oikan 0.0.2.1__tar.gz → 0.0.2.3__tar.gz
This diff represents the content of publicly available package versions that have been released to one of the supported registries. The information contained in this diff is provided for informational purposes only and reflects changes between package versions as they appear in their respective public registries.
- {oikan-0.0.2.1 → oikan-0.0.2.3}/PKG-INFO +85 -24
- {oikan-0.0.2.1 → oikan-0.0.2.3}/README.md +84 -23
- {oikan-0.0.2.1 → oikan-0.0.2.3}/oikan.egg-info/PKG-INFO +85 -24
- {oikan-0.0.2.1 → oikan-0.0.2.3}/pyproject.toml +1 -1
- {oikan-0.0.2.1 → oikan-0.0.2.3}/LICENSE +0 -0
- {oikan-0.0.2.1 → oikan-0.0.2.3}/oikan/__init__.py +0 -0
- {oikan-0.0.2.1 → oikan-0.0.2.3}/oikan/exceptions.py +0 -0
- {oikan-0.0.2.1 → oikan-0.0.2.3}/oikan/model.py +0 -0
- {oikan-0.0.2.1 → oikan-0.0.2.3}/oikan/symbolic.py +0 -0
- {oikan-0.0.2.1 → oikan-0.0.2.3}/oikan/utils.py +0 -0
- {oikan-0.0.2.1 → oikan-0.0.2.3}/oikan.egg-info/SOURCES.txt +0 -0
- {oikan-0.0.2.1 → oikan-0.0.2.3}/oikan.egg-info/dependency_links.txt +0 -0
- {oikan-0.0.2.1 → oikan-0.0.2.3}/oikan.egg-info/requires.txt +0 -0
- {oikan-0.0.2.1 → oikan-0.0.2.3}/oikan.egg-info/top_level.txt +0 -0
- {oikan-0.0.2.1 → oikan-0.0.2.3}/setup.cfg +0 -0
- {oikan-0.0.2.1 → oikan-0.0.2.3}/setup.py +0 -0
|
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
|
|
1
1
|
Metadata-Version: 2.4
|
|
2
2
|
Name: oikan
|
|
3
|
-
Version: 0.0.2.
|
|
3
|
+
Version: 0.0.2.3
|
|
4
4
|
Summary: OIKAN: Optimized Interpretable Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks
|
|
5
5
|
Author: Arman Zhalgasbayev
|
|
6
6
|
License: MIT
|
|
@@ -43,9 +43,9 @@ OIKAN (Optimized Interpretable Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks) is a neuro-symbolic M
|
|
|
43
43
|
|
|
44
44
|
OIKAN is based on Kolmogorov's superposition theorem, which states that any multivariate continuous function can be represented as a composition of single-variable functions. We leverage this theory by:
|
|
45
45
|
|
|
46
|
-
1. Using neural networks to learn optimal basis functions
|
|
47
|
-
2.
|
|
48
|
-
3.
|
|
46
|
+
1. Using neural networks to learn optimal basis functions through interpretable edge transformations
|
|
47
|
+
2. Combining transformed features using learnable weights
|
|
48
|
+
3. Automatically extracting human-readable symbolic formulas
|
|
49
49
|
|
|
50
50
|
## Quick Start
|
|
51
51
|
|
|
@@ -71,13 +71,11 @@ from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
|
|
|
71
71
|
# Initialize model with optimal architecture
|
|
72
72
|
model = OIKANRegressor(
|
|
73
73
|
hidden_dims=[16, 8], # Network architecture
|
|
74
|
-
num_basis=10, # Number of basis functions
|
|
75
|
-
degree=3, # Polynomial degree
|
|
76
74
|
dropout=0.1 # Regularization
|
|
77
75
|
)
|
|
78
76
|
|
|
79
77
|
# Fit model (sklearn-style)
|
|
80
|
-
model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=
|
|
78
|
+
model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=100, lr=0.01)
|
|
81
79
|
|
|
82
80
|
# Get predictions
|
|
83
81
|
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
|
|
@@ -99,7 +97,7 @@ from oikan.model import OIKANClassifier
|
|
|
99
97
|
|
|
100
98
|
# Similar sklearn-style interface for classification
|
|
101
99
|
model = OIKANClassifier(hidden_dims=[16, 8])
|
|
102
|
-
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
|
|
100
|
+
model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=100, lr=0.01)
|
|
103
101
|
probas = model.predict_proba(X_test)
|
|
104
102
|
|
|
105
103
|
# Save classification formulas with implementation guidelines
|
|
@@ -114,22 +112,85 @@ model.save_symbolic_formula("classification_formula.txt")
|
|
|
114
112
|
|
|
115
113
|
## Architecture Details
|
|
116
114
|
|
|
117
|
-
OIKAN
|
|
118
|
-
|
|
119
|
-
1. **
|
|
120
|
-
-
|
|
121
|
-
|
|
122
|
-
|
|
123
|
-
|
|
124
|
-
2
|
|
125
|
-
|
|
126
|
-
|
|
127
|
-
|
|
128
|
-
|
|
129
|
-
|
|
130
|
-
|
|
131
|
-
|
|
132
|
-
|
|
115
|
+
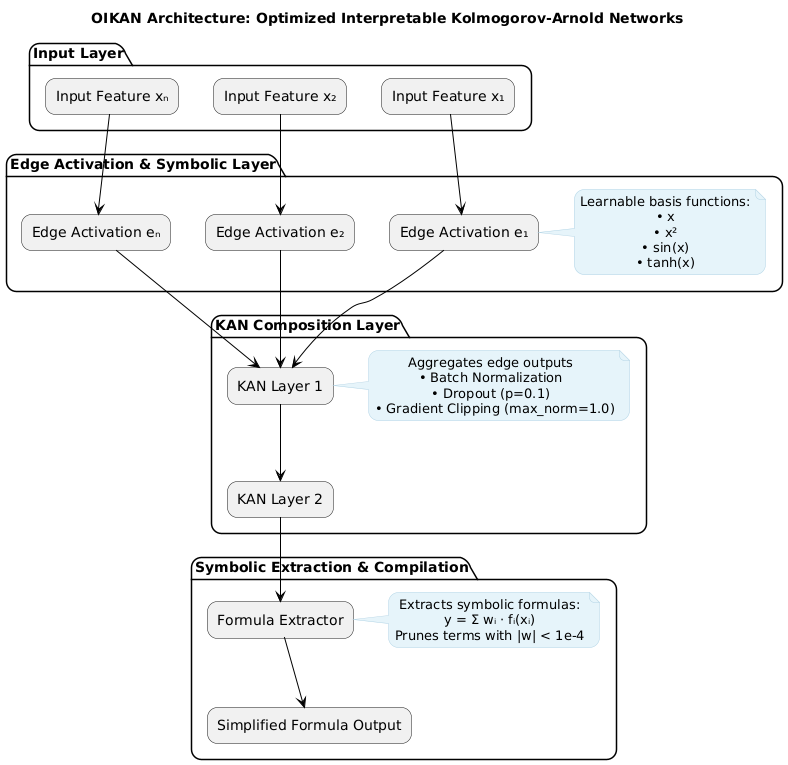
OIKAN implements a novel neuro-symbolic architecture based on Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theory through three specialized components:
|
|
116
|
+
|
|
117
|
+
1. **Edge Symbolic Layer**: Learns interpretable single-variable transformations
|
|
118
|
+
- Adaptive basis function composition using 9 core functions:
|
|
119
|
+
```python
|
|
120
|
+
ADVANCED_LIB = {
|
|
121
|
+
'x': ('x', lambda x: x),
|
|
122
|
+
'x^2': ('x^2', lambda x: x**2),
|
|
123
|
+
'x^3': ('x^3', lambda x: x**3),
|
|
124
|
+
'exp': ('exp(x)', lambda x: np.exp(x)),
|
|
125
|
+
'log': ('log(x)', lambda x: np.log(abs(x) + 1)),
|
|
126
|
+
'sqrt': ('sqrt(x)', lambda x: np.sqrt(abs(x))),
|
|
127
|
+
'tanh': ('tanh(x)', lambda x: np.tanh(x)),
|
|
128
|
+
'sin': ('sin(x)', lambda x: np.sin(x)),
|
|
129
|
+
'abs': ('abs(x)', lambda x: np.abs(x))
|
|
130
|
+
}
|
|
131
|
+
```
|
|
132
|
+
- Each input feature is transformed through these basis functions
|
|
133
|
+
- Learnable weights determine the optimal combination
|
|
134
|
+
|
|
135
|
+
2. **Neural Composition Layer**: Multi-layer feature aggregation
|
|
136
|
+
- Direct feature-to-feature connections through KAN layers
|
|
137
|
+
- Dropout regularization (p=0.1 default) for robust learning
|
|
138
|
+
- Gradient clipping (max_norm=1.0) for stable training
|
|
139
|
+
- User-configurable hidden layer dimensions
|
|
140
|
+
|
|
141
|
+
3. **Symbolic Extraction Layer**: Generates production-ready formulas
|
|
142
|
+
- Weight-based term pruning (threshold=1e-4)
|
|
143
|
+
- Automatic coefficient optimization
|
|
144
|
+
- Human-readable mathematical expressions
|
|
145
|
+
- Exportable to lightweight production code
|
|
146
|
+
|
|
147
|
+
### Architecture Diagram
|
|
148
|
+
|
|
149
|
+
|
|
150
|
+
|
|
151
|
+
### Key Design Principles
|
|
152
|
+
|
|
153
|
+
1. **Interpretability First**: All transformations maintain clear mathematical meaning
|
|
154
|
+
2. **Scikit-learn Compatibility**: Familiar `.fit()` and `.predict()` interface
|
|
155
|
+
3. **Production Ready**: Export formulas as lightweight mathematical expressions
|
|
156
|
+
4. **Automatic Simplification**: Remove insignificant terms (|w| < 1e-4)
|
|
157
|
+
|
|
158
|
+
## Model Components
|
|
159
|
+
|
|
160
|
+
1. **Symbolic Edge Functions**
|
|
161
|
+
```python
|
|
162
|
+
class EdgeActivation(nn.Module):
|
|
163
|
+
"""Learnable edge activation with basis functions"""
|
|
164
|
+
def forward(self, x):
|
|
165
|
+
return sum(self.weights[i] * basis[i](x) for i in range(self.num_basis))
|
|
166
|
+
```
|
|
167
|
+
|
|
168
|
+
2. **KAN Layer Implementation**
|
|
169
|
+
```python
|
|
170
|
+
class KANLayer(nn.Module):
|
|
171
|
+
"""Kolmogorov-Arnold Network layer"""
|
|
172
|
+
def forward(self, x):
|
|
173
|
+
edge_outputs = [self.edges[i](x[:,i]) for i in range(self.input_dim)]
|
|
174
|
+
return self.combine(edge_outputs)
|
|
175
|
+
```
|
|
176
|
+
|
|
177
|
+
3. **Formula Extraction**
|
|
178
|
+
```python
|
|
179
|
+
def get_symbolic_formula(self):
|
|
180
|
+
"""Extract interpretable mathematical expression"""
|
|
181
|
+
terms = []
|
|
182
|
+
for i, edge in enumerate(self.edges):
|
|
183
|
+
if abs(self.weights[i]) > threshold:
|
|
184
|
+
terms.append(f"{self.weights[i]:.4f} * {edge.formula}")
|
|
185
|
+
return " + ".join(terms)
|
|
186
|
+
```
|
|
187
|
+
|
|
188
|
+
### Key Design Principles
|
|
189
|
+
|
|
190
|
+
- **Modular Architecture**: Each component is independent and replaceable
|
|
191
|
+
- **Interpretability First**: All transformations maintain symbolic representations
|
|
192
|
+
- **Automatic Simplification**: Removes insignificant terms and combines similar expressions
|
|
193
|
+
- **Production Ready**: Export formulas for lightweight deployment
|
|
133
194
|
|
|
134
195
|
## Contributing
|
|
135
196
|
|
|
@@ -26,9 +26,9 @@ OIKAN (Optimized Interpretable Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks) is a neuro-symbolic M
|
|
|
26
26
|
|
|
27
27
|
OIKAN is based on Kolmogorov's superposition theorem, which states that any multivariate continuous function can be represented as a composition of single-variable functions. We leverage this theory by:
|
|
28
28
|
|
|
29
|
-
1. Using neural networks to learn optimal basis functions
|
|
30
|
-
2.
|
|
31
|
-
3.
|
|
29
|
+
1. Using neural networks to learn optimal basis functions through interpretable edge transformations
|
|
30
|
+
2. Combining transformed features using learnable weights
|
|
31
|
+
3. Automatically extracting human-readable symbolic formulas
|
|
32
32
|
|
|
33
33
|
## Quick Start
|
|
34
34
|
|
|
@@ -54,13 +54,11 @@ from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
|
|
|
54
54
|
# Initialize model with optimal architecture
|
|
55
55
|
model = OIKANRegressor(
|
|
56
56
|
hidden_dims=[16, 8], # Network architecture
|
|
57
|
-
num_basis=10, # Number of basis functions
|
|
58
|
-
degree=3, # Polynomial degree
|
|
59
57
|
dropout=0.1 # Regularization
|
|
60
58
|
)
|
|
61
59
|
|
|
62
60
|
# Fit model (sklearn-style)
|
|
63
|
-
model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=
|
|
61
|
+
model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=100, lr=0.01)
|
|
64
62
|
|
|
65
63
|
# Get predictions
|
|
66
64
|
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
|
|
@@ -82,7 +80,7 @@ from oikan.model import OIKANClassifier
|
|
|
82
80
|
|
|
83
81
|
# Similar sklearn-style interface for classification
|
|
84
82
|
model = OIKANClassifier(hidden_dims=[16, 8])
|
|
85
|
-
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
|
|
83
|
+
model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=100, lr=0.01)
|
|
86
84
|
probas = model.predict_proba(X_test)
|
|
87
85
|
|
|
88
86
|
# Save classification formulas with implementation guidelines
|
|
@@ -97,22 +95,85 @@ model.save_symbolic_formula("classification_formula.txt")
|
|
|
97
95
|
|
|
98
96
|
## Architecture Details
|
|
99
97
|
|
|
100
|
-
OIKAN
|
|
101
|
-
|
|
102
|
-
1. **
|
|
103
|
-
-
|
|
104
|
-
|
|
105
|
-
|
|
106
|
-
|
|
107
|
-
2
|
|
108
|
-
|
|
109
|
-
|
|
110
|
-
|
|
111
|
-
|
|
112
|
-
|
|
113
|
-
|
|
114
|
-
|
|
115
|
-
|
|
98
|
+
OIKAN implements a novel neuro-symbolic architecture based on Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theory through three specialized components:
|
|
99
|
+
|
|
100
|
+
1. **Edge Symbolic Layer**: Learns interpretable single-variable transformations
|
|
101
|
+
- Adaptive basis function composition using 9 core functions:
|
|
102
|
+
```python
|
|
103
|
+
ADVANCED_LIB = {
|
|
104
|
+
'x': ('x', lambda x: x),
|
|
105
|
+
'x^2': ('x^2', lambda x: x**2),
|
|
106
|
+
'x^3': ('x^3', lambda x: x**3),
|
|
107
|
+
'exp': ('exp(x)', lambda x: np.exp(x)),
|
|
108
|
+
'log': ('log(x)', lambda x: np.log(abs(x) + 1)),
|
|
109
|
+
'sqrt': ('sqrt(x)', lambda x: np.sqrt(abs(x))),
|
|
110
|
+
'tanh': ('tanh(x)', lambda x: np.tanh(x)),
|
|
111
|
+
'sin': ('sin(x)', lambda x: np.sin(x)),
|
|
112
|
+
'abs': ('abs(x)', lambda x: np.abs(x))
|
|
113
|
+
}
|
|
114
|
+
```
|
|
115
|
+
- Each input feature is transformed through these basis functions
|
|
116
|
+
- Learnable weights determine the optimal combination
|
|
117
|
+
|
|
118
|
+
2. **Neural Composition Layer**: Multi-layer feature aggregation
|
|
119
|
+
- Direct feature-to-feature connections through KAN layers
|
|
120
|
+
- Dropout regularization (p=0.1 default) for robust learning
|
|
121
|
+
- Gradient clipping (max_norm=1.0) for stable training
|
|
122
|
+
- User-configurable hidden layer dimensions
|
|
123
|
+
|
|
124
|
+
3. **Symbolic Extraction Layer**: Generates production-ready formulas
|
|
125
|
+
- Weight-based term pruning (threshold=1e-4)
|
|
126
|
+
- Automatic coefficient optimization
|
|
127
|
+
- Human-readable mathematical expressions
|
|
128
|
+
- Exportable to lightweight production code
|
|
129
|
+
|
|
130
|
+
### Architecture Diagram
|
|
131
|
+
|
|
132
|
+

|
|
133
|
+
|
|
134
|
+
### Key Design Principles
|
|
135
|
+
|
|
136
|
+
1. **Interpretability First**: All transformations maintain clear mathematical meaning
|
|
137
|
+
2. **Scikit-learn Compatibility**: Familiar `.fit()` and `.predict()` interface
|
|
138
|
+
3. **Production Ready**: Export formulas as lightweight mathematical expressions
|
|
139
|
+
4. **Automatic Simplification**: Remove insignificant terms (|w| < 1e-4)
|
|
140
|
+
|
|
141
|
+
## Model Components
|
|
142
|
+
|
|
143
|
+
1. **Symbolic Edge Functions**
|
|
144
|
+
```python
|
|
145
|
+
class EdgeActivation(nn.Module):
|
|
146
|
+
"""Learnable edge activation with basis functions"""
|
|
147
|
+
def forward(self, x):
|
|
148
|
+
return sum(self.weights[i] * basis[i](x) for i in range(self.num_basis))
|
|
149
|
+
```
|
|
150
|
+
|
|
151
|
+
2. **KAN Layer Implementation**
|
|
152
|
+
```python
|
|
153
|
+
class KANLayer(nn.Module):
|
|
154
|
+
"""Kolmogorov-Arnold Network layer"""
|
|
155
|
+
def forward(self, x):
|
|
156
|
+
edge_outputs = [self.edges[i](x[:,i]) for i in range(self.input_dim)]
|
|
157
|
+
return self.combine(edge_outputs)
|
|
158
|
+
```
|
|
159
|
+
|
|
160
|
+
3. **Formula Extraction**
|
|
161
|
+
```python
|
|
162
|
+
def get_symbolic_formula(self):
|
|
163
|
+
"""Extract interpretable mathematical expression"""
|
|
164
|
+
terms = []
|
|
165
|
+
for i, edge in enumerate(self.edges):
|
|
166
|
+
if abs(self.weights[i]) > threshold:
|
|
167
|
+
terms.append(f"{self.weights[i]:.4f} * {edge.formula}")
|
|
168
|
+
return " + ".join(terms)
|
|
169
|
+
```
|
|
170
|
+
|
|
171
|
+
### Key Design Principles
|
|
172
|
+
|
|
173
|
+
- **Modular Architecture**: Each component is independent and replaceable
|
|
174
|
+
- **Interpretability First**: All transformations maintain symbolic representations
|
|
175
|
+
- **Automatic Simplification**: Removes insignificant terms and combines similar expressions
|
|
176
|
+
- **Production Ready**: Export formulas for lightweight deployment
|
|
116
177
|
|
|
117
178
|
## Contributing
|
|
118
179
|
|
|
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
|
|
1
1
|
Metadata-Version: 2.4
|
|
2
2
|
Name: oikan
|
|
3
|
-
Version: 0.0.2.
|
|
3
|
+
Version: 0.0.2.3
|
|
4
4
|
Summary: OIKAN: Optimized Interpretable Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks
|
|
5
5
|
Author: Arman Zhalgasbayev
|
|
6
6
|
License: MIT
|
|
@@ -43,9 +43,9 @@ OIKAN (Optimized Interpretable Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks) is a neuro-symbolic M
|
|
|
43
43
|
|
|
44
44
|
OIKAN is based on Kolmogorov's superposition theorem, which states that any multivariate continuous function can be represented as a composition of single-variable functions. We leverage this theory by:
|
|
45
45
|
|
|
46
|
-
1. Using neural networks to learn optimal basis functions
|
|
47
|
-
2.
|
|
48
|
-
3.
|
|
46
|
+
1. Using neural networks to learn optimal basis functions through interpretable edge transformations
|
|
47
|
+
2. Combining transformed features using learnable weights
|
|
48
|
+
3. Automatically extracting human-readable symbolic formulas
|
|
49
49
|
|
|
50
50
|
## Quick Start
|
|
51
51
|
|
|
@@ -71,13 +71,11 @@ from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
|
|
|
71
71
|
# Initialize model with optimal architecture
|
|
72
72
|
model = OIKANRegressor(
|
|
73
73
|
hidden_dims=[16, 8], # Network architecture
|
|
74
|
-
num_basis=10, # Number of basis functions
|
|
75
|
-
degree=3, # Polynomial degree
|
|
76
74
|
dropout=0.1 # Regularization
|
|
77
75
|
)
|
|
78
76
|
|
|
79
77
|
# Fit model (sklearn-style)
|
|
80
|
-
model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=
|
|
78
|
+
model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=100, lr=0.01)
|
|
81
79
|
|
|
82
80
|
# Get predictions
|
|
83
81
|
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
|
|
@@ -99,7 +97,7 @@ from oikan.model import OIKANClassifier
|
|
|
99
97
|
|
|
100
98
|
# Similar sklearn-style interface for classification
|
|
101
99
|
model = OIKANClassifier(hidden_dims=[16, 8])
|
|
102
|
-
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
|
|
100
|
+
model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=100, lr=0.01)
|
|
103
101
|
probas = model.predict_proba(X_test)
|
|
104
102
|
|
|
105
103
|
# Save classification formulas with implementation guidelines
|
|
@@ -114,22 +112,85 @@ model.save_symbolic_formula("classification_formula.txt")
|
|
|
114
112
|
|
|
115
113
|
## Architecture Details
|
|
116
114
|
|
|
117
|
-
OIKAN
|
|
118
|
-
|
|
119
|
-
1. **
|
|
120
|
-
-
|
|
121
|
-
|
|
122
|
-
|
|
123
|
-
|
|
124
|
-
2
|
|
125
|
-
|
|
126
|
-
|
|
127
|
-
|
|
128
|
-
|
|
129
|
-
|
|
130
|
-
|
|
131
|
-
|
|
132
|
-
|
|
115
|
+
OIKAN implements a novel neuro-symbolic architecture based on Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theory through three specialized components:
|
|
116
|
+
|
|
117
|
+
1. **Edge Symbolic Layer**: Learns interpretable single-variable transformations
|
|
118
|
+
- Adaptive basis function composition using 9 core functions:
|
|
119
|
+
```python
|
|
120
|
+
ADVANCED_LIB = {
|
|
121
|
+
'x': ('x', lambda x: x),
|
|
122
|
+
'x^2': ('x^2', lambda x: x**2),
|
|
123
|
+
'x^3': ('x^3', lambda x: x**3),
|
|
124
|
+
'exp': ('exp(x)', lambda x: np.exp(x)),
|
|
125
|
+
'log': ('log(x)', lambda x: np.log(abs(x) + 1)),
|
|
126
|
+
'sqrt': ('sqrt(x)', lambda x: np.sqrt(abs(x))),
|
|
127
|
+
'tanh': ('tanh(x)', lambda x: np.tanh(x)),
|
|
128
|
+
'sin': ('sin(x)', lambda x: np.sin(x)),
|
|
129
|
+
'abs': ('abs(x)', lambda x: np.abs(x))
|
|
130
|
+
}
|
|
131
|
+
```
|
|
132
|
+
- Each input feature is transformed through these basis functions
|
|
133
|
+
- Learnable weights determine the optimal combination
|
|
134
|
+
|
|
135
|
+
2. **Neural Composition Layer**: Multi-layer feature aggregation
|
|
136
|
+
- Direct feature-to-feature connections through KAN layers
|
|
137
|
+
- Dropout regularization (p=0.1 default) for robust learning
|
|
138
|
+
- Gradient clipping (max_norm=1.0) for stable training
|
|
139
|
+
- User-configurable hidden layer dimensions
|
|
140
|
+
|
|
141
|
+
3. **Symbolic Extraction Layer**: Generates production-ready formulas
|
|
142
|
+
- Weight-based term pruning (threshold=1e-4)
|
|
143
|
+
- Automatic coefficient optimization
|
|
144
|
+
- Human-readable mathematical expressions
|
|
145
|
+
- Exportable to lightweight production code
|
|
146
|
+
|
|
147
|
+
### Architecture Diagram
|
|
148
|
+
|
|
149
|
+

|
|
150
|
+
|
|
151
|
+
### Key Design Principles
|
|
152
|
+
|
|
153
|
+
1. **Interpretability First**: All transformations maintain clear mathematical meaning
|
|
154
|
+
2. **Scikit-learn Compatibility**: Familiar `.fit()` and `.predict()` interface
|
|
155
|
+
3. **Production Ready**: Export formulas as lightweight mathematical expressions
|
|
156
|
+
4. **Automatic Simplification**: Remove insignificant terms (|w| < 1e-4)
|
|
157
|
+
|
|
158
|
+
## Model Components
|
|
159
|
+
|
|
160
|
+
1. **Symbolic Edge Functions**
|
|
161
|
+
```python
|
|
162
|
+
class EdgeActivation(nn.Module):
|
|
163
|
+
"""Learnable edge activation with basis functions"""
|
|
164
|
+
def forward(self, x):
|
|
165
|
+
return sum(self.weights[i] * basis[i](x) for i in range(self.num_basis))
|
|
166
|
+
```
|
|
167
|
+
|
|
168
|
+
2. **KAN Layer Implementation**
|
|
169
|
+
```python
|
|
170
|
+
class KANLayer(nn.Module):
|
|
171
|
+
"""Kolmogorov-Arnold Network layer"""
|
|
172
|
+
def forward(self, x):
|
|
173
|
+
edge_outputs = [self.edges[i](x[:,i]) for i in range(self.input_dim)]
|
|
174
|
+
return self.combine(edge_outputs)
|
|
175
|
+
```
|
|
176
|
+
|
|
177
|
+
3. **Formula Extraction**
|
|
178
|
+
```python
|
|
179
|
+
def get_symbolic_formula(self):
|
|
180
|
+
"""Extract interpretable mathematical expression"""
|
|
181
|
+
terms = []
|
|
182
|
+
for i, edge in enumerate(self.edges):
|
|
183
|
+
if abs(self.weights[i]) > threshold:
|
|
184
|
+
terms.append(f"{self.weights[i]:.4f} * {edge.formula}")
|
|
185
|
+
return " + ".join(terms)
|
|
186
|
+
```
|
|
187
|
+
|
|
188
|
+
### Key Design Principles
|
|
189
|
+
|
|
190
|
+
- **Modular Architecture**: Each component is independent and replaceable
|
|
191
|
+
- **Interpretability First**: All transformations maintain symbolic representations
|
|
192
|
+
- **Automatic Simplification**: Removes insignificant terms and combines similar expressions
|
|
193
|
+
- **Production Ready**: Export formulas for lightweight deployment
|
|
133
194
|
|
|
134
195
|
## Contributing
|
|
135
196
|
|
|
File without changes
|
|
File without changes
|
|
File without changes
|
|
File without changes
|
|
File without changes
|
|
File without changes
|
|
File without changes
|
|
File without changes
|
|
File without changes
|
|
File without changes
|
|
File without changes
|
|
File without changes
|