foamToPython 0.0.1__tar.gz
This diff represents the content of publicly available package versions that have been released to one of the supported registries. The information contained in this diff is provided for informational purposes only and reflects changes between package versions as they appear in their respective public registries.
- foamtopython-0.0.1/PKG-INFO +111 -0
- foamtopython-0.0.1/README.md +102 -0
- foamtopython-0.0.1/pyproject.toml +19 -0
- foamtopython-0.0.1/setup.cfg +4 -0
- foamtopython-0.0.1/src/PODopenFOAM/__init__.py +7 -0
- foamtopython-0.0.1/src/PODopenFOAM/ofmodes.py +1228 -0
- foamtopython-0.0.1/src/foamToPython/__init__.py +11 -0
- foamtopython-0.0.1/src/foamToPython/headerEnd.py +22 -0
- foamtopython-0.0.1/src/foamToPython/readOFField.py +1275 -0
- foamtopython-0.0.1/src/foamToPython/readOFList.py +205 -0
- foamtopython-0.0.1/src/foamToPython.egg-info/PKG-INFO +111 -0
- foamtopython-0.0.1/src/foamToPython.egg-info/SOURCES.txt +13 -0
- foamtopython-0.0.1/src/foamToPython.egg-info/dependency_links.txt +1 -0
- foamtopython-0.0.1/src/foamToPython.egg-info/requires.txt +1 -0
- foamtopython-0.0.1/src/foamToPython.egg-info/top_level.txt +2 -0
|
@@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
Metadata-Version: 2.4
|
|
2
|
+
Name: foamToPython
|
|
3
|
+
Version: 0.0.1
|
|
4
|
+
Summary: A py package to read and write OpenFOAM data
|
|
5
|
+
Author-email: Shenhui_Ruan <shenhui.ruan@kit.edu>
|
|
6
|
+
Requires-Python: >=3.8
|
|
7
|
+
Description-Content-Type: text/markdown
|
|
8
|
+
Requires-Dist: numpy
|
|
9
|
+
|
|
10
|
+
[foamToPython](https://github.com/Ruansh233/foamToPython.git) is an ongoing repository to read and write the OpenFOAM field and numpy array. You can also perform Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (POD) to OpenFOAM fields with this package. It can handle both serial and parallel OpenFOAM case. The package is developed in Python 3.8+ and depends on numpy.
|
|
11
|
+
|
|
12
|
+
## Features
|
|
13
|
+
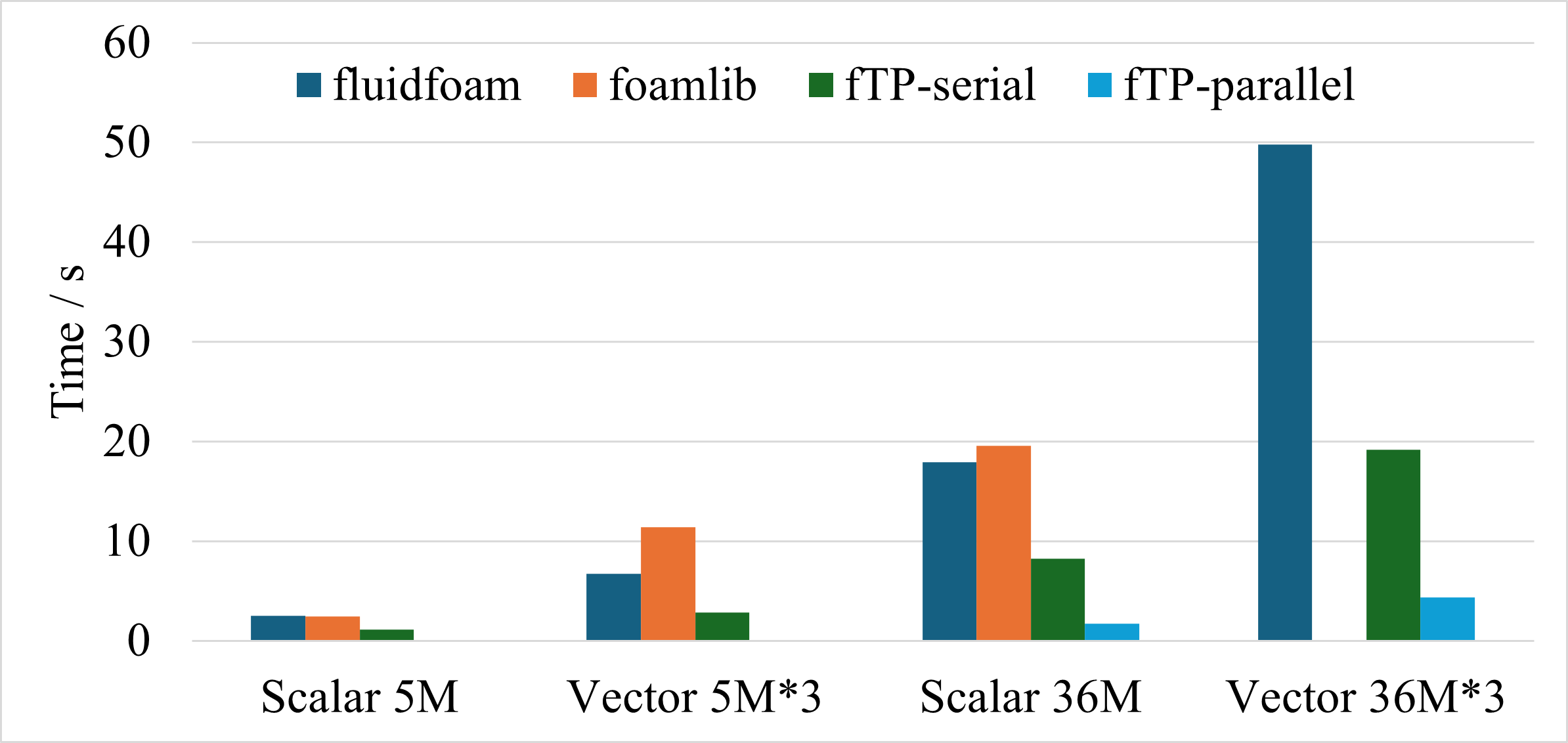
It is about __10 times faster__ than two widely used packages, [FluidFoam](https://github.com/fluiddyn/fluidfoam) and [foamlib](https://github.com/gerlero/foamlib), in reading fields. Moreover, it is capable to read and write parallel OpenFOAM case. The comparison of the performance is shown in the following figure.
|
|
14
|
+
|
|
15
|
+
|
|
16
|
+
|
|
17
|
+
The comparsion is performed for 4 conditions.
|
|
18
|
+
1. Scalar fields with 5 million cells.
|
|
19
|
+
2. Vector fields with 5 million cells.
|
|
20
|
+
3. Scalar fields with 36 million cells.
|
|
21
|
+
4. Vector fields with 36 million cells.
|
|
22
|
+
|
|
23
|
+
This test is performed on a cluster node with Intel Xeon Platinum 8358 CPU 64 cores @ 2.60GHz, 256GB RAM, and Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
|
|
24
|
+
|
|
25
|
+
foamToPython is ten times faster than FluidFoam and foamlib when reading parallel case with 36 million cells. Note that the aforementioned packages have more functions compared to the current library. [PyFoam](https://pypi.org/project/PyFoam/) is not involved in the comparsion due to the problem of version compatibility.
|
|
26
|
+
|
|
27
|
+
## Installation
|
|
28
|
+
You can install the package via pip:
|
|
29
|
+
```bash
|
|
30
|
+
pip install foamToPython
|
|
31
|
+
```
|
|
32
|
+
Or you can clone the repository and install it manually:
|
|
33
|
+
```bash
|
|
34
|
+
pip install git+https://github.com/Ruansh233/foamToPython.git
|
|
35
|
+
```
|
|
36
|
+
|
|
37
|
+
## Usage and Examples
|
|
38
|
+
|
|
39
|
+
### <span style="color:blue;">OFField</span> class
|
|
40
|
+
The class could read OpenFOAM fields.
|
|
41
|
+
It can process volScalarField or volVectorField, either uniform or non-uniform internalField.
|
|
42
|
+
|
|
43
|
+
#### read field, e.g., U
|
|
44
|
+
`U = readOFData.OFField('case/1/U', 'vector', read_data=True)`
|
|
45
|
+
|
|
46
|
+
The arguments are:
|
|
47
|
+
1. _filename_: the path of the field file.
|
|
48
|
+
2. _data_type_: the type of the field, e.g., "scalar", "vector", "label".
|
|
49
|
+
3. _read_data_: whether to read the field when initializing the class.
|
|
50
|
+
4. _parallel_: whether the case is run in parallel.
|
|
51
|
+
|
|
52
|
+
If read_data is False, the field will not be read when initializing the class. You can use `U._readField()` to read it later, or access `U.internalField` or `U.boundaryField`, which will trigger the reading of the field.
|
|
53
|
+
|
|
54
|
+
The package can read parallel case, e.g., `U = readOFData.OFField('case/1/U', 'vector', parallel=True)`.
|
|
55
|
+
|
|
56
|
+
#### load <span style="color:blue;">internalField</span> and <span style="color:blue;">boundaryField</span>
|
|
57
|
+
|
|
58
|
+
`U_cell = U.internalField`
|
|
59
|
+
`U_boundary = U.boundaryField`
|
|
60
|
+
|
|
61
|
+
1. _U_cell_ is a numpy array, store the fields values. The length is 1 for the uniform internal field.
|
|
62
|
+
2. _U_boundary_ is a dict store each patches. For each patch, it contain _type_ for the type of boundary. If the _type_ is _fixedValue_, the numpy array can be accessed by the key _value_. For example: `U.boundaryField['velocityInlet']['value']`
|
|
63
|
+
|
|
64
|
+
For parallel case, both internalField and boundaryField are read from all processors and stored as lists. For example, `U.internalField[0]` is the internalField from processor 0.
|
|
65
|
+
|
|
66
|
+
#### <span style="color:blue;">writeField</span>
|
|
67
|
+
You can modify the data of _U_ and then write it as OF field.
|
|
68
|
+
|
|
69
|
+
The arguments are:
|
|
70
|
+
1. _path_: the path to write the field. It can contain `<timeDir>` and `<fieldName>`, which will be replaced by the arguments `timeDir` and `fieldName` if provided.
|
|
71
|
+
2. _timeDir_: the time directory to write the field. Default is `None`.
|
|
72
|
+
3. _fieldName_: the name of the field to write. Default is `None`.
|
|
73
|
+
|
|
74
|
+
Same function can be used to write parallel case, e.g., `U.writeField('case/<timeDir>/<fieldName>')`.
|
|
75
|
+
|
|
76
|
+
Therefore, you can use two types of inputs, e.g.,
|
|
77
|
+
1. `U.writeField('case/<timeDir>/<fieldName>')`.
|
|
78
|
+
2. `U.writeField('case/test', timeDir=<timeDir>, fieldName=<fieldName>)`. Note that `timeDir` and `fieldName` are needed when using **Paraview** to read the fields.
|
|
79
|
+
|
|
80
|
+
### <span style="color:blue;">readList</span> function
|
|
81
|
+
The function could read field value like velocity and pressure.
|
|
82
|
+
The data type are: "lable", "scalar", "vector".
|
|
83
|
+
|
|
84
|
+
For example: `U = readList("1/U", "vector").`
|
|
85
|
+
|
|
86
|
+
### <span style="color:blue;">readListList</span> function
|
|
87
|
+
The function could read ListList, like the cellZones file.
|
|
88
|
+
The data type are: "lable", "scalar", "vector".
|
|
89
|
+
|
|
90
|
+
For example: `cellZones = readList("constant/polyMesh/cellZones", "label")`.
|
|
91
|
+
|
|
92
|
+
### Perform <span style="color:blue;">POD</span> to openfoam fields.
|
|
93
|
+
Please check the submodule _PODopenFOAM_ and the class under it _PODmodes_, which can be called `foamToPython.PODmodes`. It can be created as,
|
|
94
|
+
|
|
95
|
+
`pod = PODmodes(U, POD_algo=<POD_algo>, rank=<rank>)`.
|
|
96
|
+
|
|
97
|
+
The arguments are:
|
|
98
|
+
1. _U_: the OFField class instance, which contains the data to perform POD.
|
|
99
|
+
2. _POD_algo_: the algorithm to perform POD, can be "svd" or "eigen". Default is "eigen".
|
|
100
|
+
3. _rank_: the number of modes to compute. Default is 10, which means 10 modes are computed.
|
|
101
|
+
|
|
102
|
+
The modes can be exported with OpenFOAM format using
|
|
103
|
+
`pod.writeModes(outputDir, fieldName=<fieldName>)`.
|
|
104
|
+
|
|
105
|
+
The arguments are:
|
|
106
|
+
1. _outputDir_: the directory to write the modes. The modes will be written in folders `outputDir/1`, `outputDir/2`, ..., `outputDir/rank`.
|
|
107
|
+
2. _fieldName_: the name of the field to write. Default is `None`.
|
|
108
|
+
|
|
109
|
+
### Parallel case
|
|
110
|
+
The package can read and write parallel case.
|
|
111
|
+
However, the speed is slower than the serial case, and it will be improved in the future.
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
[foamToPython](https://github.com/Ruansh233/foamToPython.git) is an ongoing repository to read and write the OpenFOAM field and numpy array. You can also perform Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (POD) to OpenFOAM fields with this package. It can handle both serial and parallel OpenFOAM case. The package is developed in Python 3.8+ and depends on numpy.
|
|
2
|
+
|
|
3
|
+
## Features
|
|
4
|
+
It is about __10 times faster__ than two widely used packages, [FluidFoam](https://github.com/fluiddyn/fluidfoam) and [foamlib](https://github.com/gerlero/foamlib), in reading fields. Moreover, it is capable to read and write parallel OpenFOAM case. The comparison of the performance is shown in the following figure.
|
|
5
|
+
|
|
6
|
+

|
|
7
|
+
|
|
8
|
+
The comparsion is performed for 4 conditions.
|
|
9
|
+
1. Scalar fields with 5 million cells.
|
|
10
|
+
2. Vector fields with 5 million cells.
|
|
11
|
+
3. Scalar fields with 36 million cells.
|
|
12
|
+
4. Vector fields with 36 million cells.
|
|
13
|
+
|
|
14
|
+
This test is performed on a cluster node with Intel Xeon Platinum 8358 CPU 64 cores @ 2.60GHz, 256GB RAM, and Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
|
|
15
|
+
|
|
16
|
+
foamToPython is ten times faster than FluidFoam and foamlib when reading parallel case with 36 million cells. Note that the aforementioned packages have more functions compared to the current library. [PyFoam](https://pypi.org/project/PyFoam/) is not involved in the comparsion due to the problem of version compatibility.
|
|
17
|
+
|
|
18
|
+
## Installation
|
|
19
|
+
You can install the package via pip:
|
|
20
|
+
```bash
|
|
21
|
+
pip install foamToPython
|
|
22
|
+
```
|
|
23
|
+
Or you can clone the repository and install it manually:
|
|
24
|
+
```bash
|
|
25
|
+
pip install git+https://github.com/Ruansh233/foamToPython.git
|
|
26
|
+
```
|
|
27
|
+
|
|
28
|
+
## Usage and Examples
|
|
29
|
+
|
|
30
|
+
### <span style="color:blue;">OFField</span> class
|
|
31
|
+
The class could read OpenFOAM fields.
|
|
32
|
+
It can process volScalarField or volVectorField, either uniform or non-uniform internalField.
|
|
33
|
+
|
|
34
|
+
#### read field, e.g., U
|
|
35
|
+
`U = readOFData.OFField('case/1/U', 'vector', read_data=True)`
|
|
36
|
+
|
|
37
|
+
The arguments are:
|
|
38
|
+
1. _filename_: the path of the field file.
|
|
39
|
+
2. _data_type_: the type of the field, e.g., "scalar", "vector", "label".
|
|
40
|
+
3. _read_data_: whether to read the field when initializing the class.
|
|
41
|
+
4. _parallel_: whether the case is run in parallel.
|
|
42
|
+
|
|
43
|
+
If read_data is False, the field will not be read when initializing the class. You can use `U._readField()` to read it later, or access `U.internalField` or `U.boundaryField`, which will trigger the reading of the field.
|
|
44
|
+
|
|
45
|
+
The package can read parallel case, e.g., `U = readOFData.OFField('case/1/U', 'vector', parallel=True)`.
|
|
46
|
+
|
|
47
|
+
#### load <span style="color:blue;">internalField</span> and <span style="color:blue;">boundaryField</span>
|
|
48
|
+
|
|
49
|
+
`U_cell = U.internalField`
|
|
50
|
+
`U_boundary = U.boundaryField`
|
|
51
|
+
|
|
52
|
+
1. _U_cell_ is a numpy array, store the fields values. The length is 1 for the uniform internal field.
|
|
53
|
+
2. _U_boundary_ is a dict store each patches. For each patch, it contain _type_ for the type of boundary. If the _type_ is _fixedValue_, the numpy array can be accessed by the key _value_. For example: `U.boundaryField['velocityInlet']['value']`
|
|
54
|
+
|
|
55
|
+
For parallel case, both internalField and boundaryField are read from all processors and stored as lists. For example, `U.internalField[0]` is the internalField from processor 0.
|
|
56
|
+
|
|
57
|
+
#### <span style="color:blue;">writeField</span>
|
|
58
|
+
You can modify the data of _U_ and then write it as OF field.
|
|
59
|
+
|
|
60
|
+
The arguments are:
|
|
61
|
+
1. _path_: the path to write the field. It can contain `<timeDir>` and `<fieldName>`, which will be replaced by the arguments `timeDir` and `fieldName` if provided.
|
|
62
|
+
2. _timeDir_: the time directory to write the field. Default is `None`.
|
|
63
|
+
3. _fieldName_: the name of the field to write. Default is `None`.
|
|
64
|
+
|
|
65
|
+
Same function can be used to write parallel case, e.g., `U.writeField('case/<timeDir>/<fieldName>')`.
|
|
66
|
+
|
|
67
|
+
Therefore, you can use two types of inputs, e.g.,
|
|
68
|
+
1. `U.writeField('case/<timeDir>/<fieldName>')`.
|
|
69
|
+
2. `U.writeField('case/test', timeDir=<timeDir>, fieldName=<fieldName>)`. Note that `timeDir` and `fieldName` are needed when using **Paraview** to read the fields.
|
|
70
|
+
|
|
71
|
+
### <span style="color:blue;">readList</span> function
|
|
72
|
+
The function could read field value like velocity and pressure.
|
|
73
|
+
The data type are: "lable", "scalar", "vector".
|
|
74
|
+
|
|
75
|
+
For example: `U = readList("1/U", "vector").`
|
|
76
|
+
|
|
77
|
+
### <span style="color:blue;">readListList</span> function
|
|
78
|
+
The function could read ListList, like the cellZones file.
|
|
79
|
+
The data type are: "lable", "scalar", "vector".
|
|
80
|
+
|
|
81
|
+
For example: `cellZones = readList("constant/polyMesh/cellZones", "label")`.
|
|
82
|
+
|
|
83
|
+
### Perform <span style="color:blue;">POD</span> to openfoam fields.
|
|
84
|
+
Please check the submodule _PODopenFOAM_ and the class under it _PODmodes_, which can be called `foamToPython.PODmodes`. It can be created as,
|
|
85
|
+
|
|
86
|
+
`pod = PODmodes(U, POD_algo=<POD_algo>, rank=<rank>)`.
|
|
87
|
+
|
|
88
|
+
The arguments are:
|
|
89
|
+
1. _U_: the OFField class instance, which contains the data to perform POD.
|
|
90
|
+
2. _POD_algo_: the algorithm to perform POD, can be "svd" or "eigen". Default is "eigen".
|
|
91
|
+
3. _rank_: the number of modes to compute. Default is 10, which means 10 modes are computed.
|
|
92
|
+
|
|
93
|
+
The modes can be exported with OpenFOAM format using
|
|
94
|
+
`pod.writeModes(outputDir, fieldName=<fieldName>)`.
|
|
95
|
+
|
|
96
|
+
The arguments are:
|
|
97
|
+
1. _outputDir_: the directory to write the modes. The modes will be written in folders `outputDir/1`, `outputDir/2`, ..., `outputDir/rank`.
|
|
98
|
+
2. _fieldName_: the name of the field to write. Default is `None`.
|
|
99
|
+
|
|
100
|
+
### Parallel case
|
|
101
|
+
The package can read and write parallel case.
|
|
102
|
+
However, the speed is slower than the serial case, and it will be improved in the future.
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
[build-system]
|
|
2
|
+
requires = ["setuptools"]
|
|
3
|
+
build-backend = "setuptools.build_meta"
|
|
4
|
+
|
|
5
|
+
[project]
|
|
6
|
+
name = "foamToPython"
|
|
7
|
+
authors = [
|
|
8
|
+
{name = "Shenhui_Ruan", email = "shenhui.ruan@kit.edu"}
|
|
9
|
+
]
|
|
10
|
+
description = "A py package to read and write OpenFOAM data"
|
|
11
|
+
version = "0.0.1"
|
|
12
|
+
readme = "README.md"
|
|
13
|
+
requires-python = ">=3.8"
|
|
14
|
+
dependencies = [
|
|
15
|
+
"numpy"
|
|
16
|
+
]
|
|
17
|
+
|
|
18
|
+
[tool.setuptools.packages.find]
|
|
19
|
+
where = ["src"]
|