fastquadtree 1.2.3__tar.gz → 1.3.1__tar.gz
This diff represents the content of publicly available package versions that have been released to one of the supported registries. The information contained in this diff is provided for informational purposes only and reflects changes between package versions as they appear in their respective public registries.
Potentially problematic release.
This version of fastquadtree might be problematic. Click here for more details.
- fastquadtree-1.3.1/.github/workflows/test.yml +65 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/Cargo.lock +2 -1
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/Cargo.toml +2 -1
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/PKG-INFO +3 -1
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/README.md +1 -0
- fastquadtree-1.3.1/assets/quadtree_bench_throughput.png +0 -0
- fastquadtree-1.3.1/assets/quadtree_bench_time.png +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/docs/benchmark.md +10 -11
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/docs/future_features.md +13 -12
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/docs/index.md +1 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/interactive/ballpit.py +1 -1
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/pyproject.toml +1 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/pysrc/fastquadtree/_base_quadtree.py +31 -7
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/pysrc/fastquadtree/point_quadtree.py +21 -6
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/pysrc/fastquadtree/rect_quadtree.py +26 -7
- fastquadtree-1.3.1/src/geom.rs +73 -0
- fastquadtree-1.3.1/src/lib.rs +345 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/src/quadtree.rs +69 -49
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/src/rect_quadtree.rs +30 -28
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/tests/insertions.rs +2 -2
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/tests/nearest_neighbor.rs +4 -4
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/tests/query.rs +2 -2
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/tests/rect_quadtree.rs +3 -3
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/tests/test_insert_many_numpy.py +42 -0
- fastquadtree-1.3.1/tests/test_point_quadtree_dtypes.py +66 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/tests/test_rect_quadtree.py +65 -38
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/tests/unconventional_bounds.rs +3 -3
- fastquadtree-1.2.3/assets/quadtree_bench_throughput.png +0 -0
- fastquadtree-1.2.3/assets/quadtree_bench_time.png +0 -0
- fastquadtree-1.2.3/src/geom.rs +0 -52
- fastquadtree-1.2.3/src/lib.rs +0 -282
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/.github/workflows/docs.yml +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/.github/workflows/release.yml +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/.gitignore +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/.pre-commit-config.yaml +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/LICENSE +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/assets/ballpit.png +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/assets/interactive_v2_rect_screenshot.png +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/assets/interactive_v2_screenshot.png +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/benchmarks/benchmark_native_vs_shim.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/benchmarks/benchmark_np_vs_list.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/benchmarks/benchmark_serialization_vs_rebuild.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/benchmarks/cross_library_bench.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/benchmarks/quadtree_bench/__init__.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/benchmarks/quadtree_bench/engines.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/benchmarks/quadtree_bench/main.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/benchmarks/quadtree_bench/plotting.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/benchmarks/quadtree_bench/runner.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/benchmarks/requirements.txt +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/benchmarks/runner.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/benchmarks/system_info_collector.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/docs/api/point_item.md +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/docs/api/pyqtree.md +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/docs/api/quadtree.md +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/docs/api/rect_item.md +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/docs/api/rect_quadtree.md +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/docs/quickstart.md +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/docs/runnables.md +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/docs/styles/overrides.css +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/interactive/interactive.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/interactive/interactive_v2.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/interactive/interactive_v2_rect.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/interactive/requirements.txt +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/mkdocs.yml +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/pysrc/fastquadtree/__init__.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/pysrc/fastquadtree/_item.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/pysrc/fastquadtree/_obj_store.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/pysrc/fastquadtree/py.typed +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/pysrc/fastquadtree/pyqtree.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/tests/rectangle_traversal.rs +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/tests/serialization.rs +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/tests/test_base_quadtree.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/tests/test_clear.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/tests/test_delete.rs +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/tests/test_delete_by_object.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/tests/test_delete_python.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/tests/test_obj_store.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/tests/test_point_quadtree_nn_runtime.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/tests/test_pyqtree_shim_compat.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/tests/test_python.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/tests/test_serialization.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/tests/test_unconventional_bounds.py +0 -0
- {fastquadtree-1.2.3 → fastquadtree-1.3.1}/tests/test_wrapper_edges.py +0 -0
|
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
# .github/workflows/test.yml
|
|
2
|
+
name: Test
|
|
3
|
+
on:
|
|
4
|
+
push:
|
|
5
|
+
branches: [ main ]
|
|
6
|
+
|
|
7
|
+
permissions:
|
|
8
|
+
contents: write
|
|
9
|
+
pages: write
|
|
10
|
+
id-token: write
|
|
11
|
+
|
|
12
|
+
jobs:
|
|
13
|
+
test:
|
|
14
|
+
name: Test build (Python ${{ matrix.python-version }})
|
|
15
|
+
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
|
16
|
+
strategy:
|
|
17
|
+
fail-fast: false
|
|
18
|
+
matrix:
|
|
19
|
+
python-version: ["3.9", "3.14"]
|
|
20
|
+
|
|
21
|
+
steps:
|
|
22
|
+
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
|
23
|
+
|
|
24
|
+
- name: Set up Python ${{ matrix.python-version }}
|
|
25
|
+
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
|
26
|
+
with:
|
|
27
|
+
python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }}
|
|
28
|
+
allow-prereleases: true
|
|
29
|
+
cache: "pip"
|
|
30
|
+
|
|
31
|
+
- name: Create venv for maturin develop
|
|
32
|
+
run: python -m venv .venv
|
|
33
|
+
|
|
34
|
+
- name: Build with maturin into this Python
|
|
35
|
+
uses: PyO3/maturin-action@v1
|
|
36
|
+
with:
|
|
37
|
+
command: develop
|
|
38
|
+
args: --release
|
|
39
|
+
manylinux: manylinux2014
|
|
40
|
+
|
|
41
|
+
- name: Install Python test deps into .venv
|
|
42
|
+
run: |
|
|
43
|
+
. .venv/bin/activate
|
|
44
|
+
pip install -e '.[dev]'
|
|
45
|
+
|
|
46
|
+
- name: Run Python tests
|
|
47
|
+
run: |
|
|
48
|
+
. .venv/bin/activate
|
|
49
|
+
pytest
|
|
50
|
+
|
|
51
|
+
- name: Run Python tests
|
|
52
|
+
run: |
|
|
53
|
+
. .venv/bin/activate
|
|
54
|
+
pytest
|
|
55
|
+
|
|
56
|
+
- name: Install Rust toolchain
|
|
57
|
+
uses: dtolnay/rust-toolchain@stable
|
|
58
|
+
|
|
59
|
+
- name: Run Rust tests
|
|
60
|
+
run: cargo test
|
|
61
|
+
|
|
62
|
+
- name: Upload coverage to Codecov
|
|
63
|
+
uses: codecov/codecov-action@v5
|
|
64
|
+
with:
|
|
65
|
+
token: ${{ secrets.CODECOV_TOKEN }}
|
|
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
|
|
1
1
|
[package]
|
|
2
2
|
name = "fastquadtree"
|
|
3
|
-
version = "1.
|
|
3
|
+
version = "1.3.1"
|
|
4
4
|
edition = "2021"
|
|
5
5
|
readme = "README.md"
|
|
6
6
|
|
|
@@ -13,6 +13,7 @@ smallvec = "1.15.1"
|
|
|
13
13
|
numpy = "0.26"
|
|
14
14
|
serde = { version = "1.0", features = ["derive"] }
|
|
15
15
|
bincode = {version = "2.0.1", features = ["serde"]}
|
|
16
|
+
num-traits = "0.2"
|
|
16
17
|
|
|
17
18
|
[profile.release]
|
|
18
19
|
opt-level = 3
|
|
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
|
|
1
1
|
Metadata-Version: 2.4
|
|
2
2
|
Name: fastquadtree
|
|
3
|
-
Version: 1.
|
|
3
|
+
Version: 1.3.1
|
|
4
4
|
Classifier: Programming Language :: Python :: 3
|
|
5
5
|
Classifier: Programming Language :: Python :: 3 :: Only
|
|
6
6
|
Classifier: Programming Language :: Rust
|
|
@@ -26,6 +26,7 @@ Requires-Dist: mkdocs-minify-plugin ; extra == 'dev'
|
|
|
26
26
|
Requires-Dist: maturin>=1.5 ; extra == 'dev'
|
|
27
27
|
Requires-Dist: pyqtree==1.0.0 ; extra == 'dev'
|
|
28
28
|
Requires-Dist: numpy ; extra == 'dev'
|
|
29
|
+
Requires-Dist: pre-commit ; extra == 'dev'
|
|
29
30
|
Provides-Extra: dev
|
|
30
31
|
License-File: LICENSE
|
|
31
32
|
Summary: Rust-accelerated quadtree for Python with fast inserts, range queries, and k-NN search.
|
|
@@ -73,6 +74,7 @@ Rust-optimized quadtree with a clean Python API
|
|
|
73
74
|
- Fast KNN and range queries
|
|
74
75
|
- Optional object tracking for id ↔ object mapping
|
|
75
76
|
- Fast [serialization](https://elan456.github.io/fastquadtree/benchmark/#serialization-vs-rebuild) to/from bytes
|
|
77
|
+
- Support for multiple data types (f32, f64, i32, i64) for coordinates
|
|
76
78
|
- [100% test coverage](https://codecov.io/gh/Elan456/fastquadtree) and CI on GitHub Actions
|
|
77
79
|
- Offers a drop-in [pyqtree shim](https://elan456.github.io/fastquadtree/benchmark/#pyqtree-drop-in-shim-performance-gains) that is 6.567x faster while keeping the same API
|
|
78
80
|
|
|
@@ -33,6 +33,7 @@ Rust-optimized quadtree with a clean Python API
|
|
|
33
33
|
- Fast KNN and range queries
|
|
34
34
|
- Optional object tracking for id ↔ object mapping
|
|
35
35
|
- Fast [serialization](https://elan456.github.io/fastquadtree/benchmark/#serialization-vs-rebuild) to/from bytes
|
|
36
|
+
- Support for multiple data types (f32, f64, i32, i64) for coordinates
|
|
36
37
|
- [100% test coverage](https://codecov.io/gh/Elan456/fastquadtree) and CI on GitHub Actions
|
|
37
38
|
- Offers a drop-in [pyqtree shim](https://elan456.github.io/fastquadtree/benchmark/#pyqtree-drop-in-shim-performance-gains) that is 6.567x faster while keeping the same API
|
|
38
39
|
|
|
Binary file
|
|
Binary file
|
|
@@ -11,21 +11,20 @@ Quadtrees are the focus of the benchmark, but Rtrees are included for reference.
|
|
|
11
11
|
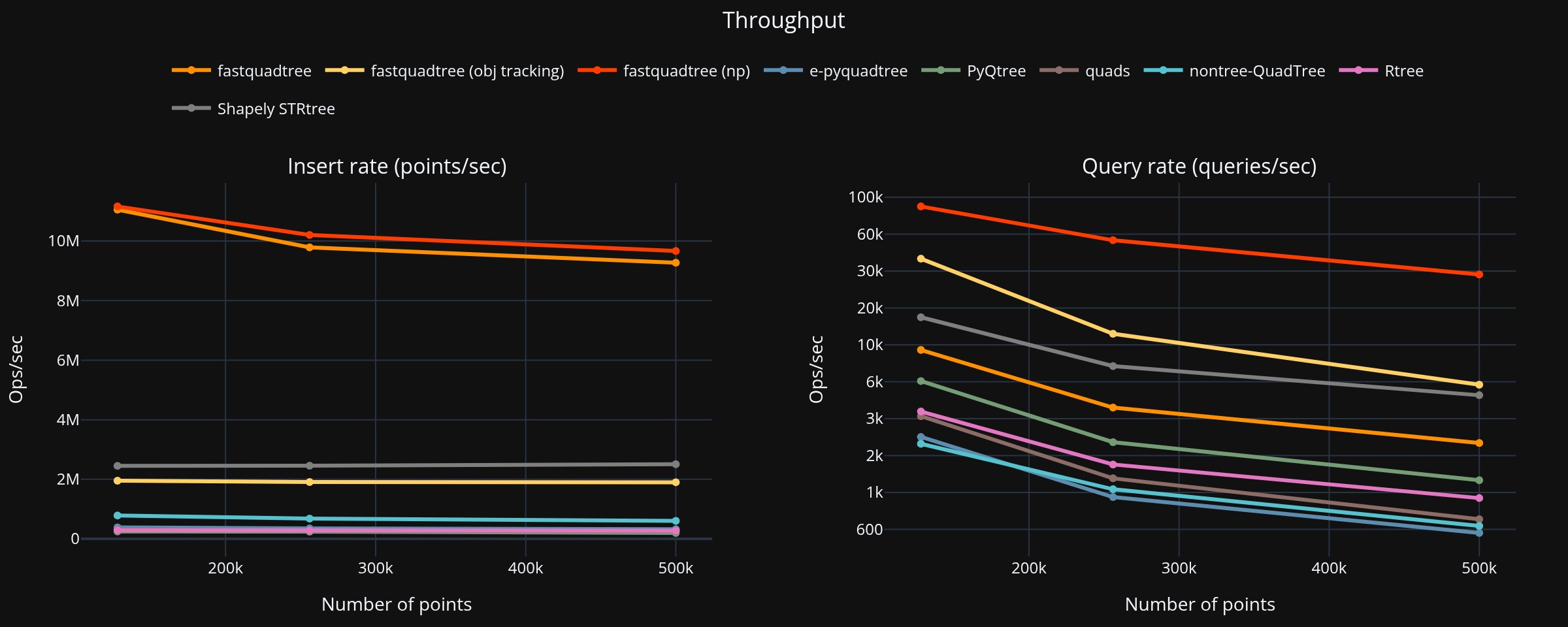
|
|
12
12
|
|
|
13
13
|
### Summary (largest dataset, PyQtree baseline)
|
|
14
|
-
|
|
15
14
|
- Points: **250,000**, Queries: **500**
|
|
16
|
-
- Fastest total: **fastquadtree** at **0.
|
|
15
|
+
- Fastest total: **fastquadtree** at **0.100 s**
|
|
17
16
|
|
|
18
17
|
| Library | Build (s) | Query (s) | Total (s) | Speed vs PyQtree |
|
|
19
18
|
|---|---:|---:|---:|---:|
|
|
20
|
-
|
|
|
21
|
-
| Shapely STRtree | 0.
|
|
22
|
-
|
|
|
23
|
-
|
|
|
24
|
-
| e-pyquadtree |
|
|
25
|
-
| PyQtree | 1.
|
|
26
|
-
| quads | 1.
|
|
27
|
-
|
|
28
|
-
|
|
19
|
+
| fastquadtree | 0.027 | 0.073 | 0.100 | 16.12× |
|
|
20
|
+
| Shapely STRtree | 0.148 | 0.083 | 0.231 | 7.00× |
|
|
21
|
+
| Rtree | 0.814 | 0.245 | 1.059 | 1.53× |
|
|
22
|
+
| nontree-QuadTree | 0.532 | 0.582 | 1.114 | 1.45× |
|
|
23
|
+
| e-pyquadtree | 0.913 | 0.641 | 1.554 | 1.04× |
|
|
24
|
+
| PyQtree | 1.352 | 0.264 | 1.616 | 1.00× |
|
|
25
|
+
| quads | 1.231 | 0.465 | 1.695 | 0.95× |
|
|
26
|
+
|
|
27
|
+
#### Benchmark Configuration
|
|
29
28
|
| Parameter | Value |
|
|
30
29
|
|---|---:|
|
|
31
30
|
| Bounds | (0, 0, 1000, 1000) |
|
|
@@ -9,27 +9,19 @@ The features will likely be implemented in the order they are listed below, but
|
|
|
9
9
|
|
|
10
10
|
## 🚧 Planned Features
|
|
11
11
|
|
|
12
|
-
### 1.
|
|
13
|
-
|
|
14
|
-
Currently, the point quadtree only uses f32 for point coordinates, limiting precision in favor of better performance.
|
|
15
|
-
To make the quadtree more flexible, we could allow users to specify the coordinate type (e.g., f64, i32, etc.) when creating a quadtree.
|
|
16
|
-
The f32 will remain the default, but users will be able to specify a different type if needed.
|
|
17
|
-
|
|
18
|
-
If the type cannot be made truly generic, then only the following types would be supported: f32, f64, i32, i64
|
|
19
|
-
|
|
20
|
-
### 2. KNN with criteria function
|
|
12
|
+
### 1. KNN with criteria function
|
|
21
13
|
|
|
22
14
|
Currently, KNN only supports finding the nearest neighbors based on euclidean distance.
|
|
23
15
|
By adding a criteria function, we could allow users to define custom criteria for finding neighbors by passing a function that
|
|
24
16
|
takes in a point and returns a score. The KNN algorithm would then use this score to determine the nearest neighbors.
|
|
25
17
|
|
|
26
|
-
###
|
|
18
|
+
### 2. KNN in rectangle quadtree
|
|
27
19
|
|
|
28
20
|
Currently, KNN is only supported in the point quadtree. By adding KNN support to the rectangle quadtree, we could allow users to find the nearest rectangles to a given point. This would be to the nearest edge of the rectangle, adding complexity to the algorithm.
|
|
29
21
|
However, it will allow for really quick collision detection between a point and a set of rectangles as the point can just do
|
|
30
22
|
robust-collision handling with the nearest rectangles.
|
|
31
23
|
|
|
32
|
-
###
|
|
24
|
+
### 3. Circle support
|
|
33
25
|
|
|
34
26
|
Currently, we support points and rectangles in two separate quadtrees.
|
|
35
27
|
For example, in the ball-pit demo, we use a point quadtree, but then query a larger area to account for the radius of the balls.
|
|
@@ -41,6 +33,15 @@ A good alternative is to use the rectangle quadtree and insert the minimum bound
|
|
|
41
33
|
|
|
42
34
|
Once a feature from above is completed, it will be moved to this section.
|
|
43
35
|
|
|
44
|
-
|
|
36
|
+
|
|
37
|
+
### Configurable Quadtree Coordinate Type (1.3.0)
|
|
38
|
+
|
|
39
|
+
Currently, the point quadtree only uses f32 for point coordinates, limiting precision in favor of better performance.
|
|
40
|
+
To make the quadtree more flexible, we could allow users to specify the coordinate type (e.g., f64, i32, etc.) when creating a quadtree.
|
|
41
|
+
The f32 will remain the default, but users will be able to specify a different type if needed.
|
|
42
|
+
|
|
43
|
+
If the type cannot be made truly generic, then only the following types would be supported: f32, f64, i32, i64
|
|
44
|
+
|
|
45
|
+
### Quadtree serialization (1.2.0)
|
|
45
46
|
|
|
46
47
|
By serializing the quadtree, we can save its state to a file and load it later. This will allow us to persist the quadtree structure and data across sessions. For example, you could pre build a quadtree with all the walls in your video game level, serialize it to a file, and then load it when the game starts. This will heavily reduce the game load time since you won't have to rebuild the quadtree from scratch every time.
|
|
@@ -42,6 +42,7 @@
|
|
|
42
42
|
- Fast KNN and range queries
|
|
43
43
|
- Optional object tracking for id ↔ object mapping
|
|
44
44
|
- Fast [serialization](benchmark.md#serialization-vs-rebuild) to/from bytes
|
|
45
|
+
- Support for multiple data types (f32, f64, i32, i64) for coordinates
|
|
45
46
|
- [100% test coverage](https://codecov.io/gh/Elan456/fastquadtree) and CI on GitHub Actions
|
|
46
47
|
|
|
47
48
|
## Examples
|
|
@@ -29,6 +29,14 @@ G = TypeVar("G") # geometry type, e.g. Point or Bounds
|
|
|
29
29
|
HitT = TypeVar("HitT") # raw native tuple, e.g. (id,x,y) or (id,x0,y0,x1,y1)
|
|
30
30
|
ItemType = TypeVar("ItemType", bound=Item) # e.g. PointItem or RectItem
|
|
31
31
|
|
|
32
|
+
# Quadtree dtype to numpy dtype mapping
|
|
33
|
+
QUADTREE_DTYPE_TO_NP_DTYPE = {
|
|
34
|
+
"f32": "float32",
|
|
35
|
+
"f64": "float64",
|
|
36
|
+
"i32": "int32",
|
|
37
|
+
"i64": "int64",
|
|
38
|
+
}
|
|
39
|
+
|
|
32
40
|
|
|
33
41
|
def _is_np_array(x: Any) -> bool:
|
|
34
42
|
mod = getattr(x.__class__, "__module__", "")
|
|
@@ -48,6 +56,7 @@ class _BaseQuadTree(Generic[G, HitT, ItemType], ABC):
|
|
|
48
56
|
"_bounds",
|
|
49
57
|
"_capacity",
|
|
50
58
|
"_count",
|
|
59
|
+
"_dtype",
|
|
51
60
|
"_max_depth",
|
|
52
61
|
"_native",
|
|
53
62
|
"_next_id",
|
|
@@ -62,7 +71,7 @@ class _BaseQuadTree(Generic[G, HitT, ItemType], ABC):
|
|
|
62
71
|
"""Create the native engine instance."""
|
|
63
72
|
|
|
64
73
|
@classmethod
|
|
65
|
-
def _new_native_from_bytes(cls, data: bytes) -> Any:
|
|
74
|
+
def _new_native_from_bytes(cls, data: bytes, dtype: str) -> Any:
|
|
66
75
|
"""Create the native engine instance from serialized bytes."""
|
|
67
76
|
|
|
68
77
|
@staticmethod
|
|
@@ -79,10 +88,12 @@ class _BaseQuadTree(Generic[G, HitT, ItemType], ABC):
|
|
|
79
88
|
*,
|
|
80
89
|
max_depth: int | None = None,
|
|
81
90
|
track_objects: bool = False,
|
|
91
|
+
dtype: str = "f32",
|
|
82
92
|
):
|
|
83
93
|
self._bounds = bounds
|
|
84
94
|
self._max_depth = max_depth
|
|
85
95
|
self._capacity = capacity
|
|
96
|
+
self._dtype = dtype
|
|
86
97
|
self._native = self._new_native(bounds, capacity, max_depth)
|
|
87
98
|
|
|
88
99
|
self._track_objects = bool(track_objects)
|
|
@@ -138,12 +149,13 @@ class _BaseQuadTree(Generic[G, HitT, ItemType], ABC):
|
|
|
138
149
|
return pickle.dumps(self.to_dict())
|
|
139
150
|
|
|
140
151
|
@classmethod
|
|
141
|
-
def from_bytes(cls, data: bytes) -> Self:
|
|
152
|
+
def from_bytes(cls, data: bytes, dtype: str = "f32") -> Self:
|
|
142
153
|
"""
|
|
143
|
-
Deserialize a quadtree from bytes.
|
|
154
|
+
Deserialize a quadtree from bytes. Specifiy the dtype if the original tree that was serialized used a non-default dtype.
|
|
144
155
|
|
|
145
156
|
Args:
|
|
146
157
|
data: Bytes representing the serialized quadtree from `to_bytes()`.
|
|
158
|
+
dtype: The data type used in the native engine ('f32', 'f64', 'i32', 'i64') when saved to bytes.
|
|
147
159
|
|
|
148
160
|
Returns:
|
|
149
161
|
A new quadtree instance with the same state as when serialized.
|
|
@@ -160,7 +172,15 @@ class _BaseQuadTree(Generic[G, HitT, ItemType], ABC):
|
|
|
160
172
|
store_dict = in_dict["store"]
|
|
161
173
|
|
|
162
174
|
qt = cls.__new__(cls) # type: ignore[call-arg]
|
|
163
|
-
|
|
175
|
+
try:
|
|
176
|
+
qt._native = cls._new_native_from_bytes(core_bytes, dtype=dtype)
|
|
177
|
+
except ValueError as ve:
|
|
178
|
+
raise ValueError(
|
|
179
|
+
"Failed to deserialize quadtree native core. "
|
|
180
|
+
"This may be due to a dtype mismatch. "
|
|
181
|
+
"Ensure the dtype used in from_bytes() matches the original tree. "
|
|
182
|
+
"Error details: " + str(ve)
|
|
183
|
+
) from ve
|
|
164
184
|
|
|
165
185
|
if store_dict is not None:
|
|
166
186
|
qt._store = ObjStore.from_dict(store_dict, qt._make_item)
|
|
@@ -238,7 +258,7 @@ class _BaseQuadTree(Generic[G, HitT, ItemType], ABC):
|
|
|
238
258
|
) -> int:
|
|
239
259
|
"""
|
|
240
260
|
Bulk insert with auto-assigned contiguous ids. Faster than inserting one-by-one.<br>
|
|
241
|
-
Can accept either a Python sequence of geometries or a NumPy array of shape (N,2) or (N,4) with dtype
|
|
261
|
+
Can accept either a Python sequence of geometries or a NumPy array of shape (N,2) or (N,4) with a dtype that matches the quadtree's dtype.
|
|
242
262
|
|
|
243
263
|
If tracking is enabled, the objects will be bulk stored internally.
|
|
244
264
|
If no objects are provided, the items will have obj=None (if tracking).
|
|
@@ -277,8 +297,12 @@ class _BaseQuadTree(Generic[G, HitT, ItemType], ABC):
|
|
|
277
297
|
if geoms.size == 0:
|
|
278
298
|
return 0
|
|
279
299
|
|
|
280
|
-
if
|
|
281
|
-
|
|
300
|
+
# Check if dtype matches quadtree dtype
|
|
301
|
+
expected_np_dtype = QUADTREE_DTYPE_TO_NP_DTYPE.get(self._dtype)
|
|
302
|
+
if geoms.dtype != expected_np_dtype:
|
|
303
|
+
raise TypeError(
|
|
304
|
+
f"Numpy array dtype {geoms.dtype} does not match quadtree dtype {self._dtype}"
|
|
305
|
+
)
|
|
282
306
|
|
|
283
307
|
if self._store is None:
|
|
284
308
|
# Simple contiguous path with native bulk insert
|
|
@@ -5,10 +5,17 @@ from typing import Any, Literal, Tuple, overload
|
|
|
5
5
|
|
|
6
6
|
from ._base_quadtree import Bounds, _BaseQuadTree
|
|
7
7
|
from ._item import Point, PointItem
|
|
8
|
-
from ._native import QuadTree as
|
|
8
|
+
from ._native import QuadTree as QuadTreeF32, QuadTreeF64, QuadTreeI32, QuadTreeI64
|
|
9
9
|
|
|
10
10
|
_IdCoord = Tuple[int, float, float]
|
|
11
11
|
|
|
12
|
+
DTYPE_MAP = {
|
|
13
|
+
"f32": QuadTreeF32,
|
|
14
|
+
"f64": QuadTreeF64,
|
|
15
|
+
"i32": QuadTreeI32,
|
|
16
|
+
"i64": QuadTreeI64,
|
|
17
|
+
}
|
|
18
|
+
|
|
12
19
|
|
|
13
20
|
class QuadTree(_BaseQuadTree[Point, _IdCoord, PointItem]):
|
|
14
21
|
"""
|
|
@@ -29,6 +36,7 @@ class QuadTree(_BaseQuadTree[Point, _IdCoord, PointItem]):
|
|
|
29
36
|
capacity: Max number of points per node before splitting.
|
|
30
37
|
max_depth: Optional max tree depth. If omitted, engine decides.
|
|
31
38
|
track_objects: Enable id <-> object mapping inside Python.
|
|
39
|
+
dtype: Data type for coordinates and ids in the native engine. Default is 'f32'. Options are 'f32', 'f64', 'i32', 'i64'.
|
|
32
40
|
|
|
33
41
|
Raises:
|
|
34
42
|
ValueError: If parameters are invalid or inserts are out of bounds.
|
|
@@ -41,12 +49,14 @@ class QuadTree(_BaseQuadTree[Point, _IdCoord, PointItem]):
|
|
|
41
49
|
*,
|
|
42
50
|
max_depth: int | None = None,
|
|
43
51
|
track_objects: bool = False,
|
|
52
|
+
dtype: str = "f32",
|
|
44
53
|
):
|
|
45
54
|
super().__init__(
|
|
46
55
|
bounds,
|
|
47
56
|
capacity,
|
|
48
57
|
max_depth=max_depth,
|
|
49
58
|
track_objects=track_objects,
|
|
59
|
+
dtype=dtype,
|
|
50
60
|
)
|
|
51
61
|
|
|
52
62
|
@overload
|
|
@@ -148,14 +158,19 @@ class QuadTree(_BaseQuadTree[Point, _IdCoord, PointItem]):
|
|
|
148
158
|
return out
|
|
149
159
|
|
|
150
160
|
def _new_native(self, bounds: Bounds, capacity: int, max_depth: int | None) -> Any:
|
|
151
|
-
|
|
152
|
-
|
|
153
|
-
|
|
161
|
+
"""Create the native engine instance."""
|
|
162
|
+
rust_cls = DTYPE_MAP.get(self._dtype)
|
|
163
|
+
if rust_cls is None:
|
|
164
|
+
raise TypeError(f"Unsupported dtype: {self._dtype}")
|
|
165
|
+
return rust_cls(bounds, capacity, max_depth)
|
|
154
166
|
|
|
155
167
|
@classmethod
|
|
156
|
-
def _new_native_from_bytes(cls, data: bytes) -> Any:
|
|
168
|
+
def _new_native_from_bytes(cls, data: bytes, dtype: str = "f32") -> Any:
|
|
157
169
|
"""Create a new native engine instance from serialized bytes."""
|
|
158
|
-
|
|
170
|
+
rust_cls = DTYPE_MAP.get(dtype)
|
|
171
|
+
if rust_cls is None:
|
|
172
|
+
raise TypeError(f"Unsupported dtype: {dtype}")
|
|
173
|
+
return rust_cls.from_bytes(data)
|
|
159
174
|
|
|
160
175
|
@staticmethod
|
|
161
176
|
def _make_item(id_: int, geom: Point, obj: Any | None) -> PointItem:
|
|
@@ -5,10 +5,21 @@ from typing import Any, Literal, Tuple, overload
|
|
|
5
5
|
|
|
6
6
|
from ._base_quadtree import Bounds, _BaseQuadTree
|
|
7
7
|
from ._item import RectItem
|
|
8
|
-
from ._native import
|
|
8
|
+
from ._native import (
|
|
9
|
+
RectQuadTree as RectQuadTreeF32,
|
|
10
|
+
RectQuadTreeF64,
|
|
11
|
+
RectQuadTreeI32,
|
|
12
|
+
RectQuadTreeI64,
|
|
13
|
+
)
|
|
9
14
|
|
|
10
15
|
_IdRect = Tuple[int, float, float, float, float]
|
|
11
|
-
|
|
16
|
+
|
|
17
|
+
DTYPE_MAP = {
|
|
18
|
+
"f32": RectQuadTreeF32,
|
|
19
|
+
"f64": RectQuadTreeF64,
|
|
20
|
+
"i32": RectQuadTreeI32,
|
|
21
|
+
"i64": RectQuadTreeI64,
|
|
22
|
+
}
|
|
12
23
|
|
|
13
24
|
|
|
14
25
|
class RectQuadTree(_BaseQuadTree[Bounds, _IdRect, RectItem]):
|
|
@@ -30,6 +41,7 @@ class RectQuadTree(_BaseQuadTree[Bounds, _IdRect, RectItem]):
|
|
|
30
41
|
capacity: Max number of points per node before splitting.
|
|
31
42
|
max_depth: Optional max tree depth. If omitted, engine decides.
|
|
32
43
|
track_objects: Enable id <-> object mapping inside Python.
|
|
44
|
+
dtype: Data type for coordinates and ids in the native engine. Default is 'f32'. Options are 'f32', 'f64', 'i32', 'i64'.
|
|
33
45
|
|
|
34
46
|
Raises:
|
|
35
47
|
ValueError: If parameters are invalid or inserts are out of bounds.
|
|
@@ -42,12 +54,14 @@ class RectQuadTree(_BaseQuadTree[Bounds, _IdRect, RectItem]):
|
|
|
42
54
|
*,
|
|
43
55
|
max_depth: int | None = None,
|
|
44
56
|
track_objects: bool = False,
|
|
57
|
+
dtype: str = "f32",
|
|
45
58
|
):
|
|
46
59
|
super().__init__(
|
|
47
60
|
bounds,
|
|
48
61
|
capacity,
|
|
49
62
|
max_depth=max_depth,
|
|
50
63
|
track_objects=track_objects,
|
|
64
|
+
dtype=dtype,
|
|
51
65
|
)
|
|
52
66
|
|
|
53
67
|
@overload
|
|
@@ -84,14 +98,19 @@ class RectQuadTree(_BaseQuadTree[Bounds, _IdRect, RectItem]):
|
|
|
84
98
|
return self._store.get_many_by_ids(self._native.query_ids(rect))
|
|
85
99
|
|
|
86
100
|
def _new_native(self, bounds: Bounds, capacity: int, max_depth: int | None) -> Any:
|
|
87
|
-
|
|
88
|
-
|
|
89
|
-
|
|
101
|
+
"""Create the native engine instance."""
|
|
102
|
+
rust_cls = DTYPE_MAP.get(self._dtype)
|
|
103
|
+
if rust_cls is None:
|
|
104
|
+
raise TypeError(f"Unsupported dtype: {self._dtype}")
|
|
105
|
+
return rust_cls(bounds, capacity, max_depth)
|
|
90
106
|
|
|
91
107
|
@classmethod
|
|
92
|
-
def _new_native_from_bytes(cls, data: bytes) -> Any:
|
|
108
|
+
def _new_native_from_bytes(cls, data: bytes, dtype: str = "f32") -> Any:
|
|
93
109
|
"""Create a new native engine instance from serialized bytes."""
|
|
94
|
-
|
|
110
|
+
rust_cls = DTYPE_MAP.get(dtype)
|
|
111
|
+
if rust_cls is None:
|
|
112
|
+
raise TypeError(f"Unsupported dtype: {dtype}")
|
|
113
|
+
return rust_cls.from_bytes(data)
|
|
95
114
|
|
|
96
115
|
@staticmethod
|
|
97
116
|
def _make_item(id_: int, geom: Bounds, obj: Any | None) -> RectItem:
|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
|
|
|
1
|
+
use core::ops::{Add, Sub, Mul, Div};
|
|
2
|
+
use num_traits::{Zero, One};
|
|
3
|
+
use serde::{de::DeserializeOwned, Deserialize, Serialize};
|
|
4
|
+
|
|
5
|
+
// Creating a set of traits for coordinate types
|
|
6
|
+
// Requires basic arithmetic operations and ordering
|
|
7
|
+
pub trait Coord:
|
|
8
|
+
Copy + PartialOrd + Add<Output = Self> + Sub<Output = Self> + Mul<Output = Self> + Div<Output = Self> + Zero + One + Serialize + DeserializeOwned
|
|
9
|
+
{}
|
|
10
|
+
|
|
11
|
+
impl<T> Coord for T where
|
|
12
|
+
T: Copy + PartialOrd + Add<Output = Self> + Sub<Output = Self> + Mul<Output = Self> + Div<Output = Self> + Zero + One + Serialize + DeserializeOwned
|
|
13
|
+
{}
|
|
14
|
+
|
|
15
|
+
// Generic mid function for all Coord types
|
|
16
|
+
#[inline(always)]
|
|
17
|
+
pub fn mid<T: Coord>(a: T, b: T) -> T {
|
|
18
|
+
// a + (b - a) / 2
|
|
19
|
+
a + (b - a) / (T::one() + T::one()) // 1 + 1 = 2 for Div
|
|
20
|
+
}
|
|
21
|
+
|
|
22
|
+
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Default, Serialize, Deserialize)]
|
|
23
|
+
#[serde(bound(serialize = "", deserialize = ""))]
|
|
24
|
+
pub struct Point<T: Coord> {
|
|
25
|
+
pub x: T,
|
|
26
|
+
pub y: T,
|
|
27
|
+
}
|
|
28
|
+
|
|
29
|
+
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Default, Serialize, Deserialize)]
|
|
30
|
+
#[serde(bound(serialize = "", deserialize = ""))]
|
|
31
|
+
pub struct Rect<T: Coord> {
|
|
32
|
+
pub min_x: T,
|
|
33
|
+
pub min_y: T,
|
|
34
|
+
pub max_x: T,
|
|
35
|
+
pub max_y: T,
|
|
36
|
+
}
|
|
37
|
+
|
|
38
|
+
impl<T: Coord> Rect<T> {
|
|
39
|
+
pub fn contains(&self, point: &Point<T>) -> bool {
|
|
40
|
+
return point.x >= self.min_x && point.x < self.max_x && point.y >= self.min_y && point.y < self.max_y;
|
|
41
|
+
}
|
|
42
|
+
|
|
43
|
+
// Check if two Rect overlap at all
|
|
44
|
+
pub fn intersects(&self, other: &Rect<T>) -> bool {
|
|
45
|
+
return self.min_x < other.max_x && self.max_x > other.min_x && self.min_y < other.max_y && self.max_y > other.min_y
|
|
46
|
+
}
|
|
47
|
+
}
|
|
48
|
+
|
|
49
|
+
pub fn dist_sq_point_to_rect<T: Coord>(p: &Point<T>, r: &Rect<T>) -> T {
|
|
50
|
+
let dx = if p.x < r.min_x {
|
|
51
|
+
r.min_x - p.x
|
|
52
|
+
} else if p.x > r.max_x {
|
|
53
|
+
p.x - r.max_x
|
|
54
|
+
} else {
|
|
55
|
+
T::zero()
|
|
56
|
+
};
|
|
57
|
+
|
|
58
|
+
let dy = if p.y < r.min_y {
|
|
59
|
+
r.min_y - p.y
|
|
60
|
+
} else if p.y > r.max_y {
|
|
61
|
+
p.y - r.max_y
|
|
62
|
+
} else {
|
|
63
|
+
T::zero()
|
|
64
|
+
};
|
|
65
|
+
|
|
66
|
+
dx * dx + dy * dy
|
|
67
|
+
}
|
|
68
|
+
|
|
69
|
+
pub fn dist_sq_points<T: Coord>(a: &Point<T>, b: &Point<T>) -> T {
|
|
70
|
+
let dx = a.x - b.x;
|
|
71
|
+
let dy = a.y - b.y;
|
|
72
|
+
dx * dx + dy * dy
|
|
73
|
+
}
|