch(:intent))
|
|
127
|
+
}
|
|
128
|
+
lex.proposed_next_state = Type::ProposedNextState.shrink_wrap(data)
|
|
129
|
+
self
|
|
130
|
+
end
|
|
131
|
+
|
|
123
132
|
def session(data)
|
|
124
133
|
lex.session_state.session_attributes.merge!(Type::SessionAttributes[data])
|
|
125
134
|
self
|
|
126
135
|
end
|
|
127
136
|
|
|
137
|
+
def transcription(opts = {})
|
|
138
|
+
data = {
|
|
139
|
+
transcription: opts.fetch(:transcription),
|
|
140
|
+
transcriptionConfidence: opts.fetch(:confidence, 1),
|
|
141
|
+
resolvedContext: {
|
|
142
|
+
intent: opts.fetch(:intent) { 'FallbackIntent' }
|
|
143
|
+
},
|
|
144
|
+
resolvedSlots: opts.fetch(:resolved_slots) { {} }
|
|
145
|
+
}
|
|
146
|
+
lex.transcriptions.push(Type::Transcription.shrink_wrap(data))
|
|
147
|
+
self
|
|
148
|
+
end
|
|
149
|
+
|
|
128
150
|
private
|
|
129
151
|
|
|
152
|
+
def lex_attributes(instance)
|
|
153
|
+
return instance unless instance.respond_to?(:to_lex)
|
|
154
|
+
|
|
155
|
+
instance.to_lex
|
|
156
|
+
end
|
|
157
|
+
|
|
130
158
|
def current_interpretation
|
|
131
159
|
lex.interpretations.find { |i| i.intent.name == lex.session_state.intent.name }
|
|
132
160
|
end
|
|
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ module Aws
|
|
|
6
6
|
module Slot
|
|
7
7
|
class Elicitation
|
|
8
8
|
attr_accessor :name, :elicit, :messages, :follow_up_messages,
|
|
9
|
-
:fallback, :
|
|
9
|
+
:fallback, :max_retries, :conversation
|
|
10
10
|
|
|
11
11
|
def initialize(opts = {})
|
|
12
12
|
self.name = opts.fetch(:name)
|
|
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ module Aws
|
|
|
14
14
|
self.messages = opts.fetch(:messages)
|
|
15
15
|
self.follow_up_messages = opts.fetch(:follow_up_messages) { opts.fetch(:messages) }
|
|
16
16
|
self.fallback = opts[:fallback]
|
|
17
|
-
self.
|
|
17
|
+
self.max_retries = opts[:max_retries] || opts[:maximum_elicitations] || 0
|
|
18
18
|
end
|
|
19
19
|
|
|
20
20
|
def elicit!
|
|
@@ -53,9 +53,7 @@ module Aws
|
|
|
53
53
|
end
|
|
54
54
|
|
|
55
55
|
def maximum_elicitations?
|
|
56
|
-
|
|
57
|
-
|
|
58
|
-
elicitation_attempts > maximum_elicitations
|
|
56
|
+
elicitation_attempts > max_retries
|
|
59
57
|
end
|
|
60
58
|
|
|
61
59
|
def first_elicitation?
|
|
@@ -20,6 +20,28 @@ module Aws
|
|
|
20
20
|
fulfillment_state: FulfillmentState
|
|
21
21
|
)
|
|
22
22
|
|
|
23
|
+
class << self
|
|
24
|
+
def build(opts = {})
|
|
25
|
+
new(normalize_parameters(opts))
|
|
26
|
+
end
|
|
27
|
+
|
|
28
|
+
private
|
|
29
|
+
|
|
30
|
+
def normalize_parameters(opts)
|
|
31
|
+
params = opts.dup # we don't want to mutate our arguments
|
|
32
|
+
|
|
33
|
+
if params[:dialog_action_type].is_a?(String)
|
|
34
|
+
params[:dialog_action_type] = DialogActionType.new(params[:dialog_action_type])
|
|
35
|
+
end
|
|
36
|
+
|
|
37
|
+
if params[:fulfillment_state].is_a?(String)
|
|
38
|
+
params[:fulfillment_state] = FulfillmentState.new(params[:fulfillment_state])
|
|
39
|
+
end
|
|
40
|
+
|
|
41
|
+
params
|
|
42
|
+
end
|
|
43
|
+
end
|
|
44
|
+
|
|
23
45
|
# restore the checkpoint AND remove it from session
|
|
24
46
|
def restore!(conversation, opts = {})
|
|
25
47
|
conversation.checkpoints.delete_if { |c| c.label == label }
|
|
@@ -8,10 +8,12 @@ module Aws
|
|
|
8
8
|
include Base
|
|
9
9
|
|
|
10
10
|
optional :slot_to_elicit
|
|
11
|
+
optional :slot_elicitation_style, default: -> { 'Default' }
|
|
11
12
|
required :type
|
|
12
13
|
|
|
13
14
|
coerce(
|
|
14
|
-
type: DialogActionType
|
|
15
|
+
type: DialogActionType,
|
|
16
|
+
slot_elicitation_style: SlotElicitationStyle
|
|
15
17
|
)
|
|
16
18
|
end
|
|
17
19
|
end
|
|
@@ -17,6 +17,8 @@ module Aws
|
|
|
17
17
|
required :response_content_type
|
|
18
18
|
required :session_id
|
|
19
19
|
required :session_state
|
|
20
|
+
required :transcriptions, default: -> { [] }
|
|
21
|
+
optional :proposed_next_state
|
|
20
22
|
|
|
21
23
|
computed_property(:current_intent, virtual: true) do |instance|
|
|
22
24
|
instance.session_state.intent.tap do |intent|
|
|
@@ -41,9 +43,11 @@ module Aws
|
|
|
41
43
|
input_mode: InputMode,
|
|
42
44
|
interpretations: Array[Interpretation],
|
|
43
45
|
invocation_source: InvocationSource,
|
|
46
|
+
proposed_next_state: ProposedNextState,
|
|
44
47
|
request_attributes: symbolize_hash!,
|
|
45
48
|
response_content_type: Message::ContentType,
|
|
46
|
-
session_state: SessionState
|
|
49
|
+
session_state: SessionState,
|
|
50
|
+
transcriptions: Array[Transcription]
|
|
47
51
|
)
|
|
48
52
|
end
|
|
49
53
|
end
|
|
@@ -15,6 +15,11 @@ module Aws
|
|
|
15
15
|
content_type: Message::ContentType,
|
|
16
16
|
image_response_card: Aws::Lex::Conversation::Type::ResponseCard
|
|
17
17
|
)
|
|
18
|
+
|
|
19
|
+
def initialize(opts = {})
|
|
20
|
+
assign_attributes!(opts)
|
|
21
|
+
self.content_type ||= ContentType.new('PlainText')
|
|
22
|
+
end
|
|
18
23
|
end
|
|
19
24
|
end
|
|
20
25
|
end
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
# frozen_string_literal: true
|
|
2
|
+
|
|
3
|
+
module Aws
|
|
4
|
+
module Lex
|
|
5
|
+
class Conversation
|
|
6
|
+
module Type
|
|
7
|
+
class ProposedNextState
|
|
8
|
+
include Base
|
|
9
|
+
|
|
10
|
+
required :dialog_action
|
|
11
|
+
required :intent
|
|
12
|
+
|
|
13
|
+
coerce(
|
|
14
|
+
dialog_action: DialogAction,
|
|
15
|
+
intent: Intent
|
|
16
|
+
)
|
|
17
|
+
end
|
|
18
|
+
end
|
|
19
|
+
end
|
|
20
|
+
end
|
|
21
|
+
end
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
# frozen_string_literal: true
|
|
2
|
+
|
|
3
|
+
module Aws
|
|
4
|
+
module Lex
|
|
5
|
+
class Conversation
|
|
6
|
+
module Type
|
|
7
|
+
class SlotElicitationStyle
|
|
8
|
+
include Enumeration
|
|
9
|
+
|
|
10
|
+
enumeration('Default')
|
|
11
|
+
enumeration('SpellByLetter')
|
|
12
|
+
enumeration('SpellByWord')
|
|
13
|
+
end
|
|
14
|
+
end
|
|
15
|
+
end
|
|
16
|
+
end
|
|
17
|
+
end
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
# frozen_string_literal: true
|
|
2
|
+
|
|
3
|
+
module Aws
|
|
4
|
+
module Lex
|
|
5
|
+
class Conversation
|
|
6
|
+
module Type
|
|
7
|
+
class Transcription
|
|
8
|
+
include Base
|
|
9
|
+
|
|
10
|
+
required :transcription
|
|
11
|
+
required :transcription_confidence
|
|
12
|
+
optional :resolved_context
|
|
13
|
+
optional :resolved_slots
|
|
14
|
+
alias_method :confidence, :transcription_confidence
|
|
15
|
+
|
|
16
|
+
coerce(
|
|
17
|
+
resolved_context: Transcription::ResolvedContext,
|
|
18
|
+
resolved_slots: Array[Slot]
|
|
19
|
+
)
|
|
20
|
+
end
|
|
21
|
+
end
|
|
22
|
+
end
|
|
23
|
+
end
|
|
24
|
+
end
|
data/lib/aws/lex/conversation.rb
CHANGED
|
@@ -5,10 +5,13 @@ require_relative 'conversation/base'
|
|
|
5
5
|
module Aws
|
|
6
6
|
module Lex
|
|
7
7
|
class Conversation
|
|
8
|
+
extend Forwardable
|
|
8
9
|
include Support::Mixins::Responses
|
|
9
10
|
|
|
10
11
|
attr_accessor :event, :context, :lex
|
|
11
12
|
|
|
13
|
+
def_delegators :@lex, :proposed_next_state, :transcriptions
|
|
14
|
+
|
|
12
15
|
def initialize(opts = {})
|
|
13
16
|
self.event = opts.fetch(:event)
|
|
14
17
|
self.context = opts.fetch(:context)
|
|
@@ -62,9 +65,9 @@ module Aws
|
|
|
62
65
|
label = opts.fetch(:label)
|
|
63
66
|
params = {
|
|
64
67
|
label: label,
|
|
65
|
-
dialog_action_type: opts.fetch(:dialog_action_type),
|
|
68
|
+
dialog_action_type: opts.fetch(:dialog_action_type) { 'Delegate' },
|
|
66
69
|
fulfillment_state: opts[:fulfillment_state],
|
|
67
|
-
intent: lex.current_intent,
|
|
70
|
+
intent: opts.fetch(:intent) { lex.current_intent },
|
|
68
71
|
slot_to_elicit: opts[:slot_to_elicit]
|
|
69
72
|
}.compact
|
|
70
73
|
|
|
@@ -72,9 +75,8 @@ module Aws
|
|
|
72
75
|
# update the existing checkpoint
|
|
73
76
|
checkpoint(label: label).assign_attributes!(params)
|
|
74
77
|
else
|
|
75
|
-
# push a new checkpoint to the recent_intent_summary_view
|
|
76
78
|
checkpoints.unshift(
|
|
77
|
-
Type::Checkpoint.
|
|
79
|
+
Type::Checkpoint.build(params)
|
|
78
80
|
)
|
|
79
81
|
end
|
|
80
82
|
end
|
|
@@ -91,6 +93,21 @@ module Aws
|
|
|
91
93
|
lex.session_state.session_attributes.checkpoints
|
|
92
94
|
end
|
|
93
95
|
|
|
96
|
+
def restore_from!(checkpoint)
|
|
97
|
+
# we're done with the stored checkpoint once it's been restored
|
|
98
|
+
checkpoints.delete_if { |c| c.label == checkpoint.label }
|
|
99
|
+
# remove any memoized intent data
|
|
100
|
+
lex.current_intent = nil
|
|
101
|
+
# replace the intent with data from the checkpoint
|
|
102
|
+
lex.session_state.intent = checkpoint.intent
|
|
103
|
+
dialog_action = Type::DialogAction.new(
|
|
104
|
+
type: checkpoint.dialog_action_type,
|
|
105
|
+
slot_to_elicit: checkpoint.slot_to_elicit
|
|
106
|
+
)
|
|
107
|
+
lex.session_state.dialog_action = dialog_action
|
|
108
|
+
self
|
|
109
|
+
end
|
|
110
|
+
|
|
94
111
|
def active_context?(name:)
|
|
95
112
|
!active_context(name: name).nil?
|
|
96
113
|
end
|
|
@@ -104,7 +121,7 @@ module Aws
|
|
|
104
121
|
instance = active_context(name: name)
|
|
105
122
|
|
|
106
123
|
if instance
|
|
107
|
-
|
|
124
|
+
clear_context!(name: name)
|
|
108
125
|
else
|
|
109
126
|
instance = Type::Context.new
|
|
110
127
|
end
|
|
@@ -128,6 +145,10 @@ module Aws
|
|
|
128
145
|
lex.session_state.active_contexts = []
|
|
129
146
|
end
|
|
130
147
|
|
|
148
|
+
def proposed_next_state?
|
|
149
|
+
!proposed_next_state.nil?
|
|
150
|
+
end
|
|
151
|
+
|
|
131
152
|
def stash
|
|
132
153
|
@stash ||= {}
|
|
133
154
|
end
|
metadata
CHANGED
|
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
|
|
1
1
|
--- !ruby/object:Gem::Specification
|
|
2
2
|
name: aws-lex-conversation
|
|
3
3
|
version: !ruby/object:Gem::Version
|
|
4
|
-
version: 6.
|
|
4
|
+
version: 6.4.0
|
|
5
5
|
platform: ruby
|
|
6
6
|
authors:
|
|
7
7
|
- Jesse Doyle
|
|
@@ -9,10 +9,10 @@ authors:
|
|
|
9
9
|
- Darko Dosenovic
|
|
10
10
|
- Zoie Carnegie
|
|
11
11
|
- Carlos Mejia Castelo
|
|
12
|
-
autorequire:
|
|
12
|
+
autorequire:
|
|
13
13
|
bindir: exe
|
|
14
14
|
cert_chain: []
|
|
15
|
-
date:
|
|
15
|
+
date: 2022-02-10 00:00:00.000000000 Z
|
|
16
16
|
dependencies:
|
|
17
17
|
- !ruby/object:Gem::Dependency
|
|
18
18
|
name: shrink_wrap
|
|
@@ -92,6 +92,7 @@ files:
|
|
|
92
92
|
- lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/invocation_source.rb
|
|
93
93
|
- lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/message.rb
|
|
94
94
|
- lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/message/content_type.rb
|
|
95
|
+
- lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/proposed_next_state.rb
|
|
95
96
|
- lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/response.rb
|
|
96
97
|
- lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/response_card.rb
|
|
97
98
|
- lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/response_card/button.rb
|
|
@@ -101,16 +102,20 @@ files:
|
|
|
101
102
|
- lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/session_attributes.rb
|
|
102
103
|
- lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/session_state.rb
|
|
103
104
|
- lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/slot.rb
|
|
105
|
+
- lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/slot_elicitation_style.rb
|
|
104
106
|
- lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/slot_shape.rb
|
|
105
107
|
- lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/slot_value.rb
|
|
106
108
|
- lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/time_to_live.rb
|
|
109
|
+
- lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/transcription.rb
|
|
110
|
+
- lib/aws/lex/conversation/type/transcription/resolved_context.rb
|
|
107
111
|
- lib/aws/lex/conversation/version.rb
|
|
108
112
|
homepage: https://github.com/amaabca/aws-lex-conversation
|
|
109
113
|
licenses:
|
|
110
114
|
- MIT
|
|
111
115
|
metadata:
|
|
112
116
|
homepage_uri: https://github.com/amaabca/aws-lex-conversation
|
|
113
|
-
|
|
117
|
+
rubygems_mfa_required: 'true'
|
|
118
|
+
post_install_message:
|
|
114
119
|
rdoc_options: []
|
|
115
120
|
require_paths:
|
|
116
121
|
- lib
|
|
@@ -126,7 +131,7 @@ required_rubygems_version: !ruby/object:Gem::Requirement
|
|
|
126
131
|
version: '0'
|
|
127
132
|
requirements: []
|
|
128
133
|
rubygems_version: 3.1.2
|
|
129
|
-
signing_key:
|
|
134
|
+
signing_key:
|
|
130
135
|
specification_version: 4
|
|
131
136
|
summary: AWS Lex Conversation Dialog Management
|
|
132
137
|
test_files: []
|