q3dviewer 1.0.7__tar.gz
This diff represents the content of publicly available package versions that have been released to one of the supported registries. The information contained in this diff is provided for informational purposes only and reflects changes between package versions as they appear in their respective public registries.
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/PKG-INFO +10 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/README.md +164 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/__init__.py +5 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/base_glwidget.py +261 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/base_item.py +57 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/custom_items/__init__.py +9 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/custom_items/axis_item.py +148 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/custom_items/cloud_io_item.py +79 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/custom_items/cloud_item.py +313 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/custom_items/frame_item.py +194 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/custom_items/gaussian_item.py +254 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/custom_items/grid_item.py +88 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/custom_items/image_item.py +172 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/custom_items/line_item.py +120 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/custom_items/text_item.py +63 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/glwidget.py +131 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/tools/__init__.py +1 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/tools/cloud_viewer.py +123 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/tools/example_viewer.py +47 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/tools/gaussian_viewer.py +60 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/tools/lidar_calib.py +294 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/tools/lidar_cam_calib.py +314 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/tools/ros_viewer.py +85 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/utils/__init__.py +4 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/utils/cloud_io.py +323 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/utils/convert_ros_msg.py +51 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/utils/gl_helper.py +40 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/utils/maths.py +168 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/utils/range_slider.py +86 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer/viewer.py +58 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer.egg-info/PKG-INFO +10 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer.egg-info/SOURCES.txt +36 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer.egg-info/dependency_links.txt +1 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer.egg-info/entry_points.txt +8 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer.egg-info/requires.txt +8 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/q3dviewer.egg-info/top_level.txt +1 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/setup.cfg +4 -0
- q3dviewer-1.0.7/setup.py +31 -0
q3dviewer-1.0.7/PKG-INFO
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,164 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
## q3dviewer
|
|
2
|
+
|
|
3
|
+
`q3dviewer` is a library designed for quickly deploying a 3D viewer. It is based on Qt (pyside6) and provides efficient OpenGL items for displaying 3D objects (e.g., point clouds, cameras, and 3D Gaussians). You can use it to visualize your 3D data or set up an efficient viewer application. It is inspired by PyQtGraph, but it focuses more on efficient 3D rendering.
|
|
4
|
+
|
|
5
|
+
## Installation
|
|
6
|
+
|
|
7
|
+
To install `q3dviewer`, execute the following command in your terminal on either Linux or Windows:
|
|
8
|
+
|
|
9
|
+
```bash
|
|
10
|
+
pip install q3dviewer
|
|
11
|
+
```
|
|
12
|
+
|
|
13
|
+
### Note for Windows Users
|
|
14
|
+
|
|
15
|
+
- Ensure that you have a Python 3 environment set up:
|
|
16
|
+
- Download and install Python 3 from the [official Python website](https://www.python.org/downloads/).
|
|
17
|
+
- During installation, make sure to check the "Add Python to PATH" option.
|
|
18
|
+
|
|
19
|
+
## Tools
|
|
20
|
+
|
|
21
|
+
Once installed, you can directly use the following tools:
|
|
22
|
+
|
|
23
|
+
### 1. Cloud Viewer
|
|
24
|
+
|
|
25
|
+
A tool for visualizing point cloud files. Launch it by executing the following command in your terminal:
|
|
26
|
+
|
|
27
|
+
```sh
|
|
28
|
+
cloud_viewer # The viewer will be displayed
|
|
29
|
+
# Use the command below if the path is not set, though it's not recommended
|
|
30
|
+
python3 -m q3dviewer.tools.cloud_viewer
|
|
31
|
+
```
|
|
32
|
+
|
|
33
|
+
After the viewer launches, you can drag and drop files onto the window to display the point clouds. Multiple files can be dropped simultaneously to view them together. Supported formats include LAS, PCD, PLY, and E57.
|
|
34
|
+
|
|
35
|
+
For example, you can download and check point clouds of Tokyo in LAS format from the following link:
|
|
36
|
+
|
|
37
|
+
[Tokyo Point Clouds](https://www.geospatial.jp/ckan/dataset/tokyopc-23ku-2024/resource/7807d6d1-29f3-4b36-b0c8-f7aa0ea2cff3)
|
|
38
|
+
|
|
39
|
+

|
|
40
|
+
|
|
41
|
+
Press `M` on your keyboard to display a menu on the screen, where you can modify visualization settings for each item. for example, You can adjust various settings such as shape, size, color, and transparency of the point clouds for CloudItem,.
|
|
42
|
+
|
|
43
|
+
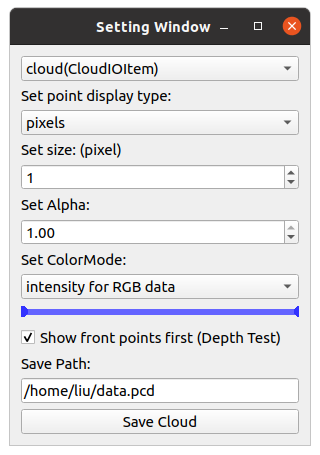
|
|
44
|
+
|
|
45
|
+
### 2. ROS Viewer
|
|
46
|
+
|
|
47
|
+
A high-performance SLAM viewer with strong compatibility with ROS, serving as an alternative to RVIZ.
|
|
48
|
+
|
|
49
|
+
```sh
|
|
50
|
+
roscore &
|
|
51
|
+
ros_viewer
|
|
52
|
+
```
|
|
53
|
+
|
|
54
|
+
### 3. Gaussian Viewer
|
|
55
|
+
|
|
56
|
+
A simple viewer for 3D Gaussian.
|
|
57
|
+
see: https://github.com/scomup/EasyGaussianSplatting
|
|
58
|
+
|
|
59
|
+
|
|
60
|
+
```sh
|
|
61
|
+
gaussian_viewer # Drag and drop your Gaussian file onto the window
|
|
62
|
+
```
|
|
63
|
+
|
|
64
|
+
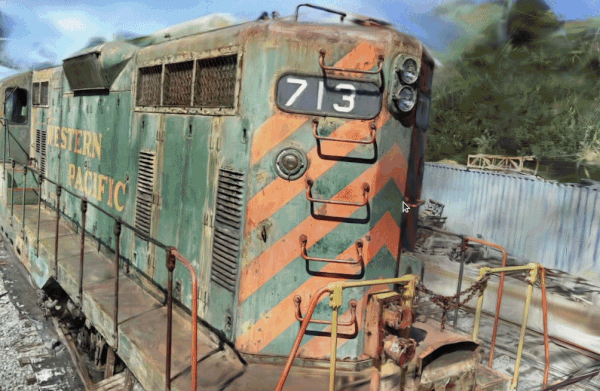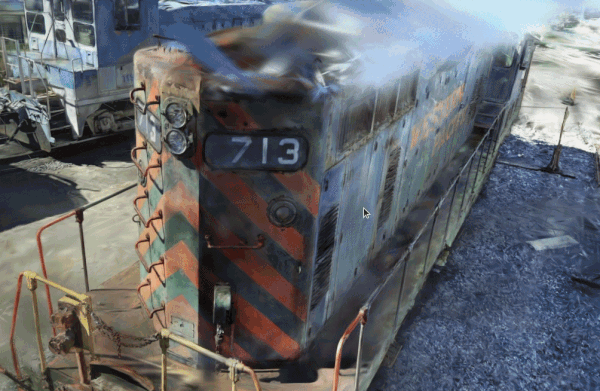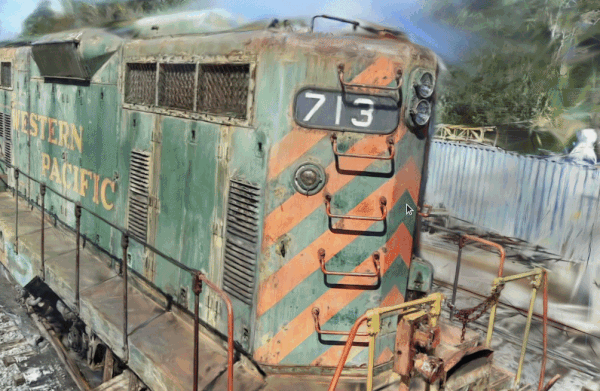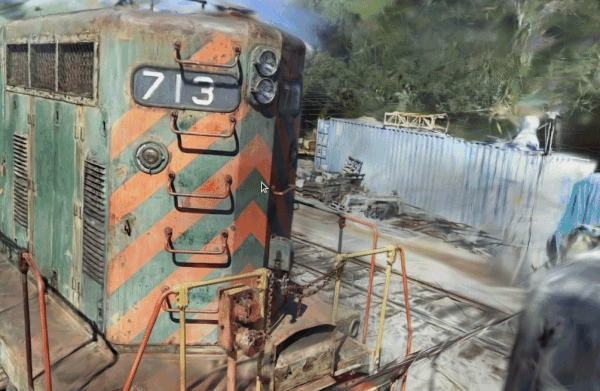
|
|
65
|
+
|
|
66
|
+
### 4. LiDAR-LiDAR Calibration Tools
|
|
67
|
+
|
|
68
|
+
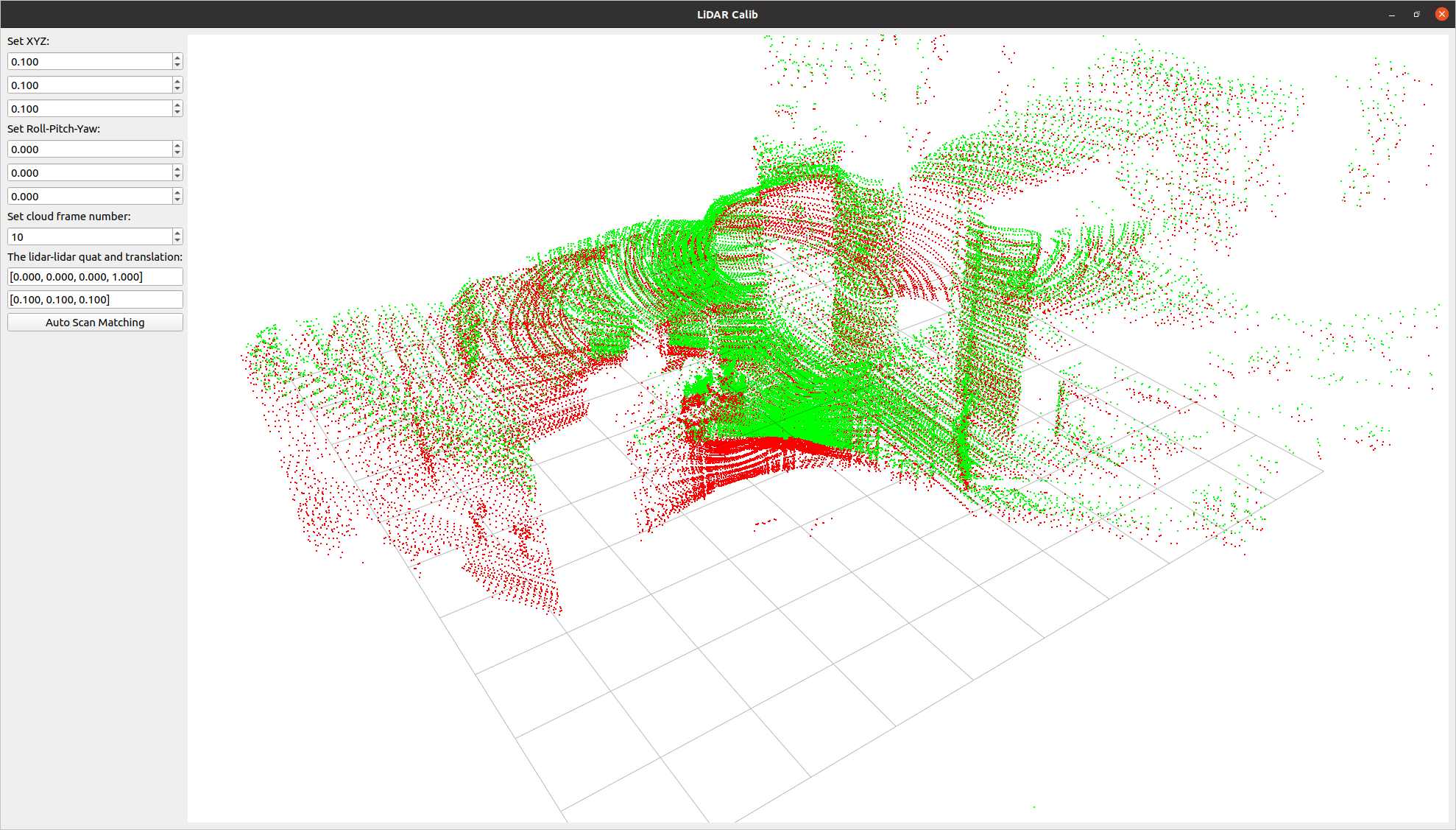
A tool to compute the relative pose between two LiDARs. It allows for both manual adjustment in the settings screen and automatic calibration.
|
|
69
|
+
|
|
70
|
+
```sh
|
|
71
|
+
lidar_calib --lidar0=/YOUR_LIDAR0_TOPIC --lidar1=/YOUR_LIDAR1_TOPIC
|
|
72
|
+
```
|
|
73
|
+
|
|
74
|
+
|
|
75
|
+
|
|
76
|
+
### 5. LiDAR-Camera Calibration Tools
|
|
77
|
+
|
|
78
|
+
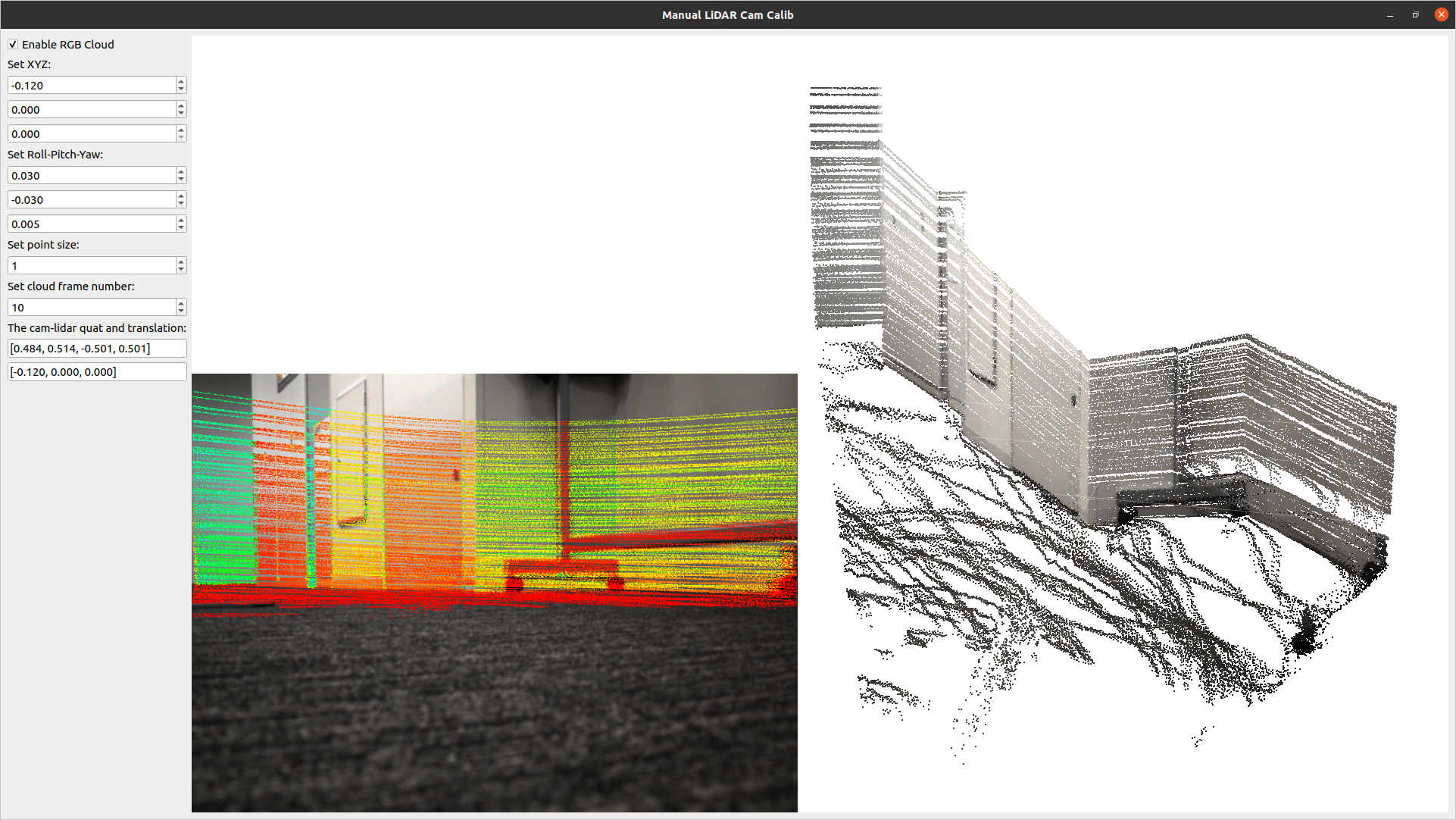
A tool for calculating the relative pose between a LiDAR and a camera. It allows for manual adjustment in the settings screen and real-time verification of LiDAR point projection onto images.
|
|
79
|
+
|
|
80
|
+
```sh
|
|
81
|
+
lidar_cam_calib --lidar=/YOUR_LIDAR_TOPIC --camera=/YOUR_CAMERA_TOPIC --camera_info=/YOUR_CAMERA_INFO_TOPIC
|
|
82
|
+
```
|
|
83
|
+
|
|
84
|
+
|
|
85
|
+
|
|
86
|
+
## Using as a Library
|
|
87
|
+
|
|
88
|
+
Using the examples above, you can easily customize and develop your own 3D viewer with `q3dviewer`. Below is a coding example.
|
|
89
|
+
|
|
90
|
+
### Custom 3D Viewer
|
|
91
|
+
|
|
92
|
+
```python
|
|
93
|
+
#!/usr/bin/env python3
|
|
94
|
+
|
|
95
|
+
import q3dviewer as q3d # Import q3dviewer
|
|
96
|
+
|
|
97
|
+
def main():
|
|
98
|
+
# Create a Qt application
|
|
99
|
+
app = q3d.QApplication([])
|
|
100
|
+
|
|
101
|
+
# Create various 3D items
|
|
102
|
+
axis_item = q3d.AxisItem(size=0.5, width=5)
|
|
103
|
+
grid_item = q3d.GridItem(size=10, spacing=1)
|
|
104
|
+
|
|
105
|
+
# Create a viewer
|
|
106
|
+
viewer = q3d.Viewer(name='example')
|
|
107
|
+
# Add items to the viewer
|
|
108
|
+
viewer.add_items({
|
|
109
|
+
'grid': grid_item,
|
|
110
|
+
'axis': axis_item,
|
|
111
|
+
})
|
|
112
|
+
|
|
113
|
+
# Show the viewer & run the Qt application
|
|
114
|
+
viewer.show()
|
|
115
|
+
app.exec()
|
|
116
|
+
|
|
117
|
+
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
|
118
|
+
main()
|
|
119
|
+
```
|
|
120
|
+
|
|
121
|
+
`q3dviewer` provides the following 3D items:
|
|
122
|
+
|
|
123
|
+
- **AxisItem**: Displaying coordinate axes or self-position
|
|
124
|
+
- **CloudItem**: Displaying point clouds
|
|
125
|
+
- **CloudIOItem**: Displaying point clouds with I/O capabilities
|
|
126
|
+
- **GaussianItem**: Displaying 3D Gaussians
|
|
127
|
+
- **GridItem**: Displaying grids
|
|
128
|
+
- **ImageItem**: Displaying 2D images
|
|
129
|
+
- **Text2DItem**: Displaying 2D text
|
|
130
|
+
- **LineItem**: Displaying lines or trajectories
|
|
131
|
+
|
|
132
|
+
### Developing Custom Items
|
|
133
|
+
|
|
134
|
+
In addition to the standard 3D items provided, you can visualize custom 3D items with simple coding. Below is a sample:
|
|
135
|
+
|
|
136
|
+
```python
|
|
137
|
+
from OpenGL.GL import *
|
|
138
|
+
import numpy as np
|
|
139
|
+
import q3dviewer as q3d
|
|
140
|
+
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QLabel, QSpinBox
|
|
141
|
+
|
|
142
|
+
class YourItem(q3d.BaseItem):
|
|
143
|
+
def __init__(self):
|
|
144
|
+
super(YourItem, self).__init__()
|
|
145
|
+
pass # Necessary initialization
|
|
146
|
+
|
|
147
|
+
def add_setting(self, layout):
|
|
148
|
+
# Initialize the settings screen
|
|
149
|
+
label = QLabel("Add your setting:")
|
|
150
|
+
layout.addWidget(label)
|
|
151
|
+
box = QSpinBox()
|
|
152
|
+
layout.addWidget(box)
|
|
153
|
+
|
|
154
|
+
def set_data(self, data):
|
|
155
|
+
pass # Obtain the data you want to visualize
|
|
156
|
+
|
|
157
|
+
def initialize_gl(self):
|
|
158
|
+
pass # OpenGL initialization settings (if needed)
|
|
159
|
+
|
|
160
|
+
def paint(self):
|
|
161
|
+
pass # Visualize 3D objects using OpenGL
|
|
162
|
+
```
|
|
163
|
+
|
|
164
|
+
Enjoy using `q3dviewer`!
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,261 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
"""
|
|
2
|
+
Copyright 2024 Panasonic Advanced Technology Development Co.,Ltd. (Liu Yang)
|
|
3
|
+
Distributed under MIT license. See LICENSE for more information.
|
|
4
|
+
"""
|
|
5
|
+
|
|
6
|
+
from OpenGL.GL import *
|
|
7
|
+
from math import radians, tan
|
|
8
|
+
import numpy as np
|
|
9
|
+
from PySide6 import QtCore, QtGui, QtOpenGLWidgets
|
|
10
|
+
from q3dviewer.utils.maths import frustum, euler_to_matrix, makeT
|
|
11
|
+
|
|
12
|
+
|
|
13
|
+
class BaseGLWidget(QtOpenGLWidgets.QOpenGLWidget):
|
|
14
|
+
def __init__(self, parent=None):
|
|
15
|
+
QtOpenGLWidgets.QOpenGLWidget.__init__(self, parent)
|
|
16
|
+
self.setFocusPolicy(QtCore.Qt.FocusPolicy.ClickFocus)
|
|
17
|
+
self.reset()
|
|
18
|
+
self._fov = 60
|
|
19
|
+
self.items = []
|
|
20
|
+
self.keyTimer = QtCore.QTimer()
|
|
21
|
+
self.color = np.array([0, 0, 0, 0])
|
|
22
|
+
self.dist = 40
|
|
23
|
+
self.euler = np.array([np.pi/3, 0, np.pi/4])
|
|
24
|
+
self.center = np.array([0, 0, 0.])
|
|
25
|
+
self.active_keys = set()
|
|
26
|
+
self.show_center = False
|
|
27
|
+
self.enable_show_center = True
|
|
28
|
+
|
|
29
|
+
def keyPressEvent(self, ev: QtGui.QKeyEvent):
|
|
30
|
+
if ev.key() == QtCore.Qt.Key_Up or \
|
|
31
|
+
ev.key() == QtCore.Qt.Key_Down or \
|
|
32
|
+
ev.key() == QtCore.Qt.Key_Left or \
|
|
33
|
+
ev.key() == QtCore.Qt.Key_Right or \
|
|
34
|
+
ev.key() == QtCore.Qt.Key_Z or \
|
|
35
|
+
ev.key() == QtCore.Qt.Key_X or \
|
|
36
|
+
ev.key() == QtCore.Qt.Key_A or \
|
|
37
|
+
ev.key() == QtCore.Qt.Key_D or \
|
|
38
|
+
ev.key() == QtCore.Qt.Key_W or \
|
|
39
|
+
ev.key() == QtCore.Qt.Key_S:
|
|
40
|
+
self.active_keys.add(ev.key())
|
|
41
|
+
self.active_keys.add(ev.key())
|
|
42
|
+
|
|
43
|
+
def keyReleaseEvent(self, ev: QtGui.QKeyEvent):
|
|
44
|
+
self.active_keys.discard(ev.key())
|
|
45
|
+
|
|
46
|
+
def current_width(self):
|
|
47
|
+
"""
|
|
48
|
+
Return the current width of the widget.
|
|
49
|
+
"""
|
|
50
|
+
return int(self.width() * self.devicePixelRatioF())
|
|
51
|
+
|
|
52
|
+
def current_height(self):
|
|
53
|
+
"""
|
|
54
|
+
Return the current height of the widget.
|
|
55
|
+
"""
|
|
56
|
+
return int(self.height() * self.devicePixelRatioF())
|
|
57
|
+
|
|
58
|
+
def reset(self):
|
|
59
|
+
pass
|
|
60
|
+
|
|
61
|
+
def add_item(self, item):
|
|
62
|
+
"""
|
|
63
|
+
Add the item to the glwidget.
|
|
64
|
+
"""
|
|
65
|
+
self.items.append(item)
|
|
66
|
+
item.set_glwidget(self)
|
|
67
|
+
|
|
68
|
+
def remove_item(self, item):
|
|
69
|
+
"""
|
|
70
|
+
Remove the item from the glwidget.
|
|
71
|
+
"""
|
|
72
|
+
self.items.remove(item)
|
|
73
|
+
item.set_glwidget(None)
|
|
74
|
+
|
|
75
|
+
def clear(self):
|
|
76
|
+
"""
|
|
77
|
+
Remove all items from the glwidget.
|
|
78
|
+
"""
|
|
79
|
+
for item in self.items:
|
|
80
|
+
item.set_glwidget(None)
|
|
81
|
+
self.items = []
|
|
82
|
+
|
|
83
|
+
def initializeGL(self):
|
|
84
|
+
"""
|
|
85
|
+
the method is herted from QOpenGLWidget,
|
|
86
|
+
and it is called when the widget is first shown.
|
|
87
|
+
"""
|
|
88
|
+
for item in self.items:
|
|
89
|
+
item.initialize()
|
|
90
|
+
|
|
91
|
+
def mouseReleaseEvent(self, ev):
|
|
92
|
+
if hasattr(self, 'mousePos'):
|
|
93
|
+
delattr(self, 'mousePos')
|
|
94
|
+
|
|
95
|
+
def update_dist(self, delta):
|
|
96
|
+
self.dist += delta
|
|
97
|
+
if self.dist < 0.1:
|
|
98
|
+
self.dist = 0.1
|
|
99
|
+
|
|
100
|
+
def wheelEvent(self, ev):
|
|
101
|
+
delta = ev.angleDelta().x()
|
|
102
|
+
if delta == 0:
|
|
103
|
+
delta = ev.angleDelta().y()
|
|
104
|
+
self.update_dist(-delta * self.dist * 0.001)
|
|
105
|
+
self.show_center = True
|
|
106
|
+
|
|
107
|
+
def mouseMoveEvent(self, ev):
|
|
108
|
+
lpos = ev.localPos()
|
|
109
|
+
if not hasattr(self, 'mousePos'):
|
|
110
|
+
self.mousePos = lpos
|
|
111
|
+
diff = lpos - self.mousePos
|
|
112
|
+
self.mousePos = lpos
|
|
113
|
+
if ev.buttons() == QtCore.Qt.MouseButton.RightButton:
|
|
114
|
+
rot_speed = 0.2
|
|
115
|
+
dyaw = radians(-diff.x() * rot_speed)
|
|
116
|
+
droll = radians(-diff.y() * rot_speed)
|
|
117
|
+
self.rotate(droll, 0, dyaw)
|
|
118
|
+
elif ev.buttons() == QtCore.Qt.MouseButton.LeftButton:
|
|
119
|
+
Rwc = euler_to_matrix(self.euler)
|
|
120
|
+
Kinv = np.linalg.inv(self.get_K())
|
|
121
|
+
dist = max(self.dist, 0.5)
|
|
122
|
+
self.center += Rwc @ Kinv @ np.array([-diff.x(), diff.y(), 0]) * dist
|
|
123
|
+
self.show_center = True
|
|
124
|
+
|
|
125
|
+
def paintGL(self):
|
|
126
|
+
pass
|
|
127
|
+
self.update_model_projection()
|
|
128
|
+
self.update_model_view()
|
|
129
|
+
bgcolor = self.color
|
|
130
|
+
glClearColor(*bgcolor)
|
|
131
|
+
glClear(GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT | GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT)
|
|
132
|
+
for item in self.items:
|
|
133
|
+
if not item.visible():
|
|
134
|
+
continue
|
|
135
|
+
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW)
|
|
136
|
+
glPushMatrix()
|
|
137
|
+
glPushAttrib(GL_ALL_ATTRIB_BITS)
|
|
138
|
+
try:
|
|
139
|
+
item.paint()
|
|
140
|
+
finally:
|
|
141
|
+
glPopAttrib()
|
|
142
|
+
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW)
|
|
143
|
+
glPopMatrix()
|
|
144
|
+
|
|
145
|
+
# Show center as a point if updated by mouse move event
|
|
146
|
+
if self.enable_show_center and self.show_center:
|
|
147
|
+
point_size = np.clip((self.get_K()[0, 0] / self.dist), 10, 100)
|
|
148
|
+
glPointSize(point_size)
|
|
149
|
+
glBegin(GL_POINTS)
|
|
150
|
+
glColor3f(1.0, 0.0, 0.0) # Red color for the center point
|
|
151
|
+
glVertex3f(*self.center)
|
|
152
|
+
glEnd()
|
|
153
|
+
self.show_center = False
|
|
154
|
+
|
|
155
|
+
def update_movement(self):
|
|
156
|
+
"""
|
|
157
|
+
Update the movement of the camera based on the active keys.
|
|
158
|
+
"""
|
|
159
|
+
if not self.active_keys:
|
|
160
|
+
return
|
|
161
|
+
rot_speed = 0.5
|
|
162
|
+
trans_speed = max(self.dist * 0.005, 0.1)
|
|
163
|
+
# Handle rotation keys
|
|
164
|
+
if QtCore.Qt.Key_Up in self.active_keys:
|
|
165
|
+
self.rotate(radians(rot_speed), 0, 0)
|
|
166
|
+
if QtCore.Qt.Key_Down in self.active_keys:
|
|
167
|
+
self.rotate(radians(-rot_speed), 0, 0)
|
|
168
|
+
if QtCore.Qt.Key_Left in self.active_keys:
|
|
169
|
+
self.rotate(0, 0, radians(rot_speed))
|
|
170
|
+
if QtCore.Qt.Key_Right in self.active_keys:
|
|
171
|
+
self.rotate(0, 0, radians(-rot_speed))
|
|
172
|
+
# Handle zoom keys
|
|
173
|
+
xz_keys = {QtCore.Qt.Key_Z, QtCore.Qt.Key_X}
|
|
174
|
+
if self.active_keys & xz_keys:
|
|
175
|
+
Rwc = euler_to_matrix(self.euler)
|
|
176
|
+
if QtCore.Qt.Key_Z in self.active_keys:
|
|
177
|
+
self.center += Rwc @ np.array([0, 0, -trans_speed])
|
|
178
|
+
if QtCore.Qt.Key_X in self.active_keys:
|
|
179
|
+
self.center += Rwc @ np.array([0, 0, trans_speed])
|
|
180
|
+
# Handle translation keys on the z plane
|
|
181
|
+
dir_keys = {QtCore.Qt.Key_W, QtCore.Qt.Key_S, QtCore.Qt.Key_A, QtCore.Qt.Key_D}
|
|
182
|
+
if self.active_keys & dir_keys:
|
|
183
|
+
Rz = euler_to_matrix([0, 0, self.euler[2]])
|
|
184
|
+
if QtCore.Qt.Key_W in self.active_keys:
|
|
185
|
+
self.center += Rz @ np.array([0, trans_speed, 0])
|
|
186
|
+
if QtCore.Qt.Key_S in self.active_keys:
|
|
187
|
+
self.center += Rz @ np.array([0, -trans_speed, 0])
|
|
188
|
+
if QtCore.Qt.Key_A in self.active_keys:
|
|
189
|
+
self.center += Rz @ np.array([-trans_speed, 0, 0])
|
|
190
|
+
if QtCore.Qt.Key_D in self.active_keys:
|
|
191
|
+
self.center += Rz @ np.array([trans_speed, 0, 0])
|
|
192
|
+
|
|
193
|
+
def update_model_view(self):
|
|
194
|
+
m = self.get_view_matrix()
|
|
195
|
+
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW)
|
|
196
|
+
glLoadMatrixf(m.T)
|
|
197
|
+
|
|
198
|
+
def get_view_matrix(self):
|
|
199
|
+
two = self.center # the origin(center) in the world frame
|
|
200
|
+
tco = np.array([0, 0, self.dist]) # the origin(center) in camera frame
|
|
201
|
+
Rwc = euler_to_matrix(self.euler)
|
|
202
|
+
twc = two + Rwc @ tco
|
|
203
|
+
Rcw = Rwc.T
|
|
204
|
+
tcw = -Rcw @ twc
|
|
205
|
+
Tcw = makeT(Rcw, tcw)
|
|
206
|
+
return Tcw
|
|
207
|
+
|
|
208
|
+
def set_cam_position(self, **kwargs):
|
|
209
|
+
pos = kwargs.get('pos', None)
|
|
210
|
+
distance = kwargs.get('distance', None)
|
|
211
|
+
if pos is not None:
|
|
212
|
+
self.center = pos
|
|
213
|
+
if distance is not None:
|
|
214
|
+
self.dist = distance
|
|
215
|
+
|
|
216
|
+
def set_color(self, color):
|
|
217
|
+
self.color = color
|
|
218
|
+
|
|
219
|
+
def update(self):
|
|
220
|
+
self.update_movement()
|
|
221
|
+
super().update()
|
|
222
|
+
|
|
223
|
+
def update_model_projection(self):
|
|
224
|
+
m = self.get_projection_matrix()
|
|
225
|
+
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION)
|
|
226
|
+
glLoadMatrixf(m.T)
|
|
227
|
+
|
|
228
|
+
def get_projection_matrix(self):
|
|
229
|
+
w, h = self.current_width(), self.current_height()
|
|
230
|
+
dist = self.dist
|
|
231
|
+
near = dist * 0.001
|
|
232
|
+
far = dist * 10000.
|
|
233
|
+
r = near * tan(0.5 * radians(self._fov))
|
|
234
|
+
t = r * h / w
|
|
235
|
+
matrix = frustum(-r, r, -t, t, near, far)
|
|
236
|
+
return matrix
|
|
237
|
+
|
|
238
|
+
def get_K(self):
|
|
239
|
+
project_matrix = self.get_projection_matrix()
|
|
240
|
+
width = self.current_width()
|
|
241
|
+
height = self.current_height()
|
|
242
|
+
fx = project_matrix[0, 0] * width / 2
|
|
243
|
+
fy = project_matrix[1, 1] * height / 2
|
|
244
|
+
cx = width / 2
|
|
245
|
+
cy = height / 2
|
|
246
|
+
K = np.array([
|
|
247
|
+
[fx, 0, cx],
|
|
248
|
+
[0, fy, cy],
|
|
249
|
+
[0, 0, 1]
|
|
250
|
+
])
|
|
251
|
+
return K
|
|
252
|
+
|
|
253
|
+
def rotate(self, rx=0, ry=0, rz=0):
|
|
254
|
+
# update the euler angles
|
|
255
|
+
self.euler += np.array([rx, ry, rz])
|
|
256
|
+
self.euler[2] = (self.euler[2] + np.pi) % (2 * np.pi) - np.pi
|
|
257
|
+
self.euler[1] = (self.euler[1] + np.pi) % (2 * np.pi) - np.pi
|
|
258
|
+
self.euler[0] = np.clip(self.euler[0], 0, np.pi)
|
|
259
|
+
|
|
260
|
+
def change_show_center(self, state):
|
|
261
|
+
self.enable_show_center = state
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
"""
|
|
2
|
+
Copyright 2024 Panasonic Advanced Technology Development Co.,Ltd. (Liu Yang)
|
|
3
|
+
Distributed under MIT license. See LICENSE for more information.
|
|
4
|
+
"""
|
|
5
|
+
|
|
6
|
+
from PySide6 import QtCore
|
|
7
|
+
import numpy as np
|
|
8
|
+
|
|
9
|
+
class BaseItem(QtCore.QObject):
|
|
10
|
+
_next_id = 0
|
|
11
|
+
|
|
12
|
+
def __init__(self):
|
|
13
|
+
super().__init__()
|
|
14
|
+
self._id = BaseItem._next_id
|
|
15
|
+
BaseItem._next_id += 1
|
|
16
|
+
self._glwidget = None
|
|
17
|
+
self._visible = True
|
|
18
|
+
self._initialized = False
|
|
19
|
+
|
|
20
|
+
def set_glwidget(self, v):
|
|
21
|
+
self._glwidget = v
|
|
22
|
+
|
|
23
|
+
def glwidget(self):
|
|
24
|
+
return self._glwidget
|
|
25
|
+
|
|
26
|
+
def hide(self):
|
|
27
|
+
self._visible = False
|
|
28
|
+
|
|
29
|
+
def show(self):
|
|
30
|
+
self._visible = True
|
|
31
|
+
|
|
32
|
+
def set_visible(self, vis):
|
|
33
|
+
self._visible = vis
|
|
34
|
+
|
|
35
|
+
def visible(self):
|
|
36
|
+
return self._visible
|
|
37
|
+
|
|
38
|
+
def initialize(self):
|
|
39
|
+
if not self._initialized:
|
|
40
|
+
self.initialize_gl()
|
|
41
|
+
|
|
42
|
+
def initialize_gl(self):
|
|
43
|
+
"""
|
|
44
|
+
Initialize OpenGL resources for the item.
|
|
45
|
+
This method should be overridden by subclasses to set up any necessary OpenGL resources.
|
|
46
|
+
"""
|
|
47
|
+
pass
|
|
48
|
+
|
|
49
|
+
def paint(self):
|
|
50
|
+
"""
|
|
51
|
+
Render the item using OpenGL.
|
|
52
|
+
This method should be overridden by subclasses to perform the actual rendering.
|
|
53
|
+
"""
|
|
54
|
+
pass
|
|
55
|
+
|
|
56
|
+
|
|
57
|
+
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
from q3dviewer.custom_items.axis_item import *
|
|
2
|
+
from q3dviewer.custom_items.cloud_item import *
|
|
3
|
+
from q3dviewer.custom_items.cloud_io_item import *
|
|
4
|
+
from q3dviewer.custom_items.gaussian_item import *
|
|
5
|
+
from q3dviewer.custom_items.frame_item import *
|
|
6
|
+
from q3dviewer.custom_items.grid_item import *
|
|
7
|
+
from q3dviewer.custom_items.text_item import *
|
|
8
|
+
from q3dviewer.custom_items.image_item import *
|
|
9
|
+
from q3dviewer.custom_items.line_item import *
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,148 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
"""
|
|
2
|
+
Copyright 2024 Panasonic Advanced Technology Development Co.,Ltd. (Liu Yang)
|
|
3
|
+
Distributed under MIT license. See LICENSE for more information.
|
|
4
|
+
"""
|
|
5
|
+
|
|
6
|
+
from q3dviewer.base_item import BaseItem
|
|
7
|
+
from q3dviewer.utils import set_uniform
|
|
8
|
+
from OpenGL.GL import *
|
|
9
|
+
import numpy as np
|
|
10
|
+
from OpenGL.GL import shaders
|
|
11
|
+
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QLabel, QDoubleSpinBox
|
|
12
|
+
|
|
13
|
+
|
|
14
|
+
# Vertex and Fragment shader source code
|
|
15
|
+
vertex_shader_source = """
|
|
16
|
+
#version 330 core
|
|
17
|
+
layout(location = 0) in vec3 position;
|
|
18
|
+
layout(location = 1) in vec3 color;
|
|
19
|
+
|
|
20
|
+
out vec3 ourColor;
|
|
21
|
+
|
|
22
|
+
uniform mat4 view_matrix;
|
|
23
|
+
uniform mat4 project_matrix;
|
|
24
|
+
uniform mat4 model_matrix;
|
|
25
|
+
uniform float size;
|
|
26
|
+
|
|
27
|
+
void main()
|
|
28
|
+
{
|
|
29
|
+
vec3 scaled_position = position * size;
|
|
30
|
+
gl_Position = project_matrix * view_matrix * model_matrix * vec4(scaled_position, 1.0);
|
|
31
|
+
ourColor = color;
|
|
32
|
+
}
|
|
33
|
+
"""
|
|
34
|
+
|
|
35
|
+
fragment_shader_source = """
|
|
36
|
+
#version 330 core
|
|
37
|
+
in vec3 ourColor;
|
|
38
|
+
out vec4 color;
|
|
39
|
+
|
|
40
|
+
void main()
|
|
41
|
+
{
|
|
42
|
+
color = vec4(ourColor, 1.0);
|
|
43
|
+
}
|
|
44
|
+
"""
|
|
45
|
+
|
|
46
|
+
|
|
47
|
+
class AxisItem(BaseItem):
|
|
48
|
+
def __init__(self, size=1.0, width=2):
|
|
49
|
+
super().__init__()
|
|
50
|
+
self.size = size
|
|
51
|
+
self.width = width
|
|
52
|
+
self.model_matrix = np.eye(4, dtype=np.float32)
|
|
53
|
+
self.need_update_setting = True
|
|
54
|
+
|
|
55
|
+
def initialize_gl(self):
|
|
56
|
+
# Axis vertices and colors
|
|
57
|
+
self.vertices = np.array([
|
|
58
|
+
# positions # colors
|
|
59
|
+
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0], # X axis (red)
|
|
60
|
+
[1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0],
|
|
61
|
+
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0], # Y axis (green)
|
|
62
|
+
[0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0],
|
|
63
|
+
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0], # Z axis (blue)
|
|
64
|
+
[0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0],
|
|
65
|
+
], dtype=np.float32)
|
|
66
|
+
|
|
67
|
+
self.vao = glGenVertexArrays(1)
|
|
68
|
+
vbo = glGenBuffers(1)
|
|
69
|
+
|
|
70
|
+
glBindVertexArray(self.vao)
|
|
71
|
+
|
|
72
|
+
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vbo)
|
|
73
|
+
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, self.vertices.nbytes, self.vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW)
|
|
74
|
+
|
|
75
|
+
# Vertex positions
|
|
76
|
+
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 24, ctypes.c_void_p(0))
|
|
77
|
+
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0)
|
|
78
|
+
|
|
79
|
+
# Vertex colors
|
|
80
|
+
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 24, ctypes.c_void_p(12))
|
|
81
|
+
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1)
|
|
82
|
+
|
|
83
|
+
# Compile shaders and create shader program
|
|
84
|
+
self.program = shaders.compileProgram(
|
|
85
|
+
shaders.compileShader(vertex_shader_source, GL_VERTEX_SHADER),
|
|
86
|
+
shaders.compileShader(fragment_shader_source, GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER),
|
|
87
|
+
)
|
|
88
|
+
|
|
89
|
+
glBindVertexArray(0)
|
|
90
|
+
|
|
91
|
+
def add_setting(self, layout):
|
|
92
|
+
label_size = QLabel("Set size:")
|
|
93
|
+
layout.addWidget(label_size)
|
|
94
|
+
spinbox_size = QDoubleSpinBox()
|
|
95
|
+
spinbox_size.setSingleStep(0.1)
|
|
96
|
+
layout.addWidget(spinbox_size)
|
|
97
|
+
spinbox_size.setValue(self.size)
|
|
98
|
+
spinbox_size.valueChanged.connect(self.set_size)
|
|
99
|
+
spinbox_size.setRange(0.0, 100)
|
|
100
|
+
|
|
101
|
+
label_width = QLabel("Set width:")
|
|
102
|
+
layout.addWidget(label_width)
|
|
103
|
+
spinbox_width = QDoubleSpinBox()
|
|
104
|
+
layout.addWidget(spinbox_width)
|
|
105
|
+
spinbox_width.setSingleStep(0.1)
|
|
106
|
+
spinbox_width.setValue(self.width)
|
|
107
|
+
spinbox_width.valueChanged.connect(self.set_width)
|
|
108
|
+
spinbox_width.setRange(0, 1000)
|
|
109
|
+
|
|
110
|
+
def set_size(self, size):
|
|
111
|
+
self.size = size
|
|
112
|
+
self.need_update_setting = True
|
|
113
|
+
|
|
114
|
+
def update_setting(self):
|
|
115
|
+
if not self.need_update_setting:
|
|
116
|
+
return
|
|
117
|
+
glUseProgram(self.program)
|
|
118
|
+
set_uniform(self.program, float(self.size), 'size')
|
|
119
|
+
set_uniform(self.program, self.model_matrix, 'model_matrix')
|
|
120
|
+
glUseProgram(0)
|
|
121
|
+
self.need_update_setting = False
|
|
122
|
+
|
|
123
|
+
def set_width(self, width):
|
|
124
|
+
self.width = width
|
|
125
|
+
|
|
126
|
+
def set_transform(self, transform):
|
|
127
|
+
"""
|
|
128
|
+
Set the transformation matrix for the axis item.
|
|
129
|
+
"""
|
|
130
|
+
self.model_matrix = transform
|
|
131
|
+
self.need_update_setting = True
|
|
132
|
+
|
|
133
|
+
def paint(self):
|
|
134
|
+
self.update_setting()
|
|
135
|
+
glLineWidth(self.width)
|
|
136
|
+
glUseProgram(self.program)
|
|
137
|
+
glBindVertexArray(self.vao)
|
|
138
|
+
|
|
139
|
+
view_matrix = self.glwidget().get_view_matrix()
|
|
140
|
+
project_matrix = self.glwidget().get_projection_matrix()
|
|
141
|
+
set_uniform(self.program, view_matrix, 'view_matrix')
|
|
142
|
+
set_uniform(self.program, project_matrix, 'project_matrix')
|
|
143
|
+
|
|
144
|
+
glDrawArrays(GL_LINES, 0, 6)
|
|
145
|
+
|
|
146
|
+
glBindVertexArray(0)
|
|
147
|
+
glUseProgram(0)
|
|
148
|
+
glLineWidth(1)
|