rubiks_cube 0.0.1 → 1.0.0
Sign up to get free protection for your applications and to get access to all the features.
- checksums.yaml +4 -4
- data/README.md +278 -2
- data/img/cube_algorithm.jpg +0 -0
- data/img/cube_blank.jpg +0 -0
- data/img/cube_instructions.jpg +0 -0
- data/img/cube_m_slice.jpg +0 -0
- data/img/cube_orientation.jpg +0 -0
- data/img/cube_permutation.jpg +0 -0
- data/img/cube_scramble_1.jpg +0 -0
- data/img/cube_scramble_2.jpg +0 -0
- data/img/cube_solved.jpg +0 -0
- data/lib/rubiks_cube.rb +0 -2
- data/lib/rubiks_cube/cube.rb +41 -73
- data/lib/rubiks_cube/cubie.rb +3 -11
- data/lib/rubiks_cube/two_cycle_solution.rb +1 -1
- data/lib/rubiks_cube/version.rb +1 -1
- data/spec/rubiks_cube/cube_spec.rb +0 -10
- data/spec/rubiks_cube/cubie_spec.rb +2 -3
- data/spec/rubiks_cube/two_cycle_solution_spec.rb +3 -3
- metadata +10 -3
- data/lib/rubiks_cube/corner_cubie.rb +0 -8
- data/lib/rubiks_cube/edge_cubie.rb +0 -7
checksums.yaml
CHANGED
|
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
|
|
1
1
|
---
|
|
2
2
|
SHA1:
|
|
3
|
-
metadata.gz:
|
|
4
|
-
data.tar.gz:
|
|
3
|
+
metadata.gz: d340c4d6ed10a679b877d834c2051ab5875ce201
|
|
4
|
+
data.tar.gz: 13e7c52e530391568ef6fc82e6e3ae30f1834788
|
|
5
5
|
SHA512:
|
|
6
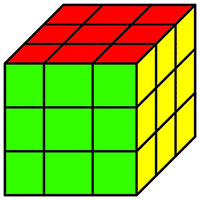
|
-
metadata.gz:
|
|
7
|
-
data.tar.gz:
|
|
6
|
+
metadata.gz: 6d04641548416231a627d4fff3d91e8a79701deeaa586b2d71fa33ff608c7b6154e53e82765f4cd8b0f390a50a89023fa7d45e50c7e17d87e7767a51b772692c
|
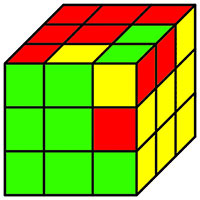
|
7
|
+
data.tar.gz: 4b167f837facba5d44b9158e7d8eedc65a68729f26d813538b6615f809e4bb744fd9b9c5901be8f98311500cbcb9c44c3cedb6b2273b34e951af70374cca2f76
|
data/README.md
CHANGED
|
@@ -1,16 +1,292 @@
|
|
|
1
1
|
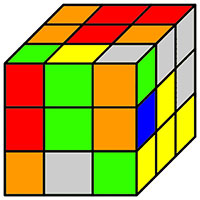
# Rubik's Cube
|
|
2
|
-

|
|
3
2
|
|
|
4
|
-
|
|
3
|
+
Can you solve the Rubik's Cube? Do you want to learn how? GREAT!
|
|
4
|
+
|
|
5
|
+
We will teach you a very simple two-cycle solution for solving the Rubik's
|
|
6
|
+
Cube. It's so simple that I used this exact solution to solve the cube
|
|
7
|
+
blindfolded in the [2005 Rubik's World
|
|
8
|
+
Championship](http://worldcubeassociation.org/results/p.php?i=2005HUNT01)
|
|
9
|
+
with a time of 5 minutes and 40 seconds.
|
|
10
|
+
|
|
11
|
+
With practice, you can easily average less than 3 minutes using this solution
|
|
12
|
+
and will have enough understanding to progress to the [Fridrich CFOP](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fridrich_Method) method - taking you to 15 second solve times.
|
|
13
|
+
WOW!
|
|
5
14
|
|
|
6
15
|
## Usage
|
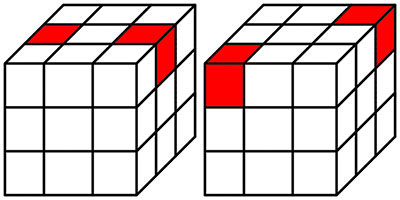
|
7
16
|
|
|
17
|
+
```ruby
|
|
18
|
+
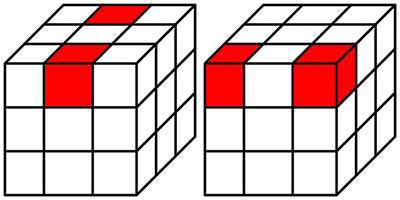
require 'rubiks_cube'
|
|
19
|
+
|
|
20
|
+
cube = RubiksCube::Cube.new
|
|
21
|
+
cube.solved? #=> true
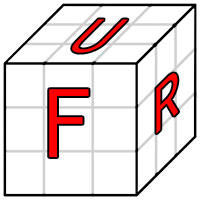
|
|
22
|
+
|
|
23
|
+
scramble = "U D B2 U B D2 B2 F' R' U2 F U' L2 F L2 B2 L2 R' U R' U' D R2 F2 B2"
|
|
24
|
+
|
|
25
|
+
cube.perform! scramble
|
|
26
|
+
cube.solved? #=> false
|
|
27
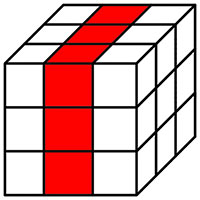
|
+
|
|
28
|
+
solution = RubiksCube::TwoCycleSolution.new(cube)
|
|
29
|
+
|
|
30
|
+
solution.length #=> 458
|
|
31
|
+
|
|
32
|
+
puts solution.pretty
|
|
33
|
+
|
|
34
|
+
# Setup: L2
|
|
35
|
+
# Fix: R U R' U' R' F R2 U' R' U' R U R' F'
|
|
36
|
+
# Undo: L2
|
|
37
|
+
#
|
|
38
|
+
# Setup: M2 D L2
|
|
39
|
+
# Fix: R U R' U' R' F R2 U' R' U' R U R' F'
|
|
40
|
+
# Undo: L2 D' M2
|
|
41
|
+
#
|
|
42
|
+
# Setup: U' F' U
|
|
43
|
+
# Fix: R U R' U' R' F R2 U' R' U' R U R' F'
|
|
44
|
+
# Undo: U' F U
|
|
45
|
+
# ...
|
|
46
|
+
```
|
|
47
|
+
|
|
48
|
+
## Setting Rubik's Cube State Manually
|
|
49
|
+
|
|
50
|
+
If we'd like to start the Rubik's Cube in a different state, we can do that.
|
|
51
|
+
Most people will want to do this if they have a cube sitting on their desk that
|
|
52
|
+
is already scrambled.
|
|
53
|
+
|
|
54
|
+
Describing a cube state may seem complicated at first, but it quickly becomes
|
|
55
|
+
easy after you've done it a few times.
|
|
56
|
+
|
|
57
|
+
Hold your Rubik's Cube in your hand. Notice that the center of each face does
|
|
58
|
+
not move when you rotate a side. The is the basis for entering cube state
|
|
59
|
+
manually. If the center of a face is red, then that face will be red when the
|
|
60
|
+
cube is solved.
|
|
61
|
+
|
|
62
|
+
Starting with top edges and working down (counter-clockwise), enter the state
|
|
63
|
+
of each cubie. After edges are entered, proceed to corners. See the
|
|
64
|
+
[examples](#examples) below for more help.
|
|
65
|
+
|
|
66
|
+

|
|
67
|
+
|
|
68
|
+
### Examples
|
|
69
|
+
|
|
70
|
+
Entering cube state manually can be confusing at first. Here are some examples
|
|
71
|
+
to help you out.
|
|
72
|
+
|
|
73
|
+
#### Solved Cube
|
|
74
|
+
|
|
75
|
+
|
|
76
|
+
|
|
77
|
+
A Rubik's Cube is solved by default, but let's take a look at entering the
|
|
78
|
+
state of a solved cube manually so it makes sense.
|
|
79
|
+
|
|
80
|
+
```ruby
|
|
81
|
+
require 'rubiks_cube'
|
|
82
|
+
|
|
83
|
+
cube = RubiksCube::Cube.new(
|
|
84
|
+
"UF UR UB UL FL FR BR BL DF DR DB DL UFL URF UBR ULB DLF DFR DRB DBL"
|
|
85
|
+
)
|
|
86
|
+
|
|
87
|
+
cube.solved? #=> true
|
|
88
|
+
```
|
|
89
|
+
|
|
90
|
+
#### Slightly Scrambled Cube
|
|
91
|
+
|
|
92
|
+
|
|
93
|
+
|
|
94
|
+
Now let's look at a slightly scrambled cube.
|
|
95
|
+
|
|
96
|
+
```ruby
|
|
97
|
+
require 'rubiks_cube'
|
|
98
|
+
|
|
99
|
+
cube = RubiksCube::Cube.new(
|
|
100
|
+
"RF FU UB UL FL UR BR BL DF DR DB DL UFL FUR UBR ULB DLF DFR DRB BLD"
|
|
101
|
+
)
|
|
102
|
+
|
|
103
|
+
cube.solved? #=> false
|
|
104
|
+
```
|
|
105
|
+
|
|
106
|
+
#### Fully Scrambled Cube
|
|
107
|
+
|
|
108
|
+
|
|
109
|
+
|
|
110
|
+
Finally, let's look at a pretty messed up cube. Here's the scramble if you'd
|
|
111
|
+
like to try this one at home:
|
|
112
|
+
|
|
113
|
+
```
|
|
114
|
+
U D B2 U B D2 B2 F' R' U2 F U' L2 F L2 B2 L2 R' U R' U' D R2 F2 B2
|
|
115
|
+
```
|
|
116
|
+
|
|
117
|
+
```ruby
|
|
118
|
+
require 'rubiks_cube'
|
|
119
|
+
|
|
120
|
+
cube = RubiksCube::Cube.new(
|
|
121
|
+
"RF DL UB DF UF DB FL LB UL DR BR UR FUR LFD UFL DRB BLD DFR BRU LBU"
|
|
122
|
+
)
|
|
123
|
+
|
|
124
|
+
cube.solved? #=> false
|
|
125
|
+
```
|
|
126
|
+
|
|
127
|
+
## Turning a Rubik's Cube
|
|
128
|
+
|
|
129
|
+
Each Rubik's Cube face (l, r, f, b, d, u) can be turned clockwise manually by
|
|
130
|
+
calling the appropriate method on the cube. For example, if we'd like to turn
|
|
131
|
+
the right face twice, the down face once, and the back face three times:
|
|
132
|
+
|
|
133
|
+
```ruby
|
|
134
|
+
require 'rubiks_cube'
|
|
135
|
+
|
|
136
|
+
cube = RubiksCube::Cube.new
|
|
137
|
+
|
|
138
|
+
cube.r.r.d.b.b.b
|
|
139
|
+
```
|
|
140
|
+
|
|
141
|
+
Most people will prefer to use standard Rubik's Cube [algorithm
|
|
142
|
+
notation](#algorithm-notation) for turning the cube. Here's the same example
|
|
143
|
+
with with cube notation:
|
|
144
|
+
|
|
145
|
+
```ruby
|
|
146
|
+
require 'rubiks_cube'
|
|
147
|
+
|
|
148
|
+
cube = RubiksCube::Cube.new
|
|
149
|
+
|
|
150
|
+
cube.perform! "R2 D B'"
|
|
151
|
+
```
|
|
152
|
+
|
|
153
|
+
Performing face turns on the cube changes the state.
|
|
154
|
+
|
|
155
|
+
```ruby
|
|
156
|
+
require 'rubiks_cube'
|
|
157
|
+
|
|
158
|
+
cube = RubiksCube::Cube.new
|
|
159
|
+
|
|
160
|
+
cube.perform!(
|
|
161
|
+
"U D2 F2 L' R' D' B' U' D L D U2 B' L2 F2 R' U D F2 B' R' F2 U F2 B"
|
|
162
|
+
)
|
|
163
|
+
|
|
164
|
+
cube.solved? #=> false
|
|
165
|
+
|
|
166
|
+
cube.state
|
|
167
|
+
# "DB UF RB RF LB DL UR RD FD UB LF UL FDL DFR UBR BDR UFL LDB FUR LBU"
|
|
168
|
+
```
|
|
169
|
+
|
|
170
|
+
## Solving a Rubik's Cube
|
|
171
|
+
|
|
172
|
+
We currently only have a very simple two-cycle solution implemented. This
|
|
173
|
+
solution is very inefficient, but wonderful for humans. Using the two-cycle
|
|
174
|
+
solution, you can quickly learn how to solve the Rubik's Cube without using the
|
|
175
|
+
computer.
|
|
176
|
+
|
|
177
|
+
### Two Cycle Solution
|
|
178
|
+
|
|
179
|
+
The two-cycle solution is a popular solution used to solve the Rubik's Cube
|
|
180
|
+
blindfolded. It requires little memorization and takes little time to learn.
|
|
181
|
+
Solutions usually range from 400-600 turns, but most of those turns are quickly
|
|
182
|
+
executed. We can easily achieve times of less than 4 minutes with this
|
|
183
|
+
solution.
|
|
184
|
+
|
|
185
|
+
The two-cycle solution solves the cube by swapping two cubies at a time until
|
|
186
|
+
all cubies are in the correct location. This is the permutation step. After the
|
|
187
|
+
cubies are permuted, we then rotate two cubies at a time (in their current
|
|
188
|
+
location) until all are oriented correctly. This is the orientation step. We
|
|
189
|
+
call this the *two-cycle* solution because everything is done in pairs.
|
|
190
|
+
|
|
191
|
+
You can use the `rubiks_cube` gem to *learn* the two-cycle solution. For each
|
|
192
|
+
step, we provide setup moves, the [fixing algorithm](#algorithms) (either
|
|
193
|
+
changing permutation or orientation), and the undo moves. Pay close attention
|
|
194
|
+
to how the cube moves and you will be solving by yourself in no time.
|
|
195
|
+
|
|
196
|
+
See [Usage](#usage) for an example of the `TwoCycleSolution`
|
|
197
|
+
|
|
198
|
+
#### How It Works: Permutation
|
|
199
|
+
|
|
200
|
+
|
|
201
|
+
|
|
202
|
+
The permutation step is completed using only two algorithms. One swaps two
|
|
203
|
+
edges and the other swaps two corners. The diagram above shows which edges and
|
|
204
|
+
corners are swapped.
|
|
205
|
+
|
|
206
|
+
When a solution is calculated, we present a 'setup' algorithm (which gets the
|
|
207
|
+
cubies into a position where they can be swapped), then we present one of the
|
|
208
|
+
two swapping algorithms, followed by an 'undo' algorithm that reverses the
|
|
209
|
+
setup move.
|
|
210
|
+
|
|
211
|
+
#### How It Works: Orientation
|
|
212
|
+
|
|
213
|
+
|
|
214
|
+
|
|
215
|
+
The orientation step is completed using only two algorithms. One flips two
|
|
216
|
+
edges and the other rotates two corners (one clockwise and the other
|
|
217
|
+
counter-clockwise). The diagram above shows which edges and corners are
|
|
218
|
+
rotated.
|
|
219
|
+
|
|
220
|
+
When a solution is calculated, we present a 'setup' algorithm (which gets the
|
|
221
|
+
cubies into a position where they can be rotated), then we present one of the
|
|
222
|
+
two rotation algorithms, followed by an 'undo' algorithm that reverses the
|
|
223
|
+
setup move.
|
|
224
|
+
|
|
225
|
+
## Algorithms
|
|
226
|
+
|
|
227
|
+
All algorithms can be found in [`RubiksCube::Algorithms`](https://github.com/chrishunt/rubiks-cube/blob/master/lib/rubiks_cube/algorithms.rb)
|
|
228
|
+
|
|
229
|
+
### Algorithm Notation
|
|
230
|
+
|
|
231
|
+
|
|
232
|
+
|
|
233
|
+
Rubik's Cube algorithm notation is easy to understand, but may look confusing
|
|
234
|
+
at first. Each face is represented by a letter:
|
|
235
|
+
|
|
236
|
+
- **L**: Left Face
|
|
237
|
+
- **R**: Right Face
|
|
238
|
+
- **F**: Front Face
|
|
239
|
+
- **B**: Back Face
|
|
240
|
+
- **U**: Up Face (top)
|
|
241
|
+
- **D**: Up Face (bottom)
|
|
242
|
+
|
|
243
|
+
When we see a letter in an algorithm, then we turn that face 90 degrees
|
|
244
|
+
clockwise. To determine which direction is clockwise, rotate the cube so that
|
|
245
|
+
you are looking at the face, then make the turn.
|
|
246
|
+
|
|
247
|
+
Faces may be followed by one of two modifiers:
|
|
248
|
+
|
|
249
|
+
- **'**: Rotate the face 90 degrees *counter*-clockwise
|
|
250
|
+
- **2**: Rotate the face 180 degrees (two turns)
|
|
251
|
+
|
|
252
|
+
For example, if we want to apply the algorithm `F2 B D' R`, then we would take
|
|
253
|
+
these steps:
|
|
254
|
+
|
|
255
|
+
1. Rotate **F** face 180 degrees (two turns)
|
|
256
|
+
2. Rotate **B** face 90 degrees clockwise
|
|
257
|
+
3. Rotate **D** face 90 degrees *counter*-clockwise
|
|
258
|
+
4. Rotate **R** face 90 degrees clockwise
|
|
259
|
+
|
|
260
|
+
#### M Slice
|
|
261
|
+
|
|
262
|
+
|
|
263
|
+
|
|
264
|
+
There is one special algorithm notation that does not map to a face. This is
|
|
265
|
+
called the M slice. The M slice is the middle vertical layer of the Rubik's
|
|
266
|
+
Cube.
|
|
267
|
+
|
|
268
|
+
When you see **M**, then rotate this slice 90 degrees clockwise. To figure out
|
|
269
|
+
which direction is clockwise, look at the **L** face.
|
|
270
|
+
|
|
271
|
+
For example, if we want to apply the algorithm `M2 F M2`, then we would take
|
|
272
|
+
these steps:
|
|
273
|
+
|
|
274
|
+
1. Rotate **M** slice 180 degrees (two turns)
|
|
275
|
+
2. Rotate **F** face 90 degrees clockwise
|
|
276
|
+
3. Rotate **M** slice 180 degrees (two turns)
|
|
277
|
+
|
|
8
278
|
## Installation
|
|
9
279
|
|
|
280
|
+
```bash
|
|
281
|
+
$ gem install rubiks_cube
|
|
282
|
+
```
|
|
283
|
+
|
|
10
284
|
## Contributing
|
|
285
|
+
|
|
11
286
|
Please see the [Contributing
|
|
12
287
|
Document](https://github.com/chrishunt/rubiks-cube/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md)
|
|
13
288
|
|
|
14
289
|
## License
|
|
290
|
+
|
|
15
291
|
Copyright (C) 2013 Chris Hunt, [MIT
|
|
16
292
|
License](https://github.com/chrishunt/rubiks-cube/blob/master/LICENSE.txt)
|
|
Binary file
|
data/img/cube_blank.jpg
ADDED
|
Binary file
|
|
Binary file
|
|
Binary file
|
|
Binary file
|
|
Binary file
|
|
Binary file
|
|
Binary file
|
data/img/cube_solved.jpg
ADDED
|
Binary file
|
data/lib/rubiks_cube.rb
CHANGED
data/lib/rubiks_cube/cube.rb
CHANGED
|
@@ -39,38 +39,6 @@ module RubiksCube
|
|
|
39
39
|
cubie_permuted? :corners, corner
|
|
40
40
|
end
|
|
41
41
|
|
|
42
|
-
def has_correct_edge_permutation?
|
|
43
|
-
incorrect_edge_permutation_locations.empty?
|
|
44
|
-
end
|
|
45
|
-
|
|
46
|
-
def has_correct_corner_permutation?
|
|
47
|
-
incorrect_corner_permutation_locations.empty?
|
|
48
|
-
end
|
|
49
|
-
|
|
50
|
-
def has_correct_edge_orientation?
|
|
51
|
-
incorrect_edge_orientation_locations.empty?
|
|
52
|
-
end
|
|
53
|
-
|
|
54
|
-
def has_correct_corner_orientation?
|
|
55
|
-
incorrect_corner_orientation_locations.empty?
|
|
56
|
-
end
|
|
57
|
-
|
|
58
|
-
def incorrect_edge_permutation_locations
|
|
59
|
-
unpermuted_locations_for :edges
|
|
60
|
-
end
|
|
61
|
-
|
|
62
|
-
def incorrect_corner_permutation_locations
|
|
63
|
-
unpermuted_locations_for :corners
|
|
64
|
-
end
|
|
65
|
-
|
|
66
|
-
def incorrect_edge_orientation_locations
|
|
67
|
-
unoriented_locations_for :edges
|
|
68
|
-
end
|
|
69
|
-
|
|
70
|
-
def incorrect_corner_orientation_locations
|
|
71
|
-
unoriented_locations_for :corners
|
|
72
|
-
end
|
|
73
|
-
|
|
74
42
|
def permuted_location_for(cubie)
|
|
75
43
|
while (location = SOLVED_STATE.index cubie.state) == nil
|
|
76
44
|
cubie = cubie.rotate
|
|
@@ -85,49 +53,37 @@ module RubiksCube
|
|
|
85
53
|
algorithm
|
|
86
54
|
end
|
|
87
55
|
|
|
88
|
-
def undo!(algorithm)
|
|
89
|
-
perform! reverse(algorithm)
|
|
90
|
-
end
|
|
91
|
-
|
|
92
56
|
def r
|
|
93
|
-
turn [1, 5, 9, 6]
|
|
94
|
-
|
|
95
|
-
rotate [13, 13, 14, 17, 18, 18]
|
|
57
|
+
turn [1, 5, 9, 6], [13, 17, 18, 14]
|
|
58
|
+
rotate [13, 14, 14, 17, 17, 18]
|
|
96
59
|
self
|
|
97
60
|
end
|
|
98
61
|
|
|
99
62
|
def l
|
|
100
|
-
turn [3, 7, 11, 4]
|
|
101
|
-
|
|
102
|
-
rotate [12, 15, 15, 16, 16, 19]
|
|
63
|
+
turn [3, 7, 11, 4], [12, 15, 19, 16]
|
|
64
|
+
rotate [12, 12, 15, 16, 19, 19]
|
|
103
65
|
self
|
|
104
66
|
end
|
|
105
67
|
|
|
106
68
|
def u
|
|
107
|
-
turn [0, 1, 2, 3]
|
|
108
|
-
turn [12, 13, 14, 15]
|
|
69
|
+
turn [0, 1, 2, 3], [12, 13, 14, 15]
|
|
109
70
|
self
|
|
110
71
|
end
|
|
111
72
|
|
|
112
73
|
def d
|
|
113
|
-
turn [8, 11, 10, 9]
|
|
114
|
-
turn [16, 19, 18, 17]
|
|
74
|
+
turn [8, 11, 10, 9], [16, 19, 18, 17]
|
|
115
75
|
self
|
|
116
76
|
end
|
|
117
77
|
|
|
118
78
|
def f
|
|
119
|
-
turn [0, 4, 8, 5]
|
|
120
|
-
rotate [0, 4, 8, 5]
|
|
121
|
-
turn [12, 16, 17, 13]
|
|
122
|
-
rotate [12, 12, 13, 16, 17, 17]
|
|
79
|
+
turn [0, 4, 8, 5], [12, 16, 17, 13]
|
|
80
|
+
rotate [0, 4, 8, 5], [12, 13, 13, 16, 16, 17]
|
|
123
81
|
self
|
|
124
82
|
end
|
|
125
83
|
|
|
126
84
|
def b
|
|
127
|
-
turn [2, 6, 10, 7]
|
|
128
|
-
rotate [2, 6, 10, 7]
|
|
129
|
-
turn [14, 18, 19, 15]
|
|
130
|
-
rotate [14, 14, 15, 18, 19, 19]
|
|
85
|
+
turn [2, 6, 10, 7], [14, 18, 19, 15]
|
|
86
|
+
rotate [2, 6, 10, 7], [14, 15, 15, 18, 18, 19]
|
|
131
87
|
self
|
|
132
88
|
end
|
|
133
89
|
|
|
@@ -137,6 +93,18 @@ module RubiksCube
|
|
|
137
93
|
self
|
|
138
94
|
end
|
|
139
95
|
|
|
96
|
+
[:edge, :corner].each do |cubie|
|
|
97
|
+
[:orientation, :permutation].each do |step|
|
|
98
|
+
define_method "incorrect_#{cubie}_#{step}_locations" do
|
|
99
|
+
send "incorrect_#{step}_locations_for", cubie
|
|
100
|
+
end
|
|
101
|
+
|
|
102
|
+
define_method "has_correct_#{cubie}_#{step}?" do
|
|
103
|
+
send("incorrect_#{cubie}_#{step}_locations").empty?
|
|
104
|
+
end
|
|
105
|
+
end
|
|
106
|
+
end
|
|
107
|
+
|
|
140
108
|
private
|
|
141
109
|
|
|
142
110
|
def build_state_from_string(state)
|
|
@@ -147,16 +115,16 @@ module RubiksCube
|
|
|
147
115
|
send(type).index(cubie) == permuted_location_for(cubie)
|
|
148
116
|
end
|
|
149
117
|
|
|
150
|
-
def
|
|
151
|
-
send(type).each_with_index.map do |cubie, location|
|
|
118
|
+
def incorrect_permutation_locations_for(type)
|
|
119
|
+
send("#{type}s").each_with_index.map do |cubie, location|
|
|
152
120
|
location unless location == permuted_location_for(cubie)
|
|
153
121
|
end.compact
|
|
154
122
|
end
|
|
155
123
|
|
|
156
|
-
def
|
|
157
|
-
send(type).each_with_index.map do |cubie, location|
|
|
124
|
+
def incorrect_orientation_locations_for(type)
|
|
125
|
+
send("#{type}s").each_with_index.map do |cubie, location|
|
|
158
126
|
oriented_state = SOLVED_STATE.fetch(
|
|
159
|
-
if type == :
|
|
127
|
+
if type == :corner
|
|
160
128
|
location + 12
|
|
161
129
|
else
|
|
162
130
|
location
|
|
@@ -167,20 +135,24 @@ module RubiksCube
|
|
|
167
135
|
end.compact
|
|
168
136
|
end
|
|
169
137
|
|
|
170
|
-
def turn(
|
|
171
|
-
|
|
172
|
-
|
|
138
|
+
def turn(*sequences)
|
|
139
|
+
sequences.each do |sequence|
|
|
140
|
+
location = sequence.shift
|
|
141
|
+
first_cubie = @state.fetch(location)
|
|
173
142
|
|
|
174
|
-
|
|
175
|
-
|
|
176
|
-
|
|
177
|
-
|
|
143
|
+
sequence.each do |next_location|
|
|
144
|
+
@state[location] = @state.fetch(next_location)
|
|
145
|
+
location = next_location
|
|
146
|
+
end
|
|
178
147
|
|
|
179
|
-
|
|
148
|
+
@state[location] = first_cubie
|
|
149
|
+
end
|
|
180
150
|
end
|
|
181
151
|
|
|
182
|
-
def rotate(
|
|
183
|
-
|
|
152
|
+
def rotate(*sequences)
|
|
153
|
+
sequences.each do |cubies|
|
|
154
|
+
cubies.each { |cubie| @state[cubie].rotate! }
|
|
155
|
+
end
|
|
184
156
|
end
|
|
185
157
|
|
|
186
158
|
def perform_move!(move)
|
|
@@ -195,9 +167,5 @@ module RubiksCube
|
|
|
195
167
|
send operation
|
|
196
168
|
end
|
|
197
169
|
end
|
|
198
|
-
|
|
199
|
-
def reverse(algorithm)
|
|
200
|
-
RubiksCube::Algorithms.reverse algorithm
|
|
201
|
-
end
|
|
202
170
|
end
|
|
203
171
|
end
|
data/lib/rubiks_cube/cubie.rb
CHANGED
|
@@ -1,20 +1,12 @@
|
|
|
1
1
|
module RubiksCube
|
|
2
2
|
# Generic cubie piece, either edge cubie or corner cubie
|
|
3
|
-
|
|
4
|
-
def initialize(state)
|
|
5
|
-
@cubie = state.size == 2 ? EdgeCubie.new(state) : CornerCubie.new(state)
|
|
6
|
-
end
|
|
7
|
-
|
|
3
|
+
Cubie = Struct.new(:state) do
|
|
8
4
|
def ==(other)
|
|
9
5
|
state == other.state
|
|
10
6
|
end
|
|
11
7
|
|
|
12
|
-
def state
|
|
13
|
-
@cubie.state
|
|
14
|
-
end
|
|
15
|
-
|
|
16
8
|
def rotate!
|
|
17
|
-
|
|
9
|
+
self.state = state.split('').rotate.join
|
|
18
10
|
self
|
|
19
11
|
end
|
|
20
12
|
|
|
@@ -23,7 +15,7 @@ module RubiksCube
|
|
|
23
15
|
end
|
|
24
16
|
|
|
25
17
|
def to_s
|
|
26
|
-
|
|
18
|
+
state
|
|
27
19
|
end
|
|
28
20
|
end
|
|
29
21
|
end
|
data/lib/rubiks_cube/version.rb
CHANGED
|
@@ -297,16 +297,6 @@ describe RubiksCube::Cube do
|
|
|
297
297
|
end
|
|
298
298
|
end
|
|
299
299
|
|
|
300
|
-
describe '#undo!' do
|
|
301
|
-
it 'performs the algorithm in reverse on the cube' do
|
|
302
|
-
subject.f.f.f.b.l.l.u.u.u.r
|
|
303
|
-
|
|
304
|
-
subject.undo! "F' B L2 U' R"
|
|
305
|
-
|
|
306
|
-
expect(subject).to be_solved
|
|
307
|
-
end
|
|
308
|
-
end
|
|
309
|
-
|
|
310
300
|
describe 'face turns' do
|
|
311
301
|
shared_examples_for 'a face turn' do
|
|
312
302
|
it "rotates the face 90 degrees clockwise" do
|
|
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ describe RubiksCube::Cubie do
|
|
|
17
17
|
end
|
|
18
18
|
|
|
19
19
|
context 'when the state does not equal the state of the other' do
|
|
20
|
-
it 'returns
|
|
20
|
+
it 'returns false' do
|
|
21
21
|
expect(subject == described_class.new('UB')).to be_false
|
|
22
22
|
end
|
|
23
23
|
end
|
|
@@ -43,8 +43,8 @@ describe RubiksCube::Cubie do
|
|
|
43
43
|
let(:state) { 'URF' }
|
|
44
44
|
|
|
45
45
|
it 'rotates the cubie once couter clockwise' do
|
|
46
|
-
expect(subject.rotate!.state).to eq 'FUR'
|
|
47
46
|
expect(subject.rotate!.state).to eq 'RFU'
|
|
47
|
+
expect(subject.rotate!.state).to eq 'FUR'
|
|
48
48
|
expect(subject.rotate!.state).to eq state
|
|
49
49
|
end
|
|
50
50
|
end
|
|
@@ -63,5 +63,4 @@ describe RubiksCube::Cubie do
|
|
|
63
63
|
expect(subject.state).to eq original_state
|
|
64
64
|
end
|
|
65
65
|
end
|
|
66
|
-
|
|
67
66
|
end
|
|
@@ -96,14 +96,14 @@ describe RubiksCube::TwoCycleSolution do
|
|
|
96
96
|
end
|
|
97
97
|
end
|
|
98
98
|
|
|
99
|
-
describe '#
|
|
99
|
+
describe '#length' do
|
|
100
100
|
it 'returns the length of the solution' do
|
|
101
101
|
cube.l.r
|
|
102
|
-
expect(subject.
|
|
102
|
+
expect(subject.length).to eq 634
|
|
103
103
|
end
|
|
104
104
|
|
|
105
105
|
it 'returns zero when cube already solved' do
|
|
106
|
-
expect(subject.
|
|
106
|
+
expect(subject.length).to be_zero
|
|
107
107
|
end
|
|
108
108
|
end
|
|
109
109
|
end
|
metadata
CHANGED
|
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
|
|
1
1
|
--- !ruby/object:Gem::Specification
|
|
2
2
|
name: rubiks_cube
|
|
3
3
|
version: !ruby/object:Gem::Version
|
|
4
|
-
version: 0.0
|
|
4
|
+
version: 1.0.0
|
|
5
5
|
platform: ruby
|
|
6
6
|
authors:
|
|
7
7
|
- Chris Hunt
|
|
@@ -79,12 +79,19 @@ files:
|
|
|
79
79
|
- LICENSE.txt
|
|
80
80
|
- README.md
|
|
81
81
|
- Rakefile
|
|
82
|
+
- img/cube_algorithm.jpg
|
|
83
|
+
- img/cube_blank.jpg
|
|
84
|
+
- img/cube_instructions.jpg
|
|
85
|
+
- img/cube_m_slice.jpg
|
|
86
|
+
- img/cube_orientation.jpg
|
|
87
|
+
- img/cube_permutation.jpg
|
|
88
|
+
- img/cube_scramble_1.jpg
|
|
89
|
+
- img/cube_scramble_2.jpg
|
|
90
|
+
- img/cube_solved.jpg
|
|
82
91
|
- lib/rubiks_cube.rb
|
|
83
92
|
- lib/rubiks_cube/algorithms.rb
|
|
84
|
-
- lib/rubiks_cube/corner_cubie.rb
|
|
85
93
|
- lib/rubiks_cube/cube.rb
|
|
86
94
|
- lib/rubiks_cube/cubie.rb
|
|
87
|
-
- lib/rubiks_cube/edge_cubie.rb
|
|
88
95
|
- lib/rubiks_cube/two_cycle_solution.rb
|
|
89
96
|
- lib/rubiks_cube/version.rb
|
|
90
97
|
- rubiks_cube.gemspec
|