q3dviewer 1.1.6__tar.gz → 1.1.9__tar.gz
This diff represents the content of publicly available package versions that have been released to one of the supported registries. The information contained in this diff is provided for informational purposes only and reflects changes between package versions as they appear in their respective public registries.
- q3dviewer-1.1.9/PKG-INFO +226 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/README.md +3 -2
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/Qt/__init__.py +1 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/base_glwidget.py +83 -1
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/custom_items/__init__.py +1 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/custom_items/cloud_io_item.py +16 -1
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/custom_items/cloud_item.py +37 -22
- q3dviewer-1.1.9/q3dviewer/custom_items/text3d_item.py +152 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/custom_items/text_item.py +19 -4
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/glwidget.py +23 -3
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/tools/cloud_viewer.py +79 -3
- q3dviewer-1.1.9/q3dviewer/tools/example_viewer.py +27 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/tools/film_maker.py +1 -1
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/tools/lidar_cam_calib.py +10 -11
- q3dviewer-1.1.9/q3dviewer/utils/convert_ros_msg.py +94 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/viewer.py +4 -1
- q3dviewer-1.1.9/q3dviewer.egg-info/PKG-INFO +226 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer.egg-info/SOURCES.txt +1 -7
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer.egg-info/entry_points.txt +1 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/setup.py +1 -1
- q3dviewer-1.1.6/LICENSE +0 -21
- q3dviewer-1.1.6/PKG-INFO +0 -235
- q3dviewer-1.1.6/q3dviewer/shaders/cloud_frag.glsl +0 -28
- q3dviewer-1.1.6/q3dviewer/shaders/cloud_vert.glsl +0 -72
- q3dviewer-1.1.6/q3dviewer/shaders/gau_frag.glsl +0 -42
- q3dviewer-1.1.6/q3dviewer/shaders/gau_prep.glsl +0 -249
- q3dviewer-1.1.6/q3dviewer/shaders/gau_vert.glsl +0 -77
- q3dviewer-1.1.6/q3dviewer/shaders/sort_by_key.glsl +0 -56
- q3dviewer-1.1.6/q3dviewer/tools/example_viewer.py +0 -47
- q3dviewer-1.1.6/q3dviewer/utils/convert_ros_msg.py +0 -51
- q3dviewer-1.1.6/q3dviewer.egg-info/PKG-INFO +0 -235
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/__init__.py +0 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/base_item.py +0 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/custom_items/axis_item.py +0 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/custom_items/frame_item.py +0 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/custom_items/gaussian_item.py +0 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/custom_items/grid_item.py +0 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/custom_items/image_item.py +0 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/custom_items/line_item.py +0 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/tools/__init__.py +0 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/tools/gaussian_viewer.py +0 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/tools/lidar_calib.py +0 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/tools/ros_viewer.py +0 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/utils/__init__.py +0 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/utils/cloud_io.py +0 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/utils/gl_helper.py +0 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/utils/helpers.py +0 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/utils/maths.py +0 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer/utils/range_slider.py +0 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer.egg-info/dependency_links.txt +0 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer.egg-info/requires.txt +6 -6
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/q3dviewer.egg-info/top_level.txt +0 -0
- {q3dviewer-1.1.6 → q3dviewer-1.1.9}/setup.cfg +0 -0
q3dviewer-1.1.9/PKG-INFO
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,226 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
Metadata-Version: 2.1
|
|
2
|
+
Name: q3dviewer
|
|
3
|
+
Version: 1.1.9
|
|
4
|
+
Summary: A library designed for quickly deploying a 3D viewer.
|
|
5
|
+
Home-page: https://github.com/scomup/q3dviewer
|
|
6
|
+
Author: Liu Yang
|
|
7
|
+
License: UNKNOWN
|
|
8
|
+
Description:
|
|
9
|
+

|
|
10
|
+
|
|
11
|
+
[](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
|
|
12
|
+
[](https://badge.fury.io/py/q3dviewer)
|
|
13
|
+
|
|
14
|
+
`q3dviewer` is a library designed for quickly deploying a 3D viewer. It is based on Qt and provides efficient OpenGL items for displaying 3D objects (e.g., point clouds, cameras, and 3D Gaussians). You can use it to visualize your 3D data or set up an efficient viewer application. It is inspired by PyQtGraph but focuses more on efficient 3D rendering.
|
|
15
|
+
|
|
16
|
+
|
|
17
|
+
To show how to use `q3dviewer` as a library, we also provide some [very useful tools](#tools).
|
|
18
|
+
|
|
19
|
+
|
|
20
|
+
## Installation
|
|
21
|
+
|
|
22
|
+
To install `q3dviewer`, execute the following command in your terminal on either Linux or Windows:
|
|
23
|
+
|
|
24
|
+
```bash
|
|
25
|
+
pip install q3dviewer
|
|
26
|
+
```
|
|
27
|
+
|
|
28
|
+
### Note for Windows Users
|
|
29
|
+
|
|
30
|
+
- Ensure that you have a Python 3 environment set up:
|
|
31
|
+
- Download and install Python 3 from the [official Python website](https://www.python.org/downloads/).
|
|
32
|
+
- During installation, make sure to check the "Add Python to PATH" option.
|
|
33
|
+
|
|
34
|
+
### Note for Linux Users
|
|
35
|
+
|
|
36
|
+
If you encounter an error related to loading the shared library `libxcb-cursor.so.0` on Ubuntu 20.04 or 22.04, please install `libxcb-cursor0`:
|
|
37
|
+
|
|
38
|
+
```bash
|
|
39
|
+
sudo apt-get install libxcb-cursor0
|
|
40
|
+
```
|
|
41
|
+
|
|
42
|
+
## Tools
|
|
43
|
+
|
|
44
|
+
Once installed, you can directly use the following tools:
|
|
45
|
+
|
|
46
|
+
### 1. Cloud Viewer
|
|
47
|
+
|
|
48
|
+
A tool for visualizing point cloud files (LAS, PCD, PLY, E57). Launch it by executing the following command in your terminal:
|
|
49
|
+
|
|
50
|
+
```sh
|
|
51
|
+
cloud_viewer
|
|
52
|
+
```
|
|
53
|
+
|
|
54
|
+
*Alternatively*, if the path is not set (though it's not recommended):
|
|
55
|
+
|
|
56
|
+
```sh
|
|
57
|
+
python3 -m q3dviewer.tools.cloud_viewer
|
|
58
|
+
```
|
|
59
|
+
|
|
60
|
+
**Basic Operations**
|
|
61
|
+
* Load files: Drag and drop point cloud files onto the window (multiple files are OK).
|
|
62
|
+
* `M` key: Display the visualization settings screen for point clouds, background color, etc.
|
|
63
|
+
* `Left mouse button` & `W, A, S, D` keys: Move the viewpoint on the horizontal plane.
|
|
64
|
+
* `Z, X` keys: Move in the direction the screen is facing.
|
|
65
|
+
* `Right mouse button` & `Arrow` keys: Rotate the viewpoint while keeping the screen center unchanged.
|
|
66
|
+
* `Shift` + `Right mouse button` & `Arrow` keys: Rotate the viewpoint while keeping the camera position unchanged.
|
|
67
|
+
|
|
68
|
+
For example, you can download and view point clouds of Tokyo in LAS format from the following link:
|
|
69
|
+
|
|
70
|
+
[Tokyo Point Clouds](https://www.geospatial.jp/ckan/dataset/tokyopc-23ku-2024/resource/7807d6d1-29f3-4b36-b0c8-f7aa0ea2cff3)
|
|
71
|
+
|
|
72
|
+

|
|
73
|
+
|
|
74
|
+
Press `M` on your keyboard to display a menu on the screen, where you can modify visualization settings for each item. For example, you can adjust various settings such as shape, size, color, and transparency for `CloudItem`.
|
|
75
|
+
|
|
76
|
+
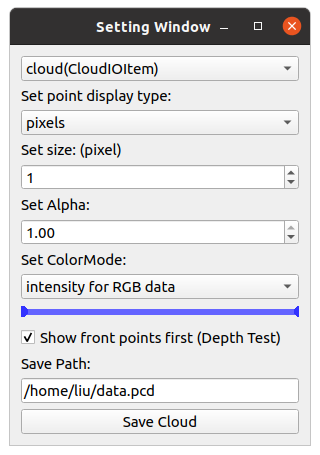
|
|
77
|
+
|
|
78
|
+
### 2. ROS Viewer
|
|
79
|
+
|
|
80
|
+
A high-performance SLAM viewer compatible with ROS, serving as an alternative to RVIZ.
|
|
81
|
+
|
|
82
|
+
```sh
|
|
83
|
+
roscore &
|
|
84
|
+
ros_viewer
|
|
85
|
+
```
|
|
86
|
+
|
|
87
|
+
### 3. Film Maker
|
|
88
|
+
|
|
89
|
+
Would you like to create a video from point cloud data? With Film Maker, you can easily create videos with simple operations. Just edit keyframes using the user-friendly GUI, and the software will automatically interpolate the keyframes to generate the video.
|
|
90
|
+
|
|
91
|
+
```sh
|
|
92
|
+
film_maker
|
|
93
|
+
```
|
|
94
|
+
|
|
95
|
+
**Basic Operations**
|
|
96
|
+
* File loading & viewpoint movement: Same as Cloud_Viewer
|
|
97
|
+
* Space key to add a keyframe.
|
|
98
|
+
* Delete key to remove a keyframe.
|
|
99
|
+
* Play button: Automatically play the video (pressing again will stop playback)
|
|
100
|
+
* Record checkbox: When checked, actions will be automatically recorded during playback
|
|
101
|
+
|
|
102
|
+
Film Maker GUI:
|
|
103
|
+
|
|
104
|
+

|
|
105
|
+
|
|
106
|
+
The demo video demonstrating how to use Film Maker utilizes the [cloud data of Kyobashi Station Area](https://www.geospatial.jp/ckan/dataset/kyoubasiekisyuuhen_las) located in Osaka, Japan.
|
|
107
|
+
|
|
108
|
+
### 4. Gaussian Viewer
|
|
109
|
+
|
|
110
|
+
A simple viewer for 3D Gaussians. See [EasyGaussianSplatting](https://github.com/scomup/EasyGaussianSplatting) for more information.
|
|
111
|
+
|
|
112
|
+
```sh
|
|
113
|
+
gaussian_viewer # Drag and drop your Gaussian file onto the window
|
|
114
|
+
```
|
|
115
|
+
|
|
116
|
+
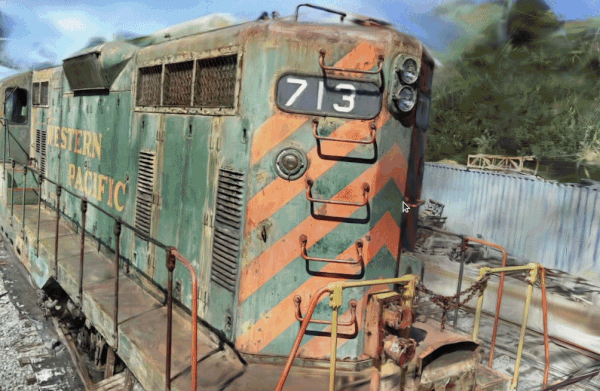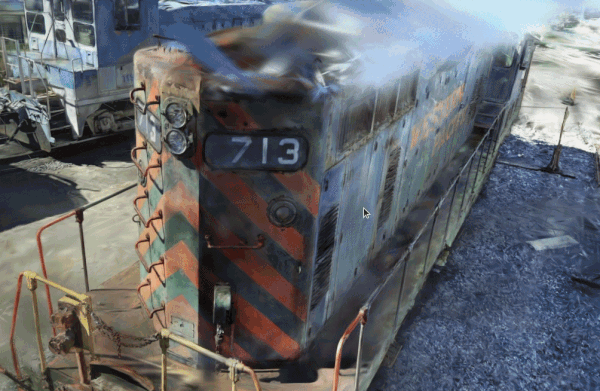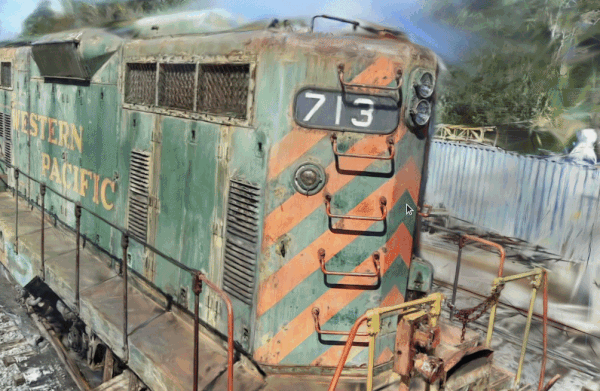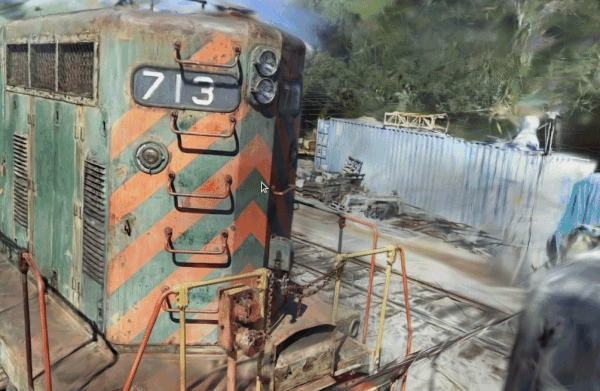
|
|
117
|
+
|
|
118
|
+
### 5. LiDAR-LiDAR Calibration Tools
|
|
119
|
+
|
|
120
|
+
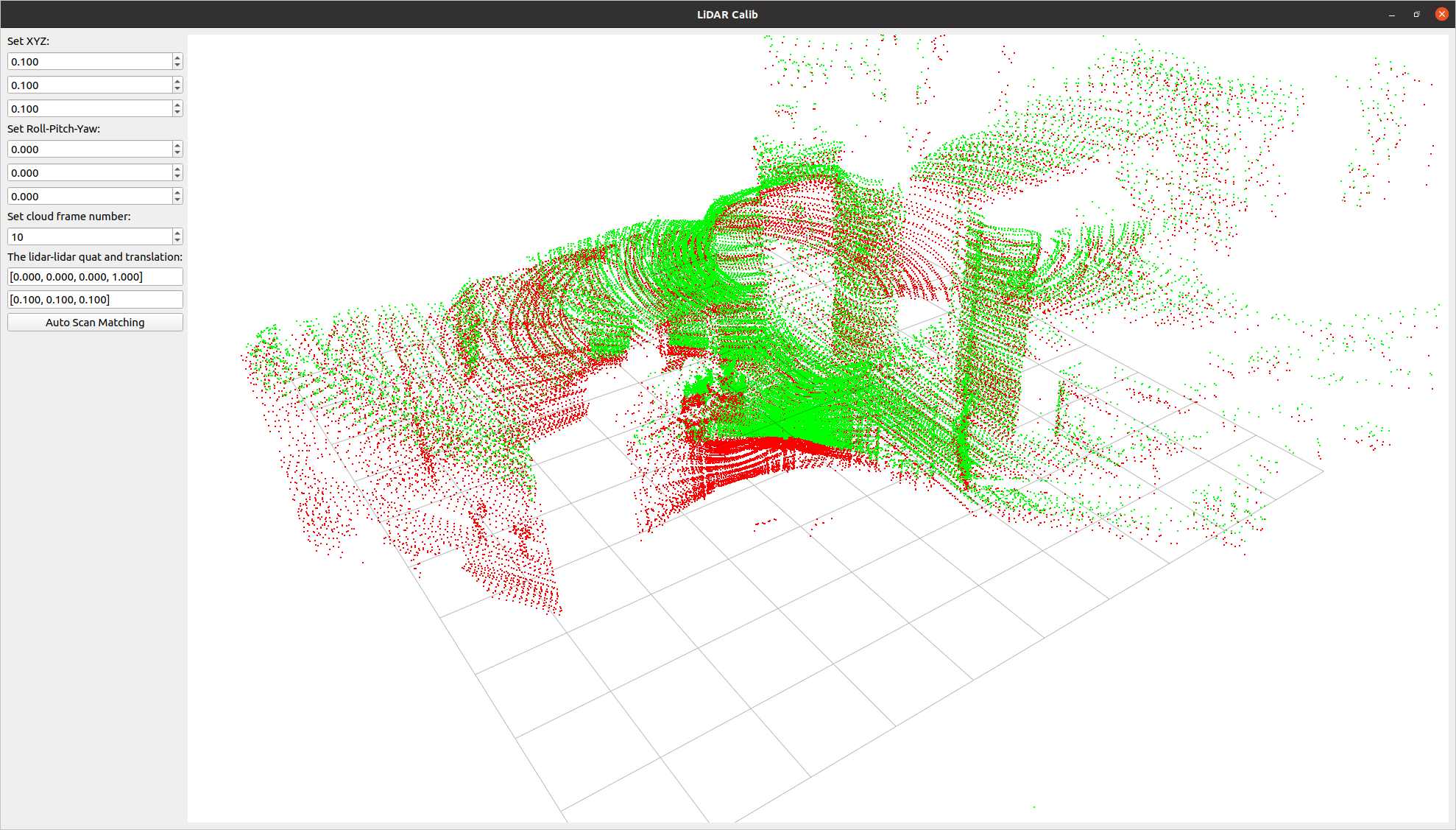
A tool to compute the relative pose between two LiDARs. It allows for both manual adjustment in the settings screen and automatic calibration.
|
|
121
|
+
|
|
122
|
+
```sh
|
|
123
|
+
lidar_calib --lidar0=/YOUR_LIDAR0_TOPIC --lidar1=/YOUR_LIDAR1_TOPIC
|
|
124
|
+
```
|
|
125
|
+
|
|
126
|
+
|
|
127
|
+
|
|
128
|
+
### 6. LiDAR-Camera Calibration Tools
|
|
129
|
+
|
|
130
|
+
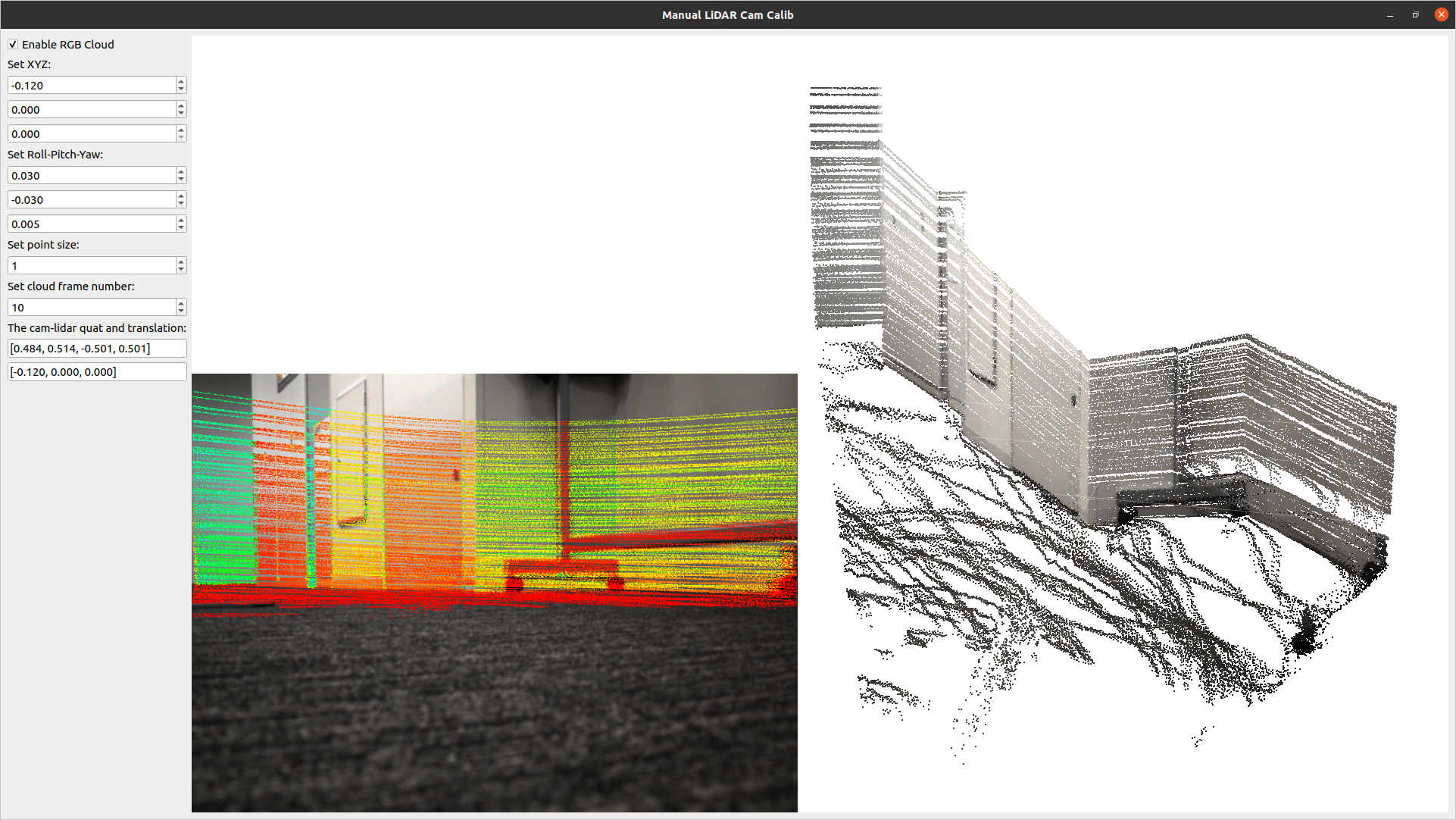
A tool for calculating the relative pose between a LiDAR and a camera. It allows for manual adjustment in the settings screen and real-time verification of LiDAR point projection onto images.
|
|
131
|
+
|
|
132
|
+
```sh
|
|
133
|
+
lidar_cam_calib --lidar=/YOUR_LIDAR_TOPIC --camera=/YOUR_CAMERA_TOPIC --camera_info=/YOUR_CAMERA_INFO_TOPIC
|
|
134
|
+
```
|
|
135
|
+
|
|
136
|
+
|
|
137
|
+
|
|
138
|
+
## Using as a Library
|
|
139
|
+
|
|
140
|
+
Using the examples above, you can easily customize and develop your own 3D viewer with `q3dviewer`. Below is a coding example.
|
|
141
|
+
|
|
142
|
+
### Custom 3D Viewer
|
|
143
|
+
|
|
144
|
+
```python
|
|
145
|
+
#!/usr/bin/env python3
|
|
146
|
+
|
|
147
|
+
import q3dviewer as q3d # Import q3dviewer
|
|
148
|
+
|
|
149
|
+
def main():
|
|
150
|
+
# Create a Qt application
|
|
151
|
+
app = q3d.QApplication([])
|
|
152
|
+
|
|
153
|
+
# Create various 3D items
|
|
154
|
+
axis_item = q3d.AxisItem(size=0.5, width=5)
|
|
155
|
+
grid_item = q3d.GridItem(size=10, spacing=1)
|
|
156
|
+
|
|
157
|
+
# Create a viewer
|
|
158
|
+
viewer = q3d.Viewer(name='example')
|
|
159
|
+
|
|
160
|
+
# Add items to the viewer
|
|
161
|
+
viewer.add_items({
|
|
162
|
+
'grid': grid_item,
|
|
163
|
+
'axis': axis_item,
|
|
164
|
+
})
|
|
165
|
+
|
|
166
|
+
# Show the viewer & run the Qt application
|
|
167
|
+
viewer.show()
|
|
168
|
+
app.exec()
|
|
169
|
+
|
|
170
|
+
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
|
171
|
+
main()
|
|
172
|
+
```
|
|
173
|
+
|
|
174
|
+
`q3dviewer` provides the following 3D items:
|
|
175
|
+
|
|
176
|
+
- **AxisItem**: Displays coordinate axes or the origin position.
|
|
177
|
+
- **CloudItem**: Displays point clouds.
|
|
178
|
+
- **CloudIOItem**: Displays point clouds with input/output capabilities.
|
|
179
|
+
- **GaussianItem**: Displays 3D Gaussians.
|
|
180
|
+
- **GridItem**: Displays grids.
|
|
181
|
+
- **ImageItem**: Displays 2D images.
|
|
182
|
+
- **Text2DItem**: Displays 2D text.
|
|
183
|
+
- **Text3DItem**: Displays 3D test and mark.
|
|
184
|
+
- **LineItem**: Displays lines or trajectories.
|
|
185
|
+
|
|
186
|
+
### Developing Custom Items
|
|
187
|
+
|
|
188
|
+
In addition to the standard 3D items provided, you can visualize custom 3D items with simple coding. Below is a sample:
|
|
189
|
+
|
|
190
|
+
```python
|
|
191
|
+
from OpenGL.GL import *
|
|
192
|
+
import numpy as np
|
|
193
|
+
import q3dviewer as q3d
|
|
194
|
+
from q3dviewer.Qt.QtWidgets import QLabel, QSpinBox
|
|
195
|
+
|
|
196
|
+
class YourItem(q3d.BaseItem):
|
|
197
|
+
def __init__(self):
|
|
198
|
+
super(YourItem, self).__init__()
|
|
199
|
+
# Necessary initialization
|
|
200
|
+
|
|
201
|
+
def add_setting(self, layout):
|
|
202
|
+
# Initialize the settings screen
|
|
203
|
+
label = QLabel("Add your setting:")
|
|
204
|
+
layout.addWidget(label)
|
|
205
|
+
box = QSpinBox()
|
|
206
|
+
layout.addWidget(box)
|
|
207
|
+
|
|
208
|
+
def set_data(self, data):
|
|
209
|
+
# Obtain the data you want to visualize
|
|
210
|
+
pass
|
|
211
|
+
|
|
212
|
+
def initialize_gl(self):
|
|
213
|
+
# OpenGL initialization settings (if needed)
|
|
214
|
+
pass
|
|
215
|
+
|
|
216
|
+
def paint(self):
|
|
217
|
+
# Visualize 3D objects using OpenGL
|
|
218
|
+
pass
|
|
219
|
+
```
|
|
220
|
+
|
|
221
|
+
Enjoy using `q3dviewer`!
|
|
222
|
+
Platform: UNKNOWN
|
|
223
|
+
Classifier: Programming Language :: Python :: 3
|
|
224
|
+
Classifier: License :: OSI Approved :: MIT License
|
|
225
|
+
Classifier: Operating System :: OS Independent
|
|
226
|
+
Description-Content-Type: text/markdown
|
|
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@
|
|
|
4
4
|
[](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
|
|
5
5
|
[](https://badge.fury.io/py/q3dviewer)
|
|
6
6
|
|
|
7
|
-
`q3dviewer` is a library designed for quickly deploying a 3D viewer. It is based on Qt
|
|
7
|
+
`q3dviewer` is a library designed for quickly deploying a 3D viewer. It is based on Qt and provides efficient OpenGL items for displaying 3D objects (e.g., point clouds, cameras, and 3D Gaussians). You can use it to visualize your 3D data or set up an efficient viewer application. It is inspired by PyQtGraph but focuses more on efficient 3D rendering.
|
|
8
8
|
|
|
9
9
|
|
|
10
10
|
To show how to use `q3dviewer` as a library, we also provide some [very useful tools](#tools).
|
|
@@ -173,6 +173,7 @@ if __name__ == '__main__':
|
|
|
173
173
|
- **GridItem**: Displays grids.
|
|
174
174
|
- **ImageItem**: Displays 2D images.
|
|
175
175
|
- **Text2DItem**: Displays 2D text.
|
|
176
|
+
- **Text3DItem**: Displays 3D test and mark.
|
|
176
177
|
- **LineItem**: Displays lines or trajectories.
|
|
177
178
|
|
|
178
179
|
### Developing Custom Items
|
|
@@ -183,7 +184,7 @@ In addition to the standard 3D items provided, you can visualize custom 3D items
|
|
|
183
184
|
from OpenGL.GL import *
|
|
184
185
|
import numpy as np
|
|
185
186
|
import q3dviewer as q3d
|
|
186
|
-
from
|
|
187
|
+
from q3dviewer.Qt.QtWidgets import QLabel, QSpinBox
|
|
187
188
|
|
|
188
189
|
class YourItem(q3d.BaseItem):
|
|
189
190
|
def __init__(self):
|
|
@@ -89,6 +89,9 @@ class BaseGLWidget(QOpenGLWidget):
|
|
|
89
89
|
the method is herted from QOpenGLWidget,
|
|
90
90
|
and it is called when the widget is first shown.
|
|
91
91
|
"""
|
|
92
|
+
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST)
|
|
93
|
+
glDepthFunc(GL_LESS)
|
|
94
|
+
|
|
92
95
|
for item in self.items:
|
|
93
96
|
item.initialize()
|
|
94
97
|
# initialize the projection matrix and model view matrix
|
|
@@ -302,7 +305,7 @@ class BaseGLWidget(QOpenGLWidget):
|
|
|
302
305
|
near = dist * 0.001
|
|
303
306
|
far = dist * 10000.
|
|
304
307
|
r = near * tan(0.5 * radians(self._fov))
|
|
305
|
-
t = r * h / w
|
|
308
|
+
t = r * h / max(w, 1)
|
|
306
309
|
matrix = frustum(-r, r, -t, t, near, far)
|
|
307
310
|
return matrix
|
|
308
311
|
|
|
@@ -349,3 +352,82 @@ class BaseGLWidget(QOpenGLWidget):
|
|
|
349
352
|
frame = np.frombuffer(pixels, dtype=np.uint8).reshape(height, width, 3)
|
|
350
353
|
frame = np.flip(frame, 0)
|
|
351
354
|
return frame
|
|
355
|
+
|
|
356
|
+
def depth_to_meters(self, depth_buffer):
|
|
357
|
+
"""
|
|
358
|
+
Convert normalized depth buffer values [0,1] to actual distances in meters.
|
|
359
|
+
|
|
360
|
+
Args:
|
|
361
|
+
depth_buffer: numpy array with depth values in range [0,1]
|
|
362
|
+
|
|
363
|
+
Returns:
|
|
364
|
+
numpy array with distances in meters
|
|
365
|
+
"""
|
|
366
|
+
# Get near and far clipping planes
|
|
367
|
+
near = self.dist * 0.001
|
|
368
|
+
far = self.dist * 10000.
|
|
369
|
+
|
|
370
|
+
# Convert from normalized depth [0,1] to linear depth in meters
|
|
371
|
+
# OpenGL depth buffer formula: depth = (1/z - 1/near) / (1/far - 1/near)
|
|
372
|
+
# Solving for z: z = 1 / (depth * (1/far - 1/near) + 1/near)
|
|
373
|
+
|
|
374
|
+
# Avoid division by zero for depth = 1.0 (far plane)
|
|
375
|
+
depth_clamped = np.clip(depth_buffer, 0.0, 0.999999)
|
|
376
|
+
|
|
377
|
+
linear_depth = 1.0 / (depth_clamped * (1.0/far - 1.0/near) + 1.0/near)
|
|
378
|
+
|
|
379
|
+
return linear_depth
|
|
380
|
+
|
|
381
|
+
|
|
382
|
+
def get_point(self, x0, y0, radius=5):
|
|
383
|
+
"""
|
|
384
|
+
Get the 3D point in world coordinates corresponding to the given
|
|
385
|
+
screen coordinates (x0, y0). It searches within a radius around the
|
|
386
|
+
given pixel to find a valid depth value.
|
|
387
|
+
"""
|
|
388
|
+
self.makeCurrent() # Ensure the OpenGL context is current
|
|
389
|
+
width = self.current_width()
|
|
390
|
+
height = self.current_height()
|
|
391
|
+
|
|
392
|
+
# Scale mouse coordinates by device pixel ratio for PySide6 compatibility
|
|
393
|
+
pixel_ratio = self.devicePixelRatioF()
|
|
394
|
+
|
|
395
|
+
points = []
|
|
396
|
+
for dx in range(-radius, radius + 1):
|
|
397
|
+
for dy in range(-radius, radius + 1):
|
|
398
|
+
if dx * dx + dy * dy <= radius * radius:
|
|
399
|
+
points.append((x0 + dx, y0 + dy))
|
|
400
|
+
points = sorted(points, key=lambda p: (p[0]-x0)**2 + (p[1]-y0)**2)
|
|
401
|
+
|
|
402
|
+
print("points to check:", len(points))
|
|
403
|
+
|
|
404
|
+
gl_y0 = height - y0 - 1
|
|
405
|
+
z = 1.0
|
|
406
|
+
for x, y in points:
|
|
407
|
+
x = int(x * pixel_ratio)
|
|
408
|
+
y = int(y * pixel_ratio)
|
|
409
|
+
|
|
410
|
+
gl_y = height - y - 1
|
|
411
|
+
z = glReadPixels(x, gl_y, 1, 1, GL_DEPTH_COMPONENT, GL_FLOAT)
|
|
412
|
+
z = np.frombuffer(z, dtype=np.float32)[0]
|
|
413
|
+
if z != 1.0 and z != 0.0:
|
|
414
|
+
print("dist to p:", np.sqrt((x - x0)**2 + (y - y0)**2))
|
|
415
|
+
break
|
|
416
|
+
|
|
417
|
+
if z == 1.0 or z == 0.0:
|
|
418
|
+
return None
|
|
419
|
+
|
|
420
|
+
# Retrieve OpenGL matrices (column-major), convert to numpy arrays and transpose
|
|
421
|
+
view = np.array(glGetFloatv(GL_MODELVIEW_MATRIX), dtype=np.float32).reshape((4,4)).T
|
|
422
|
+
proj = np.array(glGetFloatv(GL_PROJECTION_MATRIX), dtype=np.float32).reshape((4,4)).T
|
|
423
|
+
|
|
424
|
+
# Convert screen (x, y, z) to normalized device coordinates (NDC)
|
|
425
|
+
ndc_x = (x0 / width) * 2.0 - 1.0
|
|
426
|
+
ndc_y = (gl_y0 / height) * 2.0 - 1.0
|
|
427
|
+
ndc_z = 2.0 * z - 1.0
|
|
428
|
+
ndc = np.array([ndc_x, ndc_y, ndc_z, 1.0], dtype=np.float32)
|
|
429
|
+
|
|
430
|
+
inv_projview = np.linalg.inv(proj @ view)
|
|
431
|
+
world_p = inv_projview @ ndc
|
|
432
|
+
world_p /= world_p[3]
|
|
433
|
+
return world_p[:3]
|
|
@@ -7,3 +7,4 @@ from q3dviewer.custom_items.grid_item import GridItem
|
|
|
7
7
|
from q3dviewer.custom_items.text_item import Text2DItem
|
|
8
8
|
from q3dviewer.custom_items.image_item import ImageItem
|
|
9
9
|
from q3dviewer.custom_items.line_item import LineItem
|
|
10
|
+
from q3dviewer.custom_items.text3d_item import Text3DItem
|
|
@@ -11,7 +11,22 @@ from q3dviewer.utils.cloud_io import save_pcd, save_ply, save_e57, save_las, loa
|
|
|
11
11
|
|
|
12
12
|
class CloudIOItem(CloudItem):
|
|
13
13
|
"""
|
|
14
|
-
|
|
14
|
+
A OpenGL point cloud item with input/output capabilities.
|
|
15
|
+
Attributes:
|
|
16
|
+
size (float): The size of each point. When `point_type` is 'PIXEL', this is the size in screen pixels.
|
|
17
|
+
When `point_type` is 'SQUARE' or 'SPHERE', this is the size in centimeters in 3D space.
|
|
18
|
+
alpha (float): The transparency of the points, in the range [0, 1], where 0 is fully transparent and 1 is fully opaque.
|
|
19
|
+
color_mode (str): The coloring mode for the points.
|
|
20
|
+
- 'FLAT': Single flat color for all points (uses the `color` attribute).
|
|
21
|
+
- 'I': Color by intensity.
|
|
22
|
+
- 'RGB': Per-point RGB color.
|
|
23
|
+
- 'GRAY': Per-point grayscale color.
|
|
24
|
+
color (str or tuple): The flat color to use when `color_mode` is 'FLAT'. Accepts any valid matplotlib color (e.g., 'red', '#FF4500', (1.0, 0.5, 0.0)).
|
|
25
|
+
point_type (str): The type/rendering style of each point:
|
|
26
|
+
- 'PIXEL': Draw each point as a square pixel on the screen.
|
|
27
|
+
- 'SQUARE': Draw each point as a square in 3D space.
|
|
28
|
+
- 'SPHERE': Draw each point as a sphere in 3D space.
|
|
29
|
+
depth_test (bool): Whether to enable depth testing. If True, points closer to the camera will appear in front of farther ones.
|
|
15
30
|
"""
|
|
16
31
|
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
|
|
17
32
|
super().__init__(**kwargs)
|
|
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ from OpenGL.GL import shaders
|
|
|
11
11
|
|
|
12
12
|
import threading
|
|
13
13
|
import os
|
|
14
|
-
from q3dviewer.Qt.QtWidgets import QLabel, QLineEdit, QDoubleSpinBox, QComboBox, QCheckBox
|
|
14
|
+
from q3dviewer.Qt.QtWidgets import QLabel, QLineEdit, QDoubleSpinBox, QSpinBox, QComboBox, QCheckBox
|
|
15
15
|
from q3dviewer.utils.range_slider import RangeSlider
|
|
16
16
|
from q3dviewer.utils import set_uniform
|
|
17
17
|
from q3dviewer.utils import text_to_rgba
|
|
@@ -20,6 +20,25 @@ from q3dviewer.Qt import Q3D_DEBUG
|
|
|
20
20
|
|
|
21
21
|
# draw points with color (x, y, z, color)
|
|
22
22
|
class CloudItem(BaseItem):
|
|
23
|
+
"""
|
|
24
|
+
A OpenGL point cloud item.
|
|
25
|
+
|
|
26
|
+
Attributes:
|
|
27
|
+
size (float): The size of each point. When `point_type` is 'PIXEL', this is the size in screen pixels.
|
|
28
|
+
When `point_type` is 'SQUARE' or 'SPHERE', this is the size in centimeters in 3D space.
|
|
29
|
+
alpha (float): The transparency of the points, in the range [0, 1], where 0 is fully transparent and 1 is fully opaque.
|
|
30
|
+
color_mode (str): The coloring mode for the points.
|
|
31
|
+
- 'FLAT': Single flat color for all points (uses the `color` attribute).
|
|
32
|
+
- 'I': Color by intensity.
|
|
33
|
+
- 'RGB': Per-point RGB color.
|
|
34
|
+
- 'GRAY': Per-point grayscale color.
|
|
35
|
+
color (str or tuple): The flat color to use when `color_mode` is 'FLAT'. Accepts any valid matplotlib color (e.g., 'red', '#FF4500', (1.0, 0.5, 0.0)).
|
|
36
|
+
point_type (str): The type/rendering style of each point:
|
|
37
|
+
- 'PIXEL': Draw each point as a square pixel on the screen.
|
|
38
|
+
- 'SQUARE': Draw each point as a square in 3D space.
|
|
39
|
+
- 'SPHERE': Draw each point as a sphere in 3D space.
|
|
40
|
+
depth_test (bool): Whether to enable depth testing. If True, points closer to the camera will appear in front of farther ones.
|
|
41
|
+
"""
|
|
23
42
|
def __init__(self, size, alpha,
|
|
24
43
|
color_mode='I',
|
|
25
44
|
color='white',
|
|
@@ -40,7 +59,7 @@ class CloudItem(BaseItem):
|
|
|
40
59
|
except ValueError:
|
|
41
60
|
print(f"Invalid color: {color}, please use matplotlib color format")
|
|
42
61
|
exit(1)
|
|
43
|
-
self.mode_table = {'FLAT': 0, 'I': 1, 'RGB': 2}
|
|
62
|
+
self.mode_table = {'FLAT': 0, 'I': 1, 'RGB': 2, 'GRAY': 3}
|
|
44
63
|
self.point_type_table = {'PIXEL': 0, 'SQUARE': 1, 'SPHERE': 2}
|
|
45
64
|
self.color_mode = self.mode_table[color_mode]
|
|
46
65
|
self.CAPACITY = 10000000 # 10MB * 3 (x,y,z, color) * 4
|
|
@@ -65,11 +84,10 @@ class CloudItem(BaseItem):
|
|
|
65
84
|
combo_ptype.currentIndexChanged.connect(self._on_point_type_selection)
|
|
66
85
|
layout.addWidget(combo_ptype)
|
|
67
86
|
|
|
68
|
-
self.box_size =
|
|
87
|
+
self.box_size = QSpinBox()
|
|
69
88
|
self.box_size.setPrefix("Size: ")
|
|
70
89
|
self.box_size.setSingleStep(1)
|
|
71
|
-
self.box_size.
|
|
72
|
-
self.box_size.setValue(self.size)
|
|
90
|
+
self.box_size.setValue(int(self.size))
|
|
73
91
|
self.box_size.setRange(0, 100)
|
|
74
92
|
self.box_size.valueChanged.connect(self.set_size)
|
|
75
93
|
self._on_point_type_selection(self.point_type_table[self.point_type])
|
|
@@ -89,6 +107,7 @@ class CloudItem(BaseItem):
|
|
|
89
107
|
self.combo_color.addItem("flat color")
|
|
90
108
|
self.combo_color.addItem("intensity")
|
|
91
109
|
self.combo_color.addItem("RGB")
|
|
110
|
+
self.combo_color.addItem("gray")
|
|
92
111
|
self.combo_color.setCurrentIndex(self.color_mode)
|
|
93
112
|
self.combo_color.currentIndexChanged.connect(self._on_color_mode)
|
|
94
113
|
layout.addWidget(self.combo_color)
|
|
@@ -127,10 +146,13 @@ class CloudItem(BaseItem):
|
|
|
127
146
|
self.edit_rgb.show()
|
|
128
147
|
elif (index == self.mode_table['I']): # flat color
|
|
129
148
|
self.slider_v.show()
|
|
149
|
+
elif (index == self.mode_table['GRAY']): # flat color
|
|
150
|
+
self.slider_v.show()
|
|
151
|
+
|
|
130
152
|
self.need_update_setting = True
|
|
131
153
|
|
|
132
154
|
def set_color_mode(self, color_mode):
|
|
133
|
-
if color_mode in {'FLAT', 'RGB', 'I'}:
|
|
155
|
+
if color_mode in {'FLAT', 'RGB', 'I', 'GRAY'}:
|
|
134
156
|
try:
|
|
135
157
|
self.combo_color.setCurrentIndex(self.mode_table[color_mode])
|
|
136
158
|
except:
|
|
@@ -143,17 +165,10 @@ class CloudItem(BaseItem):
|
|
|
143
165
|
self.point_type = list(self.point_type_table.keys())[index]
|
|
144
166
|
if self.point_type == 'PIXEL':
|
|
145
167
|
self.box_size.setPrefix("Set size (pixel): ")
|
|
146
|
-
self.box_size.setDecimals(0)
|
|
147
|
-
self.box_size.setSingleStep(1)
|
|
148
|
-
self.size = np.ceil(self.size)
|
|
149
|
-
self.box_size.setValue(self.size)
|
|
150
168
|
else:
|
|
151
|
-
self.box_size.setPrefix("Set size (
|
|
152
|
-
|
|
153
|
-
|
|
154
|
-
if self.size >= 1:
|
|
155
|
-
self.size = self.size * 0.01
|
|
156
|
-
self.box_size.setValue(self.size)
|
|
169
|
+
self.box_size.setPrefix("Set size (cm): ")
|
|
170
|
+
# self.size = 1
|
|
171
|
+
# self.box_size.setValue(self.size)
|
|
157
172
|
self.need_update_setting = True
|
|
158
173
|
|
|
159
174
|
def set_alpha(self, alpha):
|
|
@@ -222,7 +237,7 @@ class CloudItem(BaseItem):
|
|
|
222
237
|
set_uniform(self.program, float(self.vmax), 'vmax')
|
|
223
238
|
set_uniform(self.program, float(self.vmin), 'vmin')
|
|
224
239
|
set_uniform(self.program, float(self.alpha), 'alpha')
|
|
225
|
-
set_uniform(self.program,
|
|
240
|
+
set_uniform(self.program, int(self.size), 'point_size')
|
|
226
241
|
set_uniform(self.program, int(self.point_type_table[self.point_type]), 'point_type')
|
|
227
242
|
glUseProgram(0)
|
|
228
243
|
self.need_update_setting = False
|
|
@@ -292,10 +307,12 @@ class CloudItem(BaseItem):
|
|
|
292
307
|
glEnable(GL_BLEND)
|
|
293
308
|
glEnable(GL_PROGRAM_POINT_SIZE)
|
|
294
309
|
glEnable(GL_POINT_SPRITE)
|
|
295
|
-
|
|
296
|
-
|
|
310
|
+
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST)
|
|
311
|
+
|
|
312
|
+
if not self.depth_test:
|
|
313
|
+
glDepthFunc(GL_ALWAYS) # Always pass depth test but still write depth
|
|
297
314
|
else:
|
|
298
|
-
|
|
315
|
+
glDepthFunc(GL_LESS) # Normal depth testing
|
|
299
316
|
|
|
300
317
|
glBlendFunc(GL_SRC_ALPHA, GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA)
|
|
301
318
|
glUseProgram(self.program)
|
|
@@ -325,5 +342,3 @@ class CloudItem(BaseItem):
|
|
|
325
342
|
glDisable(GL_POINT_SPRITE)
|
|
326
343
|
glDisable(GL_PROGRAM_POINT_SIZE)
|
|
327
344
|
glDisable(GL_BLEND)
|
|
328
|
-
if self.depth_test:
|
|
329
|
-
glDisable(GL_DEPTH_TEST) # Disable depth testing if it was enabled
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,152 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
"""
|
|
2
|
+
Copyright 2024 Panasonic Advanced Technology Development Co.,Ltd. (Liu Yang)
|
|
3
|
+
Distributed under MIT license. See LICENSE for more information.
|
|
4
|
+
"""
|
|
5
|
+
|
|
6
|
+
|
|
7
|
+
from q3dviewer.base_item import BaseItem
|
|
8
|
+
from OpenGL.GL import *
|
|
9
|
+
import numpy as np
|
|
10
|
+
|
|
11
|
+
try:
|
|
12
|
+
from OpenGL.GLUT import glutBitmapCharacter, glutInit
|
|
13
|
+
from OpenGL.GLUT import (
|
|
14
|
+
GLUT_BITMAP_HELVETICA_10,
|
|
15
|
+
GLUT_BITMAP_HELVETICA_12,
|
|
16
|
+
GLUT_BITMAP_HELVETICA_18,
|
|
17
|
+
GLUT_BITMAP_TIMES_ROMAN_24,
|
|
18
|
+
)
|
|
19
|
+
GLUT_AVAILABLE = True
|
|
20
|
+
except ImportError:
|
|
21
|
+
GLUT_AVAILABLE = False
|
|
22
|
+
print("Warning: GLUT not available. Text will not be rendered.")
|
|
23
|
+
|
|
24
|
+
def get_glut_font(font_size):
|
|
25
|
+
"""Get GLUT font based on size, only if GLUT is available"""
|
|
26
|
+
if not GLUT_AVAILABLE:
|
|
27
|
+
return None
|
|
28
|
+
|
|
29
|
+
# Map requested font_size to a GLUT font object
|
|
30
|
+
if font_size <= 10:
|
|
31
|
+
return GLUT_BITMAP_HELVETICA_10
|
|
32
|
+
elif font_size <= 12:
|
|
33
|
+
return GLUT_BITMAP_HELVETICA_12
|
|
34
|
+
elif font_size <= 18:
|
|
35
|
+
return GLUT_BITMAP_HELVETICA_18
|
|
36
|
+
elif font_size <= 24:
|
|
37
|
+
return GLUT_BITMAP_TIMES_ROMAN_24
|
|
38
|
+
else:
|
|
39
|
+
return GLUT_BITMAP_TIMES_ROMAN_24 # Largest available
|
|
40
|
+
|
|
41
|
+
|
|
42
|
+
# draw points with color (x, y, z, color)
|
|
43
|
+
class Text3DItem(BaseItem):
|
|
44
|
+
"""
|
|
45
|
+
A OpenGL 3d text and mark item.
|
|
46
|
+
|
|
47
|
+
Attributes:
|
|
48
|
+
data: list storing text data. Each element is a dict with keys:
|
|
49
|
+
'text': str, the text to display
|
|
50
|
+
'position': (x, y, z), the 3D position of the text
|
|
51
|
+
'color': (r, g, b, a), the color of the text
|
|
52
|
+
'font_size': float, the font size of the text
|
|
53
|
+
'point_size': float, size of point to draw at position (0 for no point)
|
|
54
|
+
'line_width': float, width of line to draw between points (0 for no line)
|
|
55
|
+
|
|
56
|
+
"""
|
|
57
|
+
def __init__(self, data=[]):
|
|
58
|
+
super().__init__()
|
|
59
|
+
self._disable_setting = True
|
|
60
|
+
self.data_list = data # map of {'text': str, 'position': (x,y,z), 'color': (r,g,b,a), 'size': float}
|
|
61
|
+
|
|
62
|
+
def add_setting(self, layout):
|
|
63
|
+
pass # No settings for Text3DItem
|
|
64
|
+
|
|
65
|
+
def set_data(self, data, append=False):
|
|
66
|
+
if not append:
|
|
67
|
+
self.data_list = []
|
|
68
|
+
self.data_list.extend(data)
|
|
69
|
+
|
|
70
|
+
def clear_data(self):
|
|
71
|
+
self.data_list = []
|
|
72
|
+
|
|
73
|
+
|
|
74
|
+
def initialize_gl(self):
|
|
75
|
+
"""Initialize OpenGL resources, with GLUT fallback handling"""
|
|
76
|
+
global GLUT_AVAILABLE
|
|
77
|
+
if GLUT_AVAILABLE:
|
|
78
|
+
try:
|
|
79
|
+
# Check if glutInit is actually callable before calling it
|
|
80
|
+
if hasattr(glutInit, '__call__') and bool(glutInit):
|
|
81
|
+
glutInit()
|
|
82
|
+
else:
|
|
83
|
+
print("Warning: glutInit not callable, using fallback text rendering")
|
|
84
|
+
GLUT_AVAILABLE = False
|
|
85
|
+
except Exception as e:
|
|
86
|
+
print(f"Warning: GLUT initialization failed: {e}. Using fallback text rendering.")
|
|
87
|
+
GLUT_AVAILABLE = False
|
|
88
|
+
# super().initialize_gl()
|
|
89
|
+
|
|
90
|
+
|
|
91
|
+
def paint(self):
|
|
92
|
+
for item in self.data_list:
|
|
93
|
+
# Handle both dictionary and string formats
|
|
94
|
+
if isinstance(item, dict):
|
|
95
|
+
text = item.get('text', '')
|
|
96
|
+
pos = item.get('position', (0.0, 0.0, 0.0))
|
|
97
|
+
font_size = item.get('font_size', 24)
|
|
98
|
+
color = item.get('color', (1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0))
|
|
99
|
+
point_size = item.get('point_size', 0.0)
|
|
100
|
+
elif isinstance(item, str):
|
|
101
|
+
# If item is a string, treat it as text with default position and color
|
|
102
|
+
text = item
|
|
103
|
+
pos = (0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
|
|
104
|
+
color = (1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0)
|
|
105
|
+
font_size = 24
|
|
106
|
+
point_size = 0.0
|
|
107
|
+
else:
|
|
108
|
+
print(f"Warning: Unsupported item type: {type(item)}")
|
|
109
|
+
continue
|
|
110
|
+
|
|
111
|
+
# Convert numpy array to tuple if needed
|
|
112
|
+
if isinstance(pos, np.ndarray):
|
|
113
|
+
pos = tuple(pos.astype(float))
|
|
114
|
+
|
|
115
|
+
glColor4f(*color)
|
|
116
|
+
|
|
117
|
+
if point_size > 0.0:
|
|
118
|
+
# draw a point at the position
|
|
119
|
+
glPointSize(point_size)
|
|
120
|
+
glBegin(GL_POINTS)
|
|
121
|
+
glVertex3f(*pos)
|
|
122
|
+
glEnd()
|
|
123
|
+
|
|
124
|
+
# Text rendering with GLUT fallback
|
|
125
|
+
if GLUT_AVAILABLE:
|
|
126
|
+
offset = 0.02
|
|
127
|
+
pos_text = (pos[0] + offset, pos[1] + offset, pos[2] + offset)
|
|
128
|
+
glRasterPos3f(*pos_text)
|
|
129
|
+
font = get_glut_font(font_size)
|
|
130
|
+
if font is not None:
|
|
131
|
+
try:
|
|
132
|
+
for ch in text:
|
|
133
|
+
glutBitmapCharacter(font, ord(ch))
|
|
134
|
+
except Exception as e:
|
|
135
|
+
print(f"Error rendering text '{text}': {e}")
|
|
136
|
+
|
|
137
|
+
# draw lines between points
|
|
138
|
+
for i in range(len(self.data_list) - 1):
|
|
139
|
+
item1 = self.data_list[i]
|
|
140
|
+
item2 = self.data_list[i + 1]
|
|
141
|
+
if isinstance(item1, dict) and isinstance(item2, dict):
|
|
142
|
+
pos1 = item1.get('position', (0.0, 0.0, 0.0))
|
|
143
|
+
pos2 = item2.get('position', (0.0, 0.0, 0.0))
|
|
144
|
+
line_width = item1.get('line_width', 0.0)
|
|
145
|
+
color = item1.get('color', (1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0))
|
|
146
|
+
if line_width > 0.0:
|
|
147
|
+
glColor4f(*color)
|
|
148
|
+
glLineWidth(line_width)
|
|
149
|
+
glBegin(GL_LINES)
|
|
150
|
+
glVertex3f(*pos1)
|
|
151
|
+
glVertex3f(*pos2)
|
|
152
|
+
glEnd()
|