liger-kernel 0.0.1__tar.gz → 0.1.1__tar.gz
This diff represents the content of publicly available package versions that have been released to one of the supported registries. The information contained in this diff is provided for informational purposes only and reflects changes between package versions as they appear in their respective public registries.
- liger_kernel-0.1.1/PKG-INFO +236 -0
- liger_kernel-0.1.1/README.md +213 -0
- liger_kernel-0.1.1/setup.py +45 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel/ops/rms_norm.py +38 -20
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel/ops/swiglu.py +16 -16
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel/transformers/__init__.py +1 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel/transformers/monkey_patch.py +30 -0
- liger_kernel-0.1.1/src/liger_kernel/transformers/trainer_integration.py +45 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel/triton/monkey_patch.py +0 -2
- liger_kernel-0.1.1/src/liger_kernel.egg-info/PKG-INFO +236 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel.egg-info/SOURCES.txt +1 -0
- liger_kernel-0.0.1/PKG-INFO +0 -6
- liger_kernel-0.0.1/README.md +0 -206
- liger_kernel-0.0.1/setup.py +0 -26
- liger_kernel-0.0.1/src/liger_kernel.egg-info/PKG-INFO +0 -6
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/LICENSE +0 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/NOTICE +0 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/setup.cfg +0 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel/ops/__init__.py +0 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel/ops/cross_entropy.py +0 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel/ops/fused_linear_cross_entropy.py +0 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel/ops/geglu.py +0 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel/ops/rope.py +0 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel/ops/utils.py +0 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel/transformers/cross_entropy.py +0 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel/transformers/fused_linear_cross_entropy.py +0 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel/transformers/geglu.py +0 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel/transformers/model/__init__.py +0 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel/transformers/model/llama.py +0 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel/transformers/rms_norm.py +0 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel/transformers/rope.py +0 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel/transformers/swiglu.py +0 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel/triton/__init__.py +0 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel.egg-info/dependency_links.txt +0 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel.egg-info/requires.txt +0 -0
- {liger_kernel-0.0.1 → liger_kernel-0.1.1}/src/liger_kernel.egg-info/top_level.txt +0 -0
|
@@ -0,0 +1,236 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
Metadata-Version: 2.1
|
|
2
|
+
Name: liger_kernel
|
|
3
|
+
Version: 0.1.1
|
|
4
|
+
Summary: Efficient Triton kernels for LLM Training
|
|
5
|
+
Home-page: https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel
|
|
6
|
+
License: BSD-2-Clause
|
|
7
|
+
Keywords: triton,kernels,LLM training,deep learning,Hugging Face,PyTorch,GPU optimization
|
|
8
|
+
Classifier: Development Status :: 4 - Beta
|
|
9
|
+
Classifier: Intended Audience :: Developers
|
|
10
|
+
Classifier: Intended Audience :: Science/Research
|
|
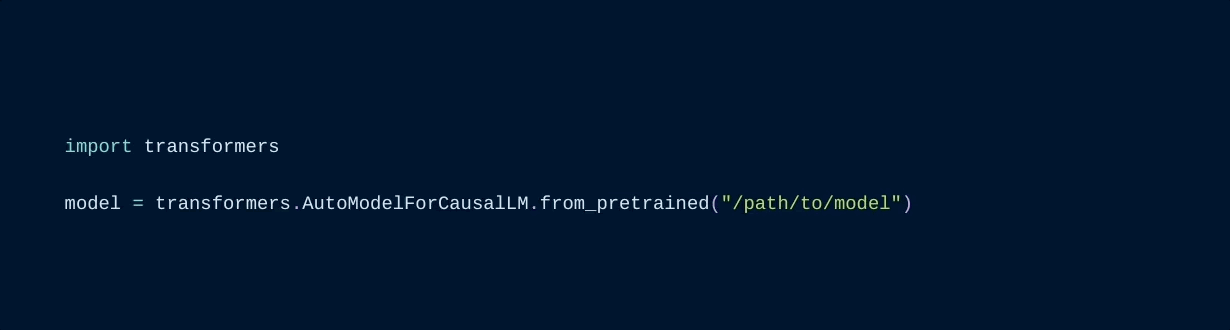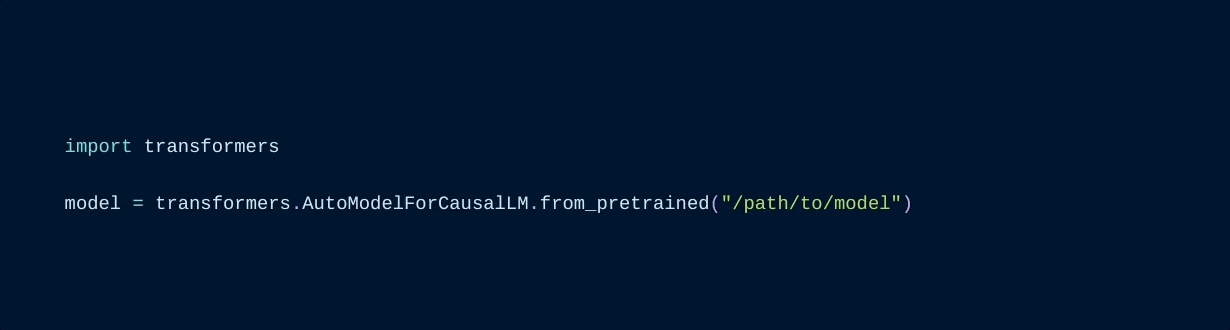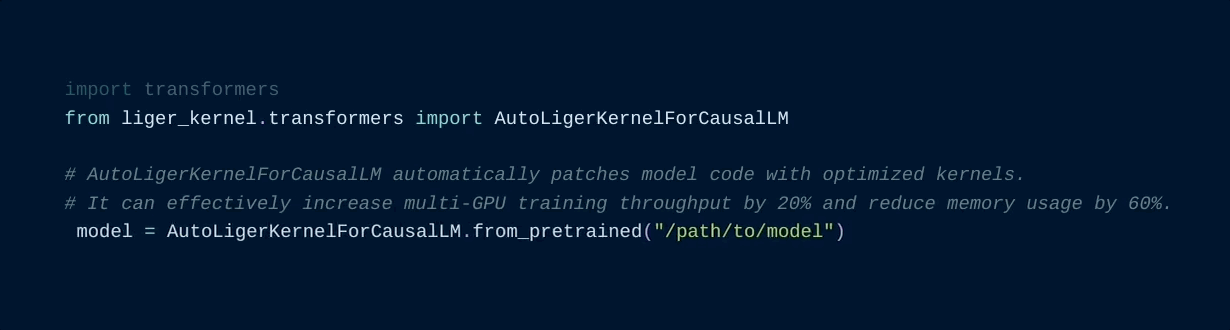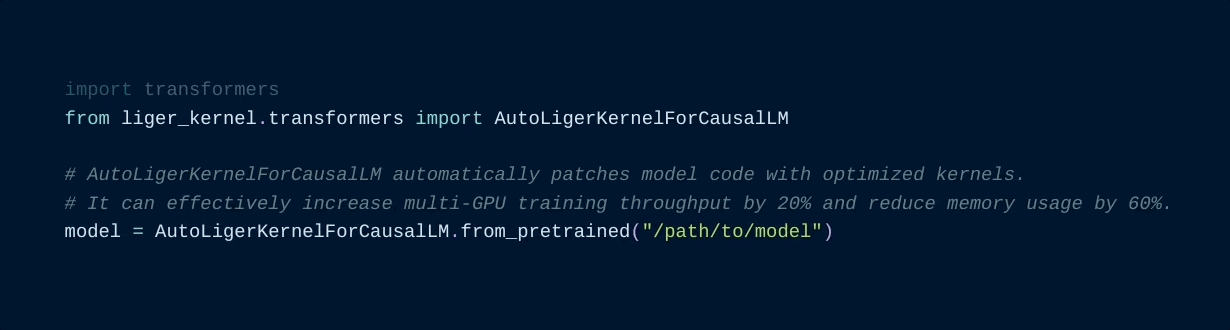
11
|
+
Classifier: Intended Audience :: Education
|
|
12
|
+
Classifier: License :: OSI Approved :: BSD License
|
|
13
|
+
Classifier: Programming Language :: Python :: 3
|
|
14
|
+
Classifier: Programming Language :: Python :: 3.8
|
|
15
|
+
Classifier: Programming Language :: Python :: 3.9
|
|
16
|
+
Classifier: Programming Language :: Python :: 3.10
|
|
17
|
+
Classifier: Topic :: Software Development :: Libraries
|
|
18
|
+
Classifier: Topic :: Scientific/Engineering :: Artificial Intelligence
|
|
19
|
+
Description-Content-Type: text/markdown
|
|
20
|
+
Provides-Extra: dev
|
|
21
|
+
License-File: LICENSE
|
|
22
|
+
License-File: NOTICE
|
|
23
|
+
|
|
24
|
+
# Liger Kernel: Efficient Triton Kernels for LLM Training
|
|
25
|
+
|
|
26
|
+
[](https://pepy.tech/project/liger-kernel) [](https://badge.fury.io/py/liger-kernel) [](https://badge.fury.io/py/liger-kernel-nightly)
|
|
27
|
+
|
|
28
|
+
|
|
29
|
+
[Installation](#installation) | [Getting Started](#getting-started) | [Examples](#examples) | [APIs](#apis) | [Structure](#structure) | [Contributing](#contributing)
|
|
30
|
+
|
|
31
|
+
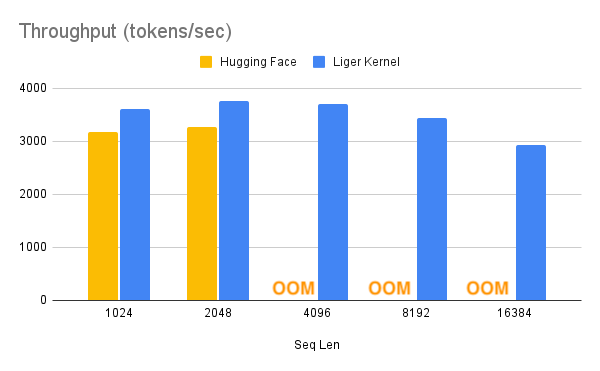
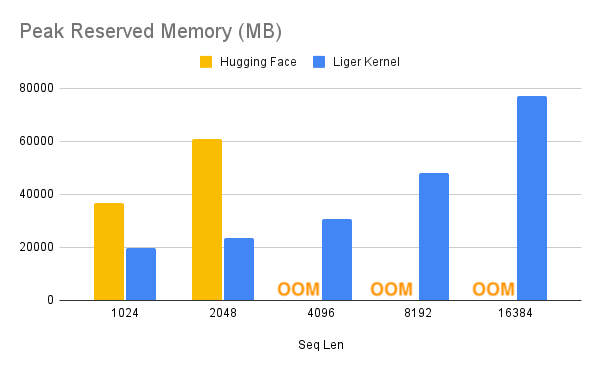
**Liger (Linkedin GPU Efficient Runtime) Kernel** is a collection of Triton kernels designed specifically for LLM training. It can effectively increase multi-GPU **training throughput by 20%** and reduces **memory usage by 60%**. We have implemented **Hugging Face Compatible** `RMSNorm`, `RoPE`, `SwiGLU`, `CrossEntropy`, `FusedLinearCrossEntropy`, and more to come. The kernel works out of the box with [Flash Attention](https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention), [PyTorch FSDP](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/FSDP_tutorial.html), and [Microsoft DeepSpeed](https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed). We welcome contributions from the community to gather the best kernels for LLM training.
|
|
32
|
+
|
|
33
|
+
## Supercharge Your Model with Liger Kernel
|
|
34
|
+
|
|
35
|
+
|
|
36
|
+
|
|
37
|
+
|
|
38
|
+
With one line of code, Liger Kernel can increase throughput by more than 20% and reduce memory usage by 60%, thereby enabling longer context lengths, larger batch sizes, and massive vocabularies.
|
|
39
|
+
|
|
40
|
+
|
|
41
|
+
| Speed Up | Memory Reduction |
|
|
42
|
+
|--------------------------|-------------------------|
|
|
43
|
+
|  |  |
|
|
44
|
+
|
|
45
|
+
> **Note:**
|
|
46
|
+
> - Benchmark conditions: LLaMA 3-8B, Batch Size = 8, Data Type = `bf16`, Optimizer = AdamW, Gradient Checkpointing = True, Distributed Strategy = FSDP1 on 8 A100s.
|
|
47
|
+
> - Hugging Face models start to OOM at a 4K context length, whereas Hugging Face + Liger Kernel scales up to 16K.
|
|
48
|
+
|
|
49
|
+
## Examples
|
|
50
|
+
|
|
51
|
+
### Basic
|
|
52
|
+
|
|
53
|
+
| **Example** | **Description** | **Lightning Studio** |
|
|
54
|
+
|------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------|
|
|
55
|
+
| [**Hugging Face Trainer**](https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel/tree/main/examples/huggingface) | Train LLaMA 3-8B ~20% faster with over 40% memory reduction on Alpaca dataset using 4 A100s with FSDP | TBA |
|
|
56
|
+
| [**Lightning Trainer**](https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel/tree/main/examples/lightning) | Increase 15% throughput and reduce memory usage by 40% with LLaMA3-8B on MMLU dataset using 8 A100s with DeepSpeed ZeRO3 | TBA |
|
|
57
|
+
|
|
58
|
+
### Advanced
|
|
59
|
+
|
|
60
|
+
| **Example** | **Description** | **Lightning Studio** |
|
|
61
|
+
|------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------|
|
|
62
|
+
| [**Medusa Multi-head LLM (Retraining Phase)**](https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel/tree/main/examples/medusa) | Reduce memory usage by 80% with 5 LM heads and improve throughput by 40% using 8 A100s with FSDP | TBA |
|
|
63
|
+
|
|
64
|
+
## Key Features
|
|
65
|
+
|
|
66
|
+
- **Ease of use:** Simply patch your Hugging Face model with one line of code, or compose your own model using our Liger Kernel modules.
|
|
67
|
+
- **Time and memory efficient:** In the same spirit as Flash-Attn, but for layers like **RMSNorm**, **RoPE**, **SwiGLU**, and **CrossEntropy**! Increases multi-GPU training throughput by 20% and reduces memory usage by 60% with **kernel fusion**, **in-place replacement**, and **chunking** techniques.
|
|
68
|
+
- **Exact:** Computation is exact—no approximations! Both forward and backward passes are implemented with rigorous unit tests and undergo convergence testing against training runs without Liger Kernel to ensure accuracy.
|
|
69
|
+
- **Lightweight:** Liger Kernel has minimal dependencies, requiring only Torch and Triton—no extra libraries needed! Say goodbye to dependency headaches!
|
|
70
|
+
- **Multi-GPU supported:** Compatible with multi-GPU setups (PyTorch FSDP, DeepSpeed, DDP, etc.).
|
|
71
|
+
|
|
72
|
+
## Target Audiences
|
|
73
|
+
|
|
74
|
+
- **Researchers**: Looking to compose models using efficient and reliable kernels for frontier experiments.
|
|
75
|
+
- **ML Practitioners**: Focused on maximizing GPU training efficiency with optimal, high-performance kernels.
|
|
76
|
+
- **Curious Novices**: Eager to learn how to write reliable Triton kernels to enhance training efficiency.
|
|
77
|
+
|
|
78
|
+
|
|
79
|
+
## Installation
|
|
80
|
+
|
|
81
|
+
### Dependencies
|
|
82
|
+
|
|
83
|
+
- `torch >= 2.1.2`
|
|
84
|
+
- `triton >= 2.3.0`
|
|
85
|
+
- `transformers >= 4.40.1`
|
|
86
|
+
|
|
87
|
+
To install the stable version:
|
|
88
|
+
|
|
89
|
+
```bash
|
|
90
|
+
$ pip install liger-kernel
|
|
91
|
+
```
|
|
92
|
+
|
|
93
|
+
To install the nightly version:
|
|
94
|
+
|
|
95
|
+
```bash
|
|
96
|
+
$ pip install liger-kernel-nightly
|
|
97
|
+
```
|
|
98
|
+
|
|
99
|
+
## Getting Started
|
|
100
|
+
|
|
101
|
+
### 1. Patch Existing Hugging Face Models
|
|
102
|
+
|
|
103
|
+
Using the [patching APIs](#patching), you can swap Hugging Face models with optimized Liger Kernels.
|
|
104
|
+
|
|
105
|
+
```python
|
|
106
|
+
import transformers
|
|
107
|
+
from liger_kernel.transformers import apply_liger_kernel_to_llama
|
|
108
|
+
|
|
109
|
+
model = transformers.AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("<some llama model>")
|
|
110
|
+
|
|
111
|
+
# Adding this line automatically monkey-patches the model with the optimized Liger kernels
|
|
112
|
+
apply_liger_kernel_to_llama()
|
|
113
|
+
```
|
|
114
|
+
|
|
115
|
+
### 2. Compose Your Own Model
|
|
116
|
+
|
|
117
|
+
You can take individual [kernels](#kernels) to compose your models.
|
|
118
|
+
|
|
119
|
+
```python
|
|
120
|
+
from liger_kernel.transformers import LigerFusedLinearCrossEntropyLoss
|
|
121
|
+
import torch.nn as nn
|
|
122
|
+
import torch
|
|
123
|
+
|
|
124
|
+
model = nn.Linear(128, 256).cuda()
|
|
125
|
+
|
|
126
|
+
# fuses linear + cross entropy layers together and performs chunk-by-chunk computation to reduce memory
|
|
127
|
+
loss_fn = LigerFusedLinearCrossEntropyLoss()
|
|
128
|
+
|
|
129
|
+
input = torch.randn(4, 128, requires_grad=True, device="cuda")
|
|
130
|
+
target = torch.randint(256, (4, ), device="cuda")
|
|
131
|
+
|
|
132
|
+
loss = loss_fn(model.weight, input, target)
|
|
133
|
+
loss.backward()
|
|
134
|
+
```
|
|
135
|
+
|
|
136
|
+
|
|
137
|
+
## Structure
|
|
138
|
+
|
|
139
|
+
### Source Code
|
|
140
|
+
|
|
141
|
+
- `ops/`: Core Triton operations.
|
|
142
|
+
- `transformers/`: PyTorch `nn.Module` implementations built on Triton operations, compliant with the `transformers` API.
|
|
143
|
+
|
|
144
|
+
### Tests
|
|
145
|
+
|
|
146
|
+
- `transformers/`: Correctness tests for the Triton-based layers.
|
|
147
|
+
- `convergence/`: Patches Hugging Face models with all kernels, runs multiple iterations, and compares weights, logits, and loss layer-by-layer.
|
|
148
|
+
|
|
149
|
+
### Benchmark
|
|
150
|
+
|
|
151
|
+
- `benchmark/`: Execution time and memory benchmarks compared to Hugging Face layers.
|
|
152
|
+
|
|
153
|
+
## APIs
|
|
154
|
+
|
|
155
|
+
### Patching
|
|
156
|
+
|
|
157
|
+
| **Model** | **API** | **Supported Operations** |
|
|
158
|
+
|-------------|--------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
|
159
|
+
| LLaMA (2 & 3) | `liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_llama` | RoPE, RMSNorm, SwiGLU, CrossEntropyLoss, FusedLinearCrossEntropy |
|
|
160
|
+
| Mistral | `liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_mistral` | RoPE, RMSNorm, SwiGLU, CrossEntropyLoss |
|
|
161
|
+
| Mixtral | `liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_mixtral` | RoPE, RMSNorm, SwiGLU, CrossEntropyLoss |
|
|
162
|
+
| Gemma2 | `liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_gemma` | RoPE, RMSNorm, GeGLU, CrossEntropyLoss |
|
|
163
|
+
|
|
164
|
+
### Kernels
|
|
165
|
+
|
|
166
|
+
| **Kernel** | **API** |
|
|
167
|
+
|---------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------|
|
|
168
|
+
| RMSNorm | `liger_kernel.transformers.LigerRMSNorm` |
|
|
169
|
+
| RoPE | `liger_kernel.transformers.liger_rotary_pos_emb` |
|
|
170
|
+
| SwiGLU | `liger_kernel.transformers.LigerSwiGLUMLP` |
|
|
171
|
+
| GeGLU | `liger_kernel.transformers.LigerGEGLUMLP` |
|
|
172
|
+
| CrossEntropy | `liger_kernel.transformers.LigerCrossEntropyLoss` |
|
|
173
|
+
| FusedLinearCrossEntropy | `liger_kernel.transformers.LigerFusedLinearCrossEntropyLoss`|
|
|
174
|
+
|
|
175
|
+
- **RMSNorm**: [RMSNorm](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1910.07467), which normalizes activations using their root mean square, is implemented by fusing the normalization and scaling steps into a single Triton kernel, and achieves ~3X speedup with ~3X peak memory reduction.
|
|
176
|
+
- **RoPE**: [Rotary Positional Embedding](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2104.09864) is implemented by fusing the query and key embedding rotary into a single kernel with inplace replacement, and achieves ~3X speedup with ~3X peak memory reduction.
|
|
177
|
+
- **SwiGLU**: [Swish Gated Linear Units](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2002.05202), given by
|
|
178
|
+
$$\text{SwiGLU}(x)=\text{Swish}_{\beta}(xW+b)\otimes(xV+c)$$
|
|
179
|
+
, is implemented by fusing the elementwise multiplication (denoted by $\otimes$) into a single kernel with inplace replacement, and achieves parity speed with ~1.5X peak memory reduction.
|
|
180
|
+
- **GeGLU**: [GELU Gated Linear Units](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2002.05202), given by
|
|
181
|
+
$$\text{GeGLU}(x)=\text{GELU}(xW+b)\otimes(xV+c)$$
|
|
182
|
+
, is implemented by fusing the elementwise multiplication into a single kernel with inplace replacement, and achieves parity speed with ~1.5X peak memory reduction. Note that the [tanh approximation form of GELU](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.GELU.html) is used.
|
|
183
|
+
- **CrossEntropy**: [Cross entropy loss](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss.html) is implemented by computing both the loss and gradient in the forward pass with inplace replacement of input to reduce the peak memory by avoiding simultaneous materialization of both input logits and gradient. It achieves >2X speedup and >4X memory reduction for common vocab sizes (e.g., 32K, 128K, etc.).
|
|
184
|
+
<!-- TODO: verify vocab sizes are accurate -->
|
|
185
|
+
- **FusedLinearCrossEntropy**: Peak memory usage of cross entropy loss is further improved by fusing the model head with the CE loss and chunking the input for block-wise loss and gradient calculation, a technique inspired by [Efficient Cross Entropy](https://github.com/mgmalek/efficient_cross_entropy). It achieves >4X memory reduction for 128k vocab size. **This is highly effective for large batch size, large sequence length, and large vocabulary sizes.** Please refer to the [Medusa example](https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel/tree/main/examples/medusa) for individual kernel usage.
|
|
186
|
+
|
|
187
|
+
|
|
188
|
+
<!-- TODO: be more specific about batch size -->
|
|
189
|
+
> **Note:**
|
|
190
|
+
> Reported speedups and memory reductions are with respect to the LLaMA 3-8B Hugging Face layer implementations. All models use 4K hidden size and 4K sequence length and are evaluated based on memory usage and wall time for the forward+backward pass on a single NVIDIA A100 80G GPU using small batch sizes. Liger kernels exhibit more efficient scaling to larger batch sizes, detailed further in the [Benchmark](./benchmark) folder.
|
|
191
|
+
|
|
192
|
+
## Note on ML Compiler
|
|
193
|
+
|
|
194
|
+
### 1. Torch Compile
|
|
195
|
+
|
|
196
|
+
Since Liger Kernel is 100% Triton-based, it works seamlessly with [`torch.compile`](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/torch_compile_tutorial.html). In the following example, Liger Kernel can further optimize the model on top of Torch Compile, reducing the memory by more than half.
|
|
197
|
+
|
|
198
|
+
| Configuration | Throughput (tokens/sec) | Memory Reserved (GB) |
|
|
199
|
+
|--------------------------------|----------------------------|-------------------------|
|
|
200
|
+
| Torch Compile | 3780 | 66.4 |
|
|
201
|
+
| Torch Compile + Liger Kernel | 3702 | 31.0 |
|
|
202
|
+
|
|
203
|
+
> **Note:**
|
|
204
|
+
> 1. Benchmark conditions: LLaMA 3-8B, Batch Size = 8, Seq Len = 4096, Data Type = `bf16`, Optimizer = AdamW, Gradient Checkpointing = True, Distributed Strategy = FSDP1 on 8 A100s.
|
|
205
|
+
> 2. Tested on torch `2.5.0.dev20240731+cu118`
|
|
206
|
+
|
|
207
|
+
### 2. Lightning Thunder
|
|
208
|
+
|
|
209
|
+
*WIP*
|
|
210
|
+
|
|
211
|
+
## Contributing
|
|
212
|
+
|
|
213
|
+
[CONTRIBUTING GUIDE](https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel/blob/main/CONTRIBUTING.md)
|
|
214
|
+
|
|
215
|
+
## Acknowledgement
|
|
216
|
+
|
|
217
|
+
- [flash-attn](https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention) and [Unsloth](https://github.com/unslothai/unsloth) for inspiration in Triton kernels for training
|
|
218
|
+
- [tiny shakespeare dataset](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/karpathy/char-rnn/master/data/tinyshakespeare/input.txt) by Andrej Karpathy for convergence testing
|
|
219
|
+
- [Efficient Cross Entropy](https://github.com/mgmalek/efficient_cross_entropy) for lm_head + cross entropy inspiration
|
|
220
|
+
|
|
221
|
+
|
|
222
|
+
## License
|
|
223
|
+
|
|
224
|
+
[BSD 2-CLAUSE](https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel/blob/main/LICENSE)
|
|
225
|
+
|
|
226
|
+
## Cite this work
|
|
227
|
+
|
|
228
|
+
Biblatex entry:
|
|
229
|
+
```bib
|
|
230
|
+
@software{liger2024,
|
|
231
|
+
title = {Liger-Kernel: Efficient Triton Kernels for LLM Training},
|
|
232
|
+
author = {Hsu, Pin-Lun and Dai, Yun and Kothapalli, Vignesh and Song, Qingquan and Tang, Shao and Zhu, Siyu},
|
|
233
|
+
url = {https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel},
|
|
234
|
+
year = {2024}
|
|
235
|
+
}
|
|
236
|
+
```
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,213 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
# Liger Kernel: Efficient Triton Kernels for LLM Training
|
|
2
|
+
|
|
3
|
+
[](https://pepy.tech/project/liger-kernel) [](https://badge.fury.io/py/liger-kernel) [](https://badge.fury.io/py/liger-kernel-nightly)
|
|
4
|
+
|
|
5
|
+
|
|
6
|
+
[Installation](#installation) | [Getting Started](#getting-started) | [Examples](#examples) | [APIs](#apis) | [Structure](#structure) | [Contributing](#contributing)
|
|
7
|
+
|
|
8
|
+
**Liger (Linkedin GPU Efficient Runtime) Kernel** is a collection of Triton kernels designed specifically for LLM training. It can effectively increase multi-GPU **training throughput by 20%** and reduces **memory usage by 60%**. We have implemented **Hugging Face Compatible** `RMSNorm`, `RoPE`, `SwiGLU`, `CrossEntropy`, `FusedLinearCrossEntropy`, and more to come. The kernel works out of the box with [Flash Attention](https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention), [PyTorch FSDP](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/FSDP_tutorial.html), and [Microsoft DeepSpeed](https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed). We welcome contributions from the community to gather the best kernels for LLM training.
|
|
9
|
+
|
|
10
|
+
## Supercharge Your Model with Liger Kernel
|
|
11
|
+
|
|
12
|
+
|
|
13
|
+

|
|
14
|
+
|
|
15
|
+
With one line of code, Liger Kernel can increase throughput by more than 20% and reduce memory usage by 60%, thereby enabling longer context lengths, larger batch sizes, and massive vocabularies.
|
|
16
|
+
|
|
17
|
+
|
|
18
|
+
| Speed Up | Memory Reduction |
|
|
19
|
+
|--------------------------|-------------------------|
|
|
20
|
+
|  |  |
|
|
21
|
+
|
|
22
|
+
> **Note:**
|
|
23
|
+
> - Benchmark conditions: LLaMA 3-8B, Batch Size = 8, Data Type = `bf16`, Optimizer = AdamW, Gradient Checkpointing = True, Distributed Strategy = FSDP1 on 8 A100s.
|
|
24
|
+
> - Hugging Face models start to OOM at a 4K context length, whereas Hugging Face + Liger Kernel scales up to 16K.
|
|
25
|
+
|
|
26
|
+
## Examples
|
|
27
|
+
|
|
28
|
+
### Basic
|
|
29
|
+
|
|
30
|
+
| **Example** | **Description** | **Lightning Studio** |
|
|
31
|
+
|------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------|
|
|
32
|
+
| [**Hugging Face Trainer**](https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel/tree/main/examples/huggingface) | Train LLaMA 3-8B ~20% faster with over 40% memory reduction on Alpaca dataset using 4 A100s with FSDP | TBA |
|
|
33
|
+
| [**Lightning Trainer**](https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel/tree/main/examples/lightning) | Increase 15% throughput and reduce memory usage by 40% with LLaMA3-8B on MMLU dataset using 8 A100s with DeepSpeed ZeRO3 | TBA |
|
|
34
|
+
|
|
35
|
+
### Advanced
|
|
36
|
+
|
|
37
|
+
| **Example** | **Description** | **Lightning Studio** |
|
|
38
|
+
|------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------|
|
|
39
|
+
| [**Medusa Multi-head LLM (Retraining Phase)**](https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel/tree/main/examples/medusa) | Reduce memory usage by 80% with 5 LM heads and improve throughput by 40% using 8 A100s with FSDP | TBA |
|
|
40
|
+
|
|
41
|
+
## Key Features
|
|
42
|
+
|
|
43
|
+
- **Ease of use:** Simply patch your Hugging Face model with one line of code, or compose your own model using our Liger Kernel modules.
|
|
44
|
+
- **Time and memory efficient:** In the same spirit as Flash-Attn, but for layers like **RMSNorm**, **RoPE**, **SwiGLU**, and **CrossEntropy**! Increases multi-GPU training throughput by 20% and reduces memory usage by 60% with **kernel fusion**, **in-place replacement**, and **chunking** techniques.
|
|
45
|
+
- **Exact:** Computation is exact—no approximations! Both forward and backward passes are implemented with rigorous unit tests and undergo convergence testing against training runs without Liger Kernel to ensure accuracy.
|
|
46
|
+
- **Lightweight:** Liger Kernel has minimal dependencies, requiring only Torch and Triton—no extra libraries needed! Say goodbye to dependency headaches!
|
|
47
|
+
- **Multi-GPU supported:** Compatible with multi-GPU setups (PyTorch FSDP, DeepSpeed, DDP, etc.).
|
|
48
|
+
|
|
49
|
+
## Target Audiences
|
|
50
|
+
|
|
51
|
+
- **Researchers**: Looking to compose models using efficient and reliable kernels for frontier experiments.
|
|
52
|
+
- **ML Practitioners**: Focused on maximizing GPU training efficiency with optimal, high-performance kernels.
|
|
53
|
+
- **Curious Novices**: Eager to learn how to write reliable Triton kernels to enhance training efficiency.
|
|
54
|
+
|
|
55
|
+
|
|
56
|
+
## Installation
|
|
57
|
+
|
|
58
|
+
### Dependencies
|
|
59
|
+
|
|
60
|
+
- `torch >= 2.1.2`
|
|
61
|
+
- `triton >= 2.3.0`
|
|
62
|
+
- `transformers >= 4.40.1`
|
|
63
|
+
|
|
64
|
+
To install the stable version:
|
|
65
|
+
|
|
66
|
+
```bash
|
|
67
|
+
$ pip install liger-kernel
|
|
68
|
+
```
|
|
69
|
+
|
|
70
|
+
To install the nightly version:
|
|
71
|
+
|
|
72
|
+
```bash
|
|
73
|
+
$ pip install liger-kernel-nightly
|
|
74
|
+
```
|
|
75
|
+
|
|
76
|
+
## Getting Started
|
|
77
|
+
|
|
78
|
+
### 1. Patch Existing Hugging Face Models
|
|
79
|
+
|
|
80
|
+
Using the [patching APIs](#patching), you can swap Hugging Face models with optimized Liger Kernels.
|
|
81
|
+
|
|
82
|
+
```python
|
|
83
|
+
import transformers
|
|
84
|
+
from liger_kernel.transformers import apply_liger_kernel_to_llama
|
|
85
|
+
|
|
86
|
+
model = transformers.AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("<some llama model>")
|
|
87
|
+
|
|
88
|
+
# Adding this line automatically monkey-patches the model with the optimized Liger kernels
|
|
89
|
+
apply_liger_kernel_to_llama()
|
|
90
|
+
```
|
|
91
|
+
|
|
92
|
+
### 2. Compose Your Own Model
|
|
93
|
+
|
|
94
|
+
You can take individual [kernels](#kernels) to compose your models.
|
|
95
|
+
|
|
96
|
+
```python
|
|
97
|
+
from liger_kernel.transformers import LigerFusedLinearCrossEntropyLoss
|
|
98
|
+
import torch.nn as nn
|
|
99
|
+
import torch
|
|
100
|
+
|
|
101
|
+
model = nn.Linear(128, 256).cuda()
|
|
102
|
+
|
|
103
|
+
# fuses linear + cross entropy layers together and performs chunk-by-chunk computation to reduce memory
|
|
104
|
+
loss_fn = LigerFusedLinearCrossEntropyLoss()
|
|
105
|
+
|
|
106
|
+
input = torch.randn(4, 128, requires_grad=True, device="cuda")
|
|
107
|
+
target = torch.randint(256, (4, ), device="cuda")
|
|
108
|
+
|
|
109
|
+
loss = loss_fn(model.weight, input, target)
|
|
110
|
+
loss.backward()
|
|
111
|
+
```
|
|
112
|
+
|
|
113
|
+
|
|
114
|
+
## Structure
|
|
115
|
+
|
|
116
|
+
### Source Code
|
|
117
|
+
|
|
118
|
+
- `ops/`: Core Triton operations.
|
|
119
|
+
- `transformers/`: PyTorch `nn.Module` implementations built on Triton operations, compliant with the `transformers` API.
|
|
120
|
+
|
|
121
|
+
### Tests
|
|
122
|
+
|
|
123
|
+
- `transformers/`: Correctness tests for the Triton-based layers.
|
|
124
|
+
- `convergence/`: Patches Hugging Face models with all kernels, runs multiple iterations, and compares weights, logits, and loss layer-by-layer.
|
|
125
|
+
|
|
126
|
+
### Benchmark
|
|
127
|
+
|
|
128
|
+
- `benchmark/`: Execution time and memory benchmarks compared to Hugging Face layers.
|
|
129
|
+
|
|
130
|
+
## APIs
|
|
131
|
+
|
|
132
|
+
### Patching
|
|
133
|
+
|
|
134
|
+
| **Model** | **API** | **Supported Operations** |
|
|
135
|
+
|-------------|--------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
|
136
|
+
| LLaMA (2 & 3) | `liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_llama` | RoPE, RMSNorm, SwiGLU, CrossEntropyLoss, FusedLinearCrossEntropy |
|
|
137
|
+
| Mistral | `liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_mistral` | RoPE, RMSNorm, SwiGLU, CrossEntropyLoss |
|
|
138
|
+
| Mixtral | `liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_mixtral` | RoPE, RMSNorm, SwiGLU, CrossEntropyLoss |
|
|
139
|
+
| Gemma2 | `liger_kernel.transformers.apply_liger_kernel_to_gemma` | RoPE, RMSNorm, GeGLU, CrossEntropyLoss |
|
|
140
|
+
|
|
141
|
+
### Kernels
|
|
142
|
+
|
|
143
|
+
| **Kernel** | **API** |
|
|
144
|
+
|---------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------|
|
|
145
|
+
| RMSNorm | `liger_kernel.transformers.LigerRMSNorm` |
|
|
146
|
+
| RoPE | `liger_kernel.transformers.liger_rotary_pos_emb` |
|
|
147
|
+
| SwiGLU | `liger_kernel.transformers.LigerSwiGLUMLP` |
|
|
148
|
+
| GeGLU | `liger_kernel.transformers.LigerGEGLUMLP` |
|
|
149
|
+
| CrossEntropy | `liger_kernel.transformers.LigerCrossEntropyLoss` |
|
|
150
|
+
| FusedLinearCrossEntropy | `liger_kernel.transformers.LigerFusedLinearCrossEntropyLoss`|
|
|
151
|
+
|
|
152
|
+
- **RMSNorm**: [RMSNorm](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1910.07467), which normalizes activations using their root mean square, is implemented by fusing the normalization and scaling steps into a single Triton kernel, and achieves ~3X speedup with ~3X peak memory reduction.
|
|
153
|
+
- **RoPE**: [Rotary Positional Embedding](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2104.09864) is implemented by fusing the query and key embedding rotary into a single kernel with inplace replacement, and achieves ~3X speedup with ~3X peak memory reduction.
|
|
154
|
+
- **SwiGLU**: [Swish Gated Linear Units](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2002.05202), given by
|
|
155
|
+
$$\text{SwiGLU}(x)=\text{Swish}_{\beta}(xW+b)\otimes(xV+c)$$
|
|
156
|
+
, is implemented by fusing the elementwise multiplication (denoted by $\otimes$) into a single kernel with inplace replacement, and achieves parity speed with ~1.5X peak memory reduction.
|
|
157
|
+
- **GeGLU**: [GELU Gated Linear Units](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2002.05202), given by
|
|
158
|
+
$$\text{GeGLU}(x)=\text{GELU}(xW+b)\otimes(xV+c)$$
|
|
159
|
+
, is implemented by fusing the elementwise multiplication into a single kernel with inplace replacement, and achieves parity speed with ~1.5X peak memory reduction. Note that the [tanh approximation form of GELU](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.GELU.html) is used.
|
|
160
|
+
- **CrossEntropy**: [Cross entropy loss](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss.html) is implemented by computing both the loss and gradient in the forward pass with inplace replacement of input to reduce the peak memory by avoiding simultaneous materialization of both input logits and gradient. It achieves >2X speedup and >4X memory reduction for common vocab sizes (e.g., 32K, 128K, etc.).
|
|
161
|
+
<!-- TODO: verify vocab sizes are accurate -->
|
|
162
|
+
- **FusedLinearCrossEntropy**: Peak memory usage of cross entropy loss is further improved by fusing the model head with the CE loss and chunking the input for block-wise loss and gradient calculation, a technique inspired by [Efficient Cross Entropy](https://github.com/mgmalek/efficient_cross_entropy). It achieves >4X memory reduction for 128k vocab size. **This is highly effective for large batch size, large sequence length, and large vocabulary sizes.** Please refer to the [Medusa example](https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel/tree/main/examples/medusa) for individual kernel usage.
|
|
163
|
+
|
|
164
|
+
|
|
165
|
+
<!-- TODO: be more specific about batch size -->
|
|
166
|
+
> **Note:**
|
|
167
|
+
> Reported speedups and memory reductions are with respect to the LLaMA 3-8B Hugging Face layer implementations. All models use 4K hidden size and 4K sequence length and are evaluated based on memory usage and wall time for the forward+backward pass on a single NVIDIA A100 80G GPU using small batch sizes. Liger kernels exhibit more efficient scaling to larger batch sizes, detailed further in the [Benchmark](./benchmark) folder.
|
|
168
|
+
|
|
169
|
+
## Note on ML Compiler
|
|
170
|
+
|
|
171
|
+
### 1. Torch Compile
|
|
172
|
+
|
|
173
|
+
Since Liger Kernel is 100% Triton-based, it works seamlessly with [`torch.compile`](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/torch_compile_tutorial.html). In the following example, Liger Kernel can further optimize the model on top of Torch Compile, reducing the memory by more than half.
|
|
174
|
+
|
|
175
|
+
| Configuration | Throughput (tokens/sec) | Memory Reserved (GB) |
|
|
176
|
+
|--------------------------------|----------------------------|-------------------------|
|
|
177
|
+
| Torch Compile | 3780 | 66.4 |
|
|
178
|
+
| Torch Compile + Liger Kernel | 3702 | 31.0 |
|
|
179
|
+
|
|
180
|
+
> **Note:**
|
|
181
|
+
> 1. Benchmark conditions: LLaMA 3-8B, Batch Size = 8, Seq Len = 4096, Data Type = `bf16`, Optimizer = AdamW, Gradient Checkpointing = True, Distributed Strategy = FSDP1 on 8 A100s.
|
|
182
|
+
> 2. Tested on torch `2.5.0.dev20240731+cu118`
|
|
183
|
+
|
|
184
|
+
### 2. Lightning Thunder
|
|
185
|
+
|
|
186
|
+
*WIP*
|
|
187
|
+
|
|
188
|
+
## Contributing
|
|
189
|
+
|
|
190
|
+
[CONTRIBUTING GUIDE](https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel/blob/main/CONTRIBUTING.md)
|
|
191
|
+
|
|
192
|
+
## Acknowledgement
|
|
193
|
+
|
|
194
|
+
- [flash-attn](https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention) and [Unsloth](https://github.com/unslothai/unsloth) for inspiration in Triton kernels for training
|
|
195
|
+
- [tiny shakespeare dataset](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/karpathy/char-rnn/master/data/tinyshakespeare/input.txt) by Andrej Karpathy for convergence testing
|
|
196
|
+
- [Efficient Cross Entropy](https://github.com/mgmalek/efficient_cross_entropy) for lm_head + cross entropy inspiration
|
|
197
|
+
|
|
198
|
+
|
|
199
|
+
## License
|
|
200
|
+
|
|
201
|
+
[BSD 2-CLAUSE](https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel/blob/main/LICENSE)
|
|
202
|
+
|
|
203
|
+
## Cite this work
|
|
204
|
+
|
|
205
|
+
Biblatex entry:
|
|
206
|
+
```bib
|
|
207
|
+
@software{liger2024,
|
|
208
|
+
title = {Liger-Kernel: Efficient Triton Kernels for LLM Training},
|
|
209
|
+
author = {Hsu, Pin-Lun and Dai, Yun and Kothapalli, Vignesh and Song, Qingquan and Tang, Shao and Zhu, Siyu},
|
|
210
|
+
url = {https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel},
|
|
211
|
+
year = {2024}
|
|
212
|
+
}
|
|
213
|
+
```
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
from setuptools import find_namespace_packages, setup
|
|
2
|
+
|
|
3
|
+
__version__ = "0.1.1"
|
|
4
|
+
|
|
5
|
+
setup(
|
|
6
|
+
name="liger_kernel",
|
|
7
|
+
version=__version__,
|
|
8
|
+
description="Efficient Triton kernels for LLM Training",
|
|
9
|
+
long_description=open("README.md").read(),
|
|
10
|
+
long_description_content_type="text/markdown",
|
|
11
|
+
license="BSD-2-Clause",
|
|
12
|
+
url="https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel",
|
|
13
|
+
package_dir={"": "src"},
|
|
14
|
+
packages=find_namespace_packages(where="src"),
|
|
15
|
+
classifiers=[
|
|
16
|
+
'Development Status :: 4 - Beta',
|
|
17
|
+
'Intended Audience :: Developers',
|
|
18
|
+
'Intended Audience :: Science/Research',
|
|
19
|
+
'Intended Audience :: Education',
|
|
20
|
+
'License :: OSI Approved :: BSD License',
|
|
21
|
+
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3',
|
|
22
|
+
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.8',
|
|
23
|
+
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.9',
|
|
24
|
+
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.10',
|
|
25
|
+
'Topic :: Software Development :: Libraries',
|
|
26
|
+
'Topic :: Scientific/Engineering :: Artificial Intelligence',
|
|
27
|
+
],
|
|
28
|
+
keywords="triton,kernels,LLM training,deep learning,Hugging Face,PyTorch,GPU optimization",
|
|
29
|
+
include_package_data=True,
|
|
30
|
+
install_requires=[
|
|
31
|
+
"torch>=2.1.2",
|
|
32
|
+
"triton>=2.3.0",
|
|
33
|
+
"transformers>=4.40.1",
|
|
34
|
+
],
|
|
35
|
+
extras_require={
|
|
36
|
+
"dev": [
|
|
37
|
+
"matplotlib>=3.7.2",
|
|
38
|
+
"flake8>=4.0.1.1",
|
|
39
|
+
"black>=24.4.2",
|
|
40
|
+
"isort>=5.13.2",
|
|
41
|
+
"pre-commit>=3.7.1",
|
|
42
|
+
"torch-tb-profiler>=0.4.1",
|
|
43
|
+
]
|
|
44
|
+
},
|
|
45
|
+
)
|
|
@@ -20,9 +20,12 @@ def _rms_norm_forward(
|
|
|
20
20
|
BLOCK_SIZE: tl.constexpr,
|
|
21
21
|
):
|
|
22
22
|
"""
|
|
23
|
+
y_i = (x_i / (RMS)) * wi, RMS = sqrt(sum(x_i^2) / N)
|
|
24
|
+
|
|
23
25
|
Reference:
|
|
24
26
|
1. https://triton-lang.org/main/getting-started/tutorials/05-layer-norm.html
|
|
25
27
|
2. https://github.com/unslothai/unsloth/blob/fd753fed99ed5f10ef8a9b7139588d9de9ddecfb/unsloth/kernels/rms_layernorm.py#L22
|
|
28
|
+
3. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1910.07467
|
|
26
29
|
"""
|
|
27
30
|
|
|
28
31
|
row_idx = tl.program_id(0)
|
|
@@ -36,16 +39,17 @@ def _rms_norm_forward(
|
|
|
36
39
|
X_row = tl.load(X_ptr + col_offsets, mask=mask, other=0)
|
|
37
40
|
W_row = tl.load(W_ptr + col_offsets, mask=mask, other=0)
|
|
38
41
|
|
|
39
|
-
|
|
40
|
-
|
|
42
|
+
mean_square = tl.sum(X_row * X_row, axis=0) / n_cols
|
|
43
|
+
inv_rms = tl.math.rsqrt(mean_square + eps)
|
|
41
44
|
|
|
42
|
-
#
|
|
43
|
-
|
|
45
|
+
# We can save time by caching rms with minimal memory overhead
|
|
46
|
+
# because rms is much smaller compared to X_row, as rms is for each row.
|
|
47
|
+
# However, on the computation side, it can save 4 operations (*, sum, /, sqrt).
|
|
48
|
+
tl.store(r_ptr, inv_rms)
|
|
44
49
|
|
|
45
|
-
|
|
50
|
+
Y_row = X_row * inv_rms * W_row
|
|
46
51
|
|
|
47
|
-
|
|
48
|
-
tl.store(Y_ptr + col_offsets, output, mask=mask)
|
|
52
|
+
tl.store(Y_ptr + col_offsets, Y_row, mask=mask)
|
|
49
53
|
|
|
50
54
|
|
|
51
55
|
@triton.jit
|
|
@@ -65,9 +69,10 @@ def _rms_norm_backward(
|
|
|
65
69
|
BLOCK_SIZE: tl.constexpr,
|
|
66
70
|
):
|
|
67
71
|
"""
|
|
68
|
-
dx = (1 /
|
|
69
|
-
dw = sum(dy * (x /
|
|
72
|
+
dx = (1 / RMS) * [dy * w - (1 / N) * (1 / RMS^2) * ((dy * w) dot x) * x]. * means element-wise multiplication, whileas dot means dot product
|
|
73
|
+
dw = sum(dy * (x / RMS)). summation over BxT dimension
|
|
70
74
|
"""
|
|
75
|
+
|
|
71
76
|
row_idx = tl.program_id(0)
|
|
72
77
|
col_offsets = tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE)
|
|
73
78
|
mask = col_offsets < n_cols
|
|
@@ -81,26 +86,33 @@ def _rms_norm_backward(
|
|
|
81
86
|
X_row = tl.load(X_ptr + col_offsets, mask=mask, other=0)
|
|
82
87
|
W_row = tl.load(W_ptr + col_offsets, mask=mask, other=0)
|
|
83
88
|
|
|
84
|
-
# Get
|
|
85
|
-
|
|
86
|
-
|
|
87
|
-
normed = X_row * inv_var
|
|
89
|
+
# Get cached rms
|
|
90
|
+
inv_rms_row = tl.load(r_ptr)
|
|
88
91
|
|
|
89
|
-
|
|
90
|
-
|
|
91
|
-
|
|
92
|
-
|
|
93
|
-
|
|
94
|
-
|
|
92
|
+
dX_row = (inv_rms_row) * (
|
|
93
|
+
dY_row * W_row
|
|
94
|
+
- (1 / n_cols)
|
|
95
|
+
* inv_rms_row
|
|
96
|
+
* inv_rms_row
|
|
97
|
+
* tl.sum(dY_row * W_row * X_row, axis=0)
|
|
98
|
+
* X_row
|
|
99
|
+
)
|
|
100
|
+
tl.store(dY_ptr + col_offsets, dX_row, mask=mask)
|
|
95
101
|
|
|
96
102
|
# calculate the gradient of W
|
|
97
|
-
|
|
103
|
+
dW_row = dY_row * X_row * inv_rms_row
|
|
104
|
+
tl.store(dW_ptr + col_offsets, dW_row, mask=mask)
|
|
98
105
|
|
|
99
106
|
|
|
100
107
|
class LigerRMSNormFunction(torch.autograd.Function):
|
|
101
108
|
@staticmethod
|
|
102
109
|
@ensure_contiguous
|
|
103
110
|
def forward(ctx, X, W, eps):
|
|
111
|
+
"""
|
|
112
|
+
X: (B, T, H) or (BxT, H)
|
|
113
|
+
W: (H,)
|
|
114
|
+
"""
|
|
115
|
+
|
|
104
116
|
shape = X.shape
|
|
105
117
|
dim = shape[-1]
|
|
106
118
|
X = X.view(-1, dim)
|
|
@@ -108,6 +120,7 @@ class LigerRMSNormFunction(torch.autograd.Function):
|
|
|
108
120
|
BLOCK_SIZE, num_warps = calculate_settings(n_cols)
|
|
109
121
|
|
|
110
122
|
Y = torch.empty((n_rows, n_cols), dtype=X.dtype, device=X.device)
|
|
123
|
+
# r is to cache (1/rms) for each row
|
|
111
124
|
r = torch.empty(n_rows, dtype=X.dtype, device=X.device)
|
|
112
125
|
|
|
113
126
|
# Check constraints.
|
|
@@ -139,6 +152,10 @@ class LigerRMSNormFunction(torch.autograd.Function):
|
|
|
139
152
|
@staticmethod
|
|
140
153
|
@ensure_contiguous
|
|
141
154
|
def backward(ctx, dY):
|
|
155
|
+
"""
|
|
156
|
+
Y: (B, T, H) or (BxT, H)
|
|
157
|
+
"""
|
|
158
|
+
|
|
142
159
|
shape = dY.shape
|
|
143
160
|
dim = shape[-1]
|
|
144
161
|
dY = dY.view(-1, dim)
|
|
@@ -146,6 +163,7 @@ class LigerRMSNormFunction(torch.autograd.Function):
|
|
|
146
163
|
n_rows, n_cols = dY.shape
|
|
147
164
|
dW = torch.zeros_like(X)
|
|
148
165
|
|
|
166
|
+
# Here we use dY to store the value of dX to save memory
|
|
149
167
|
_rms_norm_backward[(n_rows,)](
|
|
150
168
|
dY,
|
|
151
169
|
dY.stride(0),
|